
Universe Today
Space and astronomy news


How Does Light Travel?
Ever since Democritus – a Greek philosopher who lived between the 5th and 4th century’s BCE – argued that all of existence was made up of tiny indivisible atoms, scientists have been speculating as to the true nature of light. Whereas scientists ventured back and forth between the notion that light was a particle or a wave until the modern era, the 20th century led to breakthroughs that showed us that it behaves as both.
These included the discovery of the electron, the development of quantum theory, and Einstein’s Theory of Relativity . However, there remains many unanswered questions about light, many of which arise from its dual nature. For instance, how is it that light can be apparently without mass, but still behave as a particle? And how can it behave like a wave and pass through a vacuum, when all other waves require a medium to propagate?
Theory of Light to the 19th Century:
During the Scientific Revolution, scientists began moving away from Aristotelian scientific theories that had been seen as accepted canon for centuries. This included rejecting Aristotle’s theory of light, which viewed it as being a disturbance in the air (one of his four “elements” that composed matter), and embracing the more mechanistic view that light was composed of indivisible atoms.
In many ways, this theory had been previewed by atomists of Classical Antiquity – such as Democritus and Lucretius – both of whom viewed light as a unit of matter given off by the sun. By the 17th century, several scientists emerged who accepted this view, stating that light was made up of discrete particles (or “corpuscles”). This included Pierre Gassendi, a contemporary of René Descartes, Thomas Hobbes, Robert Boyle, and most famously, Sir Isaac Newton .

Newton’s corpuscular theory was an elaboration of his view of reality as an interaction of material points through forces. This theory would remain the accepted scientific view for more than 100 years, the principles of which were explained in his 1704 treatise “ Opticks, or, a Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of Light “. According to Newton, the principles of light could be summed as follows:
- Every source of light emits large numbers of tiny particles known as corpuscles in a medium surrounding the source.
- These corpuscles are perfectly elastic, rigid, and weightless.
This represented a challenge to “wave theory”, which had been advocated by 17th century Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens . . These theories were first communicated in 1678 to the Paris Academy of Sciences and were published in 1690 in his “ Traité de la lumière “ (“ Treatise on Light “). In it, he argued a revised version of Descartes views, in which the speed of light is infinite and propagated by means of spherical waves emitted along the wave front.
Double-Slit Experiment:
By the early 19th century, scientists began to break with corpuscular theory. This was due in part to the fact that corpuscular theory failed to adequately explain the diffraction, interference and polarization of light, but was also because of various experiments that seemed to confirm the still-competing view that light behaved as a wave.
The most famous of these was arguably the Double-Slit Experiment , which was originally conducted by English polymath Thomas Young in 1801 (though Sir Isaac Newton is believed to have conducted something similar in his own time). In Young’s version of the experiment, he used a slip of paper with slits cut into it, and then pointed a light source at them to measure how light passed through it.
According to classical (i.e. Newtonian) particle theory, the results of the experiment should have corresponded to the slits, the impacts on the screen appearing in two vertical lines. Instead, the results showed that the coherent beams of light were interfering, creating a pattern of bright and dark bands on the screen. This contradicted classical particle theory, in which particles do not interfere with each other, but merely collide.
The only possible explanation for this pattern of interference was that the light beams were in fact behaving as waves. Thus, this experiment dispelled the notion that light consisted of corpuscles and played a vital part in the acceptance of the wave theory of light. However subsequent research, involving the discovery of the electron and electromagnetic radiation, would lead to scientists considering yet again that light behaved as a particle too, thus giving rise to wave-particle duality theory.
Electromagnetism and Special Relativity:
Prior to the 19th and 20th centuries, the speed of light had already been determined. The first recorded measurements were performed by Danish astronomer Ole Rømer, who demonstrated in 1676 using light measurements from Jupiter’s moon Io to show that light travels at a finite speed (rather than instantaneously).
By the late 19th century, James Clerk Maxwell proposed that light was an electromagnetic wave, and devised several equations (known as Maxwell’s equations ) to describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents. By conducting measurements of different types of radiation (magnetic fields, ultraviolet and infrared radiation), he was able to calculate the speed of light in a vacuum (represented as c ).
In 1905, Albert Einstein published “ On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies ”, in which he advanced one of his most famous theories and overturned centuries of accepted notions and orthodoxies. In his paper, he postulated that the speed of light was the same in all inertial reference frames, regardless of the motion of the light source or the position of the observer.
Exploring the consequences of this theory is what led him to propose his theory of Special Relativity , which reconciled Maxwell’s equations for electricity and magnetism with the laws of mechanics, simplified the mathematical calculations, and accorded with the directly observed speed of light and accounted for the observed aberrations. It also demonstrated that the speed of light had relevance outside the context of light and electromagnetism.
For one, it introduced the idea that major changes occur when things move close the speed of light, including the time-space frame of a moving body appearing to slow down and contract in the direction of motion when measured in the frame of the observer. After centuries of increasingly precise measurements, the speed of light was determined to be 299,792,458 m/s in 1975.
Einstein and the Photon:
In 1905, Einstein also helped to resolve a great deal of confusion surrounding the behavior of electromagnetic radiation when he proposed that electrons are emitted from atoms when they absorb energy from light. Known as the photoelectric effect , Einstein based his idea on Planck’s earlier work with “black bodies” – materials that absorb electromagnetic energy instead of reflecting it (i.e. white bodies).
At the time, Einstein’s photoelectric effect was attempt to explain the “black body problem”, in which a black body emits electromagnetic radiation due to the object’s heat. This was a persistent problem in the world of physics, arising from the discovery of the electron, which had only happened eight years previous (thanks to British physicists led by J.J. Thompson and experiments using cathode ray tubes ).
At the time, scientists still believed that electromagnetic energy behaved as a wave, and were therefore hoping to be able to explain it in terms of classical physics. Einstein’s explanation represented a break with this, asserting that electromagnetic radiation behaved in ways that were consistent with a particle – a quantized form of light which he named “photons”. For this discovery, Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1921.
Wave-Particle Duality:
Subsequent theories on the behavior of light would further refine this idea, which included French physicist Louis-Victor de Broglie calculating the wavelength at which light functioned. This was followed by Heisenberg’s “uncertainty principle” (which stated that measuring the position of a photon accurately would disturb measurements of it momentum and vice versa), and Schrödinger’s paradox that claimed that all particles have a “wave function”.
In accordance with quantum mechanical explanation, Schrodinger proposed that all the information about a particle (in this case, a photon) is encoded in its wave function , a complex-valued function roughly analogous to the amplitude of a wave at each point in space. At some location, the measurement of the wave function will randomly “collapse”, or rather “decohere”, to a sharply peaked function. This was illustrated in Schrödinger famous paradox involving a closed box, a cat, and a vial of poison (known as the “ Schrödinger Cat” paradox).

According to his theory, wave function also evolves according to a differential equation (aka. the Schrödinger equation ). For particles with mass, this equation has solutions; but for particles with no mass, no solution existed. Further experiments involving the Double-Slit Experiment confirmed the dual nature of photons. where measuring devices were incorporated to observe the photons as they passed through the slits.
When this was done, the photons appeared in the form of particles and their impacts on the screen corresponded to the slits – tiny particle-sized spots distributed in straight vertical lines. By placing an observation device in place, the wave function of the photons collapsed and the light behaved as classical particles once more. As predicted by Schrödinger, this could only be resolved by claiming that light has a wave function, and that observing it causes the range of behavioral possibilities to collapse to the point where its behavior becomes predictable.
The development of Quantum Field Theory (QFT) was devised in the following decades to resolve much of the ambiguity around wave-particle duality. And in time, this theory was shown to apply to other particles and fundamental forces of interaction (such as weak and strong nuclear forces). Today, photons are part of the Standard Model of particle physics, where they are classified as boson – a class of subatomic particles that are force carriers and have no mass.
So how does light travel? Basically, traveling at incredible speeds (299 792 458 m/s) and at different wavelengths, depending on its energy. It also behaves as both a wave and a particle, able to propagate through mediums (like air and water) as well as space. It has no mass, but can still be absorbed, reflected, or refracted if it comes in contact with a medium. And in the end, the only thing that can truly divert it, or arrest it, is gravity (i.e. a black hole).
What we have learned about light and electromagnetism has been intrinsic to the revolution which took place in physics in the early 20th century, a revolution that we have been grappling with ever since. Thanks to the efforts of scientists like Maxwell, Planck, Einstein, Heisenberg and Schrodinger, we have learned much, but still have much to learn.
For instance, its interaction with gravity (along with weak and strong nuclear forces) remains a mystery. Unlocking this, and thus discovering a Theory of Everything (ToE) is something astronomers and physicists look forward to. Someday, we just might have it all figured out!
We have written many articles about light here at Universe Today. For example, here’s How Fast is the Speed of Light? , How Far is a Light Year? , What is Einstein’s Theory of Relativity?
If you’d like more info on light, check out these articles from The Physics Hypertextbook and NASA’s Mission Science page.
We’ve also recorded an entire episode of Astronomy Cast all about Interstellar Travel. Listen here, Episode 145: Interstellar Travel .
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
56 Replies to “How Does Light Travel?”
“HOW DOES LIGHT TRAVEL?”
it travels lightly. 😀
Light doesn’t exist. This is an observation from light’s point of view and not ours. Traveling at the speed of (wait for it) light, absolutely no time passes between leaving it’s source and reaching it’s destination for the photon. This means, to the photon hitting your retina, it is also still on that star you are observing 10 light years away. How is this possible? Maybe John Wheeler was right when he told Richard Feynman that there is only one electron in the universe and it travels forward in time as an electron, then back in time as a positron and every electron we see is the same electron.
MY QUESTION IS: Whether light is a wave , particle or both.. where does it get the energy to move through space/time. In other words is the energy of light infinite? Does it continue on without lose of energy…..forever…….
I believe that Special Relativity says that the energy of light is infinite due to the very fact it has no mass. E=MC^2
In reverse, this is also why something with mass to begin with. If accelerated toward the speed of light, will see their mass and gravity increase to infinite points as they near relativistic speed (it actually starts around 95% with a steep upward curve from there), with a relative slowing to a stop of time.
Join the discussion
Light and the universe are only illusions that are formed in our minds via technology that sends information from the simulation program we’re living in. That information comes in the form of invisible wavelengths that includes wavelengths that we perceive as light. The visible retinas in our eyes are like tiny video screens where these particles are arranged into patterns that form into all the various objects we think are real objects. This information is also converted into thoughts within our minds which are like computer processors that process that information.
We are living in a computer simulation that is much more advanced than anything the characters in the program have built according to the information called the Beast.
Brad,…So You’re suggesting that “life” as we know and call it “is some kind of retro-virus” or “bio-intelligent format” heaped upon a perceived “set of accepted data sets” that are not in sync with each other in most cases with exception to Math 94% of the time….Even then it can vary which suggests Your idea would mean we all live in a fairy tale. That is what you suggest,…right?……
Brad has watched the Matrix too many times.
Correction: Even gravity doesn’t slow light down. Light (EM radiation of any wavelength) always travels at speed c, relative to any local inertial (Lorentz) frame. It could also be noted that the wavelength of an EM wave is not a characteristic of that wave alone; it also depends on the state of motion of the observer. You might even say, “One man’s radio wave is another man’s gamma ray.”
Light actually “slows down” every time it has to travel through anything but a vacuum. Look up Cherenkov radiation to see what happens when light initially travels faster than it can through a particular substance, like water. Light speed is not constant when traveling through any medium except pure vacuum. In fact that is why your pencil looks bent when you drop it in a glass of water. Light bends to find it’s fastest path through any medium, and it slows down in that medium.
if all you scientist could ever get it in your pie brain that there is no time, no light speed, no warping space, no black holes for the purpose of moving through space quickly, no smallest no biggest when it comes to space and that all of everything has always been in existence but not necessarily as it is now. you will never find the smallest because if it exist it has an inside, and you will never find the end of space because it is infinite.
What are you smoking?
The article started out nicely, but I lost interest as mistakes began to appear. First Einstein did not “propose” the photoelectric effect. The photoelectric effect was first observed by Heinrich Hertz in 1887. Einstein used the idea of photons to explain the photoelectric effect and derive the photoelectric equation. Also, Max Plank had already derived the blackbody distribution, by assuming that electromagnetic energy of frequency f could only be emitted in multiples of energy E=hf, by 1900. Einstein’s paper on the photoelectric effect was published in his “miracle” year of 1905. The photoelectric effect has nothing to do with black body radiation.
Einstein did not coin the name “photons” for light quanta, as stated in this article. This term was first used by Arthur Compton in 1928.
I have to say that I do not know what the author of the article means when he says ” calculating the wavelength at which light functioned” in reference to Louis-Victor de Broglie. Louis de Broglie used the dual nature of light to suggest that electrons, previously thought of as particles, also had wave characteristics and used this notion to explain the Bohr orbits in the hydrogen atom.
I gave up on the article after seeing these errors. I’m afraid I have a low tolerance for sloppy writing.
Oh, it’s BCE now, “Before the Common Era” BC has worked for 2000 years but now the PC police have stepped in so as not to offend who? Some Muslims?
mecheng1, you must be very young. BCE has been in used in academia for decades. It’s nothing “new”, just out of your circle of knowledge.
Decades??? Really?? How does that compare to 2000 years?
Only in Euro-centric texts have your assertions been true, McCowen. The rest of the world not influenced by Christianity have used their own calendars and a “0” year or a “year 1” from which to reckon the passage of time, largely based on their own religions or celestial observations.
Over the last century or so, through commerce, most of the world has generally accepted the use of a Western calendar (or use it along with their own for domestic purposes, like we here in the US still use Imperial units of measure that have to be converted to metric for international commerce). So, we are in a “common era” insofar as non-Christian societies are incorporating the Gregorian Calendar and the generally-accepted “year 1” established by that calendar (which is supposed to be the year of Jesus’s birth, but it probably isn’t according to current scholarship). Besides, the Gregorian calendar is an improved derivative of the Roman calendar – even the names of the months come from the Romans.
In short, it is more accurate, as well as respectful, to go with BCE in these global times.
Where is the information carried on a photon hitting my eye(s), or cluster/group/pack of photons hitting my eyes(s), that I see as other distant galaxies and planets going around stars?
That’s the mystery, isn’t it? Even in scattering, light remains coherent enough to convey an enormous amount of information.
Since the miniscule equal masses with opposite charges, that make up the photon structure, interact at 90 degrees, this induces a spin (a finding from the 80’s by the LANL plasma physics program) which creates a centrifugal force that counterbalances the charge attraction of the opposite charges. This establishes a stable structure for energies less than 1.0216 MeV, the pair-formation threshold, separating these “neutrino” sub-components by a specific distance providing wavelengths varying with photon energy. This composite photon propagates transversely at c/n, the speed of light divided by the index of refraction of the material traversed. In spite of the mass being defined as zero, for convenience in calculating atomic masses, there is actually an infinitesimal but non-zero mass for the photon that is required for calculations that describe its properties.
Tim, you poor guy! You have a discombobulated brain! Everything you wrote is just gibberish.
i would like to know the temperature in a black hole…maybe absolute zero? is absolute zero the moment that time stop?
I think the temp inside a black hole would be extremely high since temperature seems to increase with mass. Comparing absolute zero to time stopping is very interesting though. To the observer they would appear the same.
Theoretically there is no temperature in a black hole from any observer POV because time is stopped. Although JALNIN does bring up that point, and he also brings up the point of increasing mass corresponding to increasing energy. Everything in Hawking and Einstein’s equations though, suggest that any energy would be absorbed back by the singularity, so there wouldn’t be any heat. In fact it should be infinitely cold. But time is no more, so technically no heat or energy is emitted anyway from any observers POV. Yet recent images of black holes from Chandra show that they emit powerful Gamma Jets along their spin axis just like Neutron stars, and Pulsars. BTW edison. The accretion disk can reach temperatures of 20MN Kelvin on a feeding SM black hole (quasar). NASA just published an article on it through the Chandra feed a while back.
Light doesn’t travel, it just IS. It is we, the condensed matter, that travels, through time.
Oh really? Is this just your imagination/illusion or you have published a paper on it?
So you don’t believe you travel through time?
I wish I understood just a portion of I just read, love sicence so bad BUT, sighs
It would be easier to understand if it wasn’t pure gibberish written by someone with no science background.
I have two “mind-bending relativity side effects” to share. At least they are mind-bending to me.
1) Light travels the same speed relative to all particles of mass, regardless of how those particles move relative to each other:
I can conceptualize this if we are only talking about two mass-particles/observers and the examples I’ve seen always involve only two observers. But if you have many mass-particles/observers, how does the space-time seem to know to adjust differently for all of them. I am sure i am understanding this correctly as it is a basic concept of special relativity and nobody seems to bring this issue up. But it “bends my mind” when i try to include more than two observers. Maybe you can help.
2) General Relativity’s (“GR”) prediction that the big bang started with “Infinite” energy and now the universe appears to have finite mass energy and Regarding the first effect: How can something infinite turn into something finite? Is the answer that at that early in the universe, quantum takes over and GR’s prediction of infinite mass-energy at the start of the universe is just wrong?
I need to correct a typo in my previous comment. Where i say “i am sure am understanding this correctly” I meant to include the word NOT. so it should read “i am sure am NOT understanding this correctly” Mark L.
Mark,….I think you’re understanding it just fine from the standpoint of multiple observers, The point might be that in space, the density of “emptiness” or “lack of emptiness” might be impacted from one area of observation to another by an observer who’s perceptions are not equal but not being taken into consideration by each observer. ( an example if I may?) If you were to use a Clear medium which is oil based beginning with 5 gallons of mineral spirits in a large barrel and keep adding 5 gallons of thicker clear oil and then heavy grease and stop with using a clear heavy wax,…what happens is you end up with a barrel of clear fluid that begins with a floating substrate but the liquid begins to keep floating and the heaviest stuff goes to the bottom,…You end up with a sort of solid tube of clear fluids which if you could keep them in shape here on the earth, “you could observe them” from several positions, #1. the fluid end #2, the less fluid part, #3, the semi solid part #4. the seemingly solid part #5. the almost solid part & #6. the solid part……all of which would be transparent….You could then shine a laser through all of it and perhaps do that again from different places and see what happens at different angles…..I think what happens as a result would be, an observer would end up be influenced as per his or her ideas thusly because of the quasi-nature of what the density of space is at the point of space is where the observation is made. just a guess.
All Special Relativity really says about light is that it appears to move at the same rate from any observer POV. There are other more advanced rules relating to light speeds. One of them is the implication of infinite energy in a photon because of the fact it’s mass-less, therefore it can move at the maximum rate a mass-less particle or wave can (not necessarily that it does) Later when the electron was discovered (also mass-less particle or wave), it was also found to conform to the rules of special relativity.
As far as the big bang, there are a lot of cracks in that theory, and many different ones are beginning to dispute some of the common ideas behind the “Big Bang” as well as “Inflationary Cosmology”. Honestly though, both standard and quantum physics applied, and yet both went out the window at the same time at some point. That’s what all the theories really say. At some point, everything we know or think we know was bunk, because the math just breaks down, and doesn’t work right anymore.
i think until there is an understanding of the actual “fabric” of space itself, the wave vs particle confusion will continue. another interesting article recently was the half integer values of rotating light. planck’s constant was broken? gravity? a bump in the data? lol these are interesting times.
There’s no fabric.
Tesla insists there is an aether, Einstein says not. Tesla enjoyed far less trial and error than Einstein. The vast majority of Tesla’s projects worked the first time around and required no development or experimentation. I’ll go with Tesla; there is an aether as a fabric of space.
http://weinsteinsletter.weebly.com/aether.html
Maybe Special Relativity is not correct? 🙂
Feynman said unequivocally that QED is NOT a wave theory. In fact, the math only looks like Maxwell’s wave function when you are looking at a single particle at a time, but the analogy breaks down as soon as you start looking at the interactions of more than one, which is the real case. There’s no light acting alone, but always an interaction between a photon and some other particle, an electron, another photon, or whatever. He said “light is particles.” So the question re: how can light travel through a vacuum if it’s waves is a nonsensical question. There are no collapsing wave functions in light. There’s only probabilities of position that look like waves on a freaking piece of paper. Even calling light properties as “wavelengths” is nonsensical. Light comes in frequencies, i.e., the number of particles traveling tightly together. Higher frequency is more energy because it’s more particles (E=MC[squared]). “Wavicles” is pure bullshit.
I don’t agree with the John Wheeler theory that there is only one electron since the computer I am using was built by ion implantation and uses a very large number of them simultaneously to function.
Black holes don’t stop or slow light, if they even exist. A black hole could phase shift light, which is why we see things emitting xrays and call them black holes….but they could be something else too.
Photons have no mass but they do have energy. Energy and mass are transformable into each other. Gravity works on energy as well as mass. As massive particles approach the speed of light their measurable mass increases to infinity. But since energy is equivalent to mass, why doesn’t the photon, which has energy, not seem to have infinite mass?
NO other wave travels thru a vacuum? what about radio?
Radio waves are a specific frequency range of light.
Technically speaking, radio waves are emitted at various frequencies that share the same space time as light. They are not however light. They’re modulated electrons. Modulated photons certainly can be used to carry a vast amount of information a great distance. It cannot do it any faster or better than a radio wave though. Both electrons and photons are mass-less, therefore they both conform to the rules of Special Relativity in the same way. Both travel at the speed of light.
I just don’t understand is it a particle of a wave? It seems like it behaves like wave and sometimes like particle and in some situations is like a what ever you are going to call it.
So, the logical idea would to have formula Photon_influence * weight_for_particle + Wave_influence * weight_for_wave
Make it more compact.
This article is good but the title is bad as by the end we still weren’t told how light travels through space. Also, there are some historical mistakes as already pointed out. Now for my contribution: I think that light and Gravity have a lot in common; for one – an atom’s electrons transmit light and an atom contains the tiny heavy place that knows everything there is to know about gravity, that is, the nucleus. Light and Gravity are both related to the same entity, the atom. Unfortunately, we, still cannot grasp how what’s heavy brings about gravitation. For those of you with a creed for new ideas go to: https://www.academia.edu/10785615/Gravity_is_emergent It’s a hypothesis…
Gravity and light are infinite, like space and time… Mind the concept that there are waves within waves, motions within motion, vibrations within vibration, endless overtones and universal harmony…
From this article, I have “And in the end, the only thing that can truly slow down or arrest the speed of light is gravity”
Doesn’t light slow down in water and glass and other mediums. I was only a Physics minor, but I do remember coivering this though way back in the early 80’s. And in my quick checking online, I found the following.
“Light travels at approximately 300,000 kilometers per second in a vacuum, which has a refractive index of 1.0, but it slows down to 225,000 kilometers per second in water (refractive index = 1.3; see Figure 1) and 200,000 kilometers per second in glass (refractive index of 1.5).”
Were they saying something else here. I did like the article.
Photons are not massless, but their mass is incredibly small even compared to a proton or neutron. So, by Einstein’s E=MC^2, the energy required for a photon to move is greatly reduced, but photons do have mass and are affected by gravity. If photons had no mass at all, then gravity would have no affect on them, but gravity does. Gravity bends light and can change it’s course through space. We see that in the actual test first performed to prove Einstein’s theory buy observing the distorted placement of stars as their light passes near the sun observed during an eclipse. We can also see it through gravitational lensing when viewing deeps space objects. And the fact that there are black holes that are black because light cannot escape it’s gravity. So photons do have mass, be it miniscule, and with that their propagation with light waves through space will eventually run out of energy and stop. but this would probably require distances greater to several widths of our universe to accomplish. Light from the furthest reaches of the universe are not as bright, or as energetic, as they are at anyplace between here and their origins. That reduction in their energy is also attributed to Einstein’s equation and the inverse square law, where the intensity of light is in relation to the inverse square of the distance. That proves that light looses energy the further it travels, but it still moves at the speed of light. As light looses energy, it doesn’t slow the light wave.
It has been proven that more energetic light does in fact travel slightly faster. You can find the experiments done with light that has traveled billions of light years, the more energetic is in fact faster over a number of seconds, around 10 -15 or so. As people encounter this information, they see that many accepted theories can now be debunked.
The point of the article is nothing new; light acts like a particle AND a beam. So when you sit behind a closed door and someone shines a light on the door, the light will engulf the door and wave through and around the edges, the particle does not just bounce straight back. You can focus a beam of light on an object, but it will sneak though the corners and underneath the door, through any opening,. And yes, light travels forever. It is a constant, that cannot be sped up. We can slow it down by focusing it through prisims or crystals. But it still is traveling at 186,000/MPS.and that speed does not change. So, that is why we can see the outer edge of the universe: 13,8B light years away *the time that it takes for light to travel in one year, is one light year. So, it has taken 13,8B light years for the light of other galaxies to get here, so those galaxies could be gone by now, since it took so long to reach us, We are truly looking back in time as we see the light emitted from those galaxies and stars.
It propagates through the quantum mish-mash know as the aether . . .
If light is a particle and particles have mass why does not the mas increase with it speed?
Wow…there are errors in the article, yes…the enthusiasm demonstrated by all the comments is encouraging…but when I read these comments, I am a bit dismayed at the lack of understanding that is evident in most of them…confusing energy and intensity and wavelength…confusing rest mass and inertial mass…not to mention some off-the-wall hypotheses with no experimental evidence to support them. There are some great primers out there…books, documentaries, podcasts (like Astronomy Cast). Good luck!
Precisely correct. Sci-fi rules basic physics, which reflects on the poor education system. Pity.
First time I heard about A. A. and his theory about light I really didn’t like him. Why? Because light was the the fastest thing in the universe and there is no other thing faster than the light. Later, when I have red about angular speed I have asked my self if you have linear and angular speed and both of them are speeds how that will result in the maximum speed. Since then, I have not had a chance to get right answer.
Comments are closed.
share this!
May 20, 2016
How does light travel?
by Matt Williams, Universe Today

Ever since Democritus – a Greek philosopher who lived between the 5th and 4th century's BCE – argued that all of existence was made up of tiny indivisible atoms, scientists have been speculating as to the true nature of light. Whereas scientists ventured back and forth between the notion that light was a particle or a wave until the modern, the 20th century led to breakthroughs that showed that it behaves as both.
These included the discovery of the electron, the development of quantum theory, and Einstein's Theory of Relativity. However, there remains many fascinating and unanswered questions when it comes to light, many of which arise from its dual nature. For instance, how is it that light can be apparently without mass, but still behave as a particle? And how can it behave like a wave and pass through a vacuum, when all other waves require a medium to propagate?
Theory of Light in the 19th Century:
During the Scientific Revolution, scientists began moving away from Aristotelian scientific theories that had been seen as accepted canon for centuries. This included rejecting Aristotle's theory of light, which viewed it as being a disturbance in the air (one of his four "elements" that composed matter), and embracing the more mechanistic view that light was composed of indivisible atoms.
In many ways, this theory had been previewed by atomists of Classical Antiquity – such as Democritus and Lucretius – both of whom viewed light as a unit of matter given off by the sun. By the 17th century, several scientists emerged who accepted this view, stating that light was made up of discrete particles (or "corpuscles"). This included Pierre Gassendi, a contemporary of René Descartes, Thomas Hobbes, Robert Boyle, and most famously, Sir Isaac Newton.
Newton's corpuscular theory was an elaboration of his view of reality as an interaction of material points through forces. This theory would remain the accepted scientific view for more than 100 years, the principles of which were explained in his 1704 treatise "Opticks, or, a Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of Light". According to Newton, the principles of light could be summed as follows:
- Every source of light emits large numbers of tiny particles known as corpuscles in a medium surrounding the source.
- These corpuscles are perfectly elastic, rigid, and weightless.
This represented a challenge to "wave theory", which had been advocated by 17th century Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens. . These theories were first communicated in 1678 to the Paris Academy of Sciences and were published in 1690 in his "Traité de la lumière" ("Treatise on Light"). In it, he argued a revised version of Descartes views, in which the speed of light is infinite and propagated by means of spherical waves emitted along the wave front.
Double-Slit Experiment:
By the early 19th century, scientists began to break with corpuscular theory. This was due in part to the fact that corpuscular theory failed to adequately explain the diffraction, interference and polarization of light, but was also because of various experiments that seemed to confirm the still-competing view that light behaved as a wave.
The most famous of these was arguably the Double-Slit Experiment, which was originally conducted by English polymath Thomas Young in 1801 (though Sir Isaac Newton is believed to have conducted something similar in his own time). In Young's version of the experiment, he used a slip of paper with slits cut into it, and then pointed a light source at them to measure how light passed through it.
According to classical (i.e. Newtonian) particle theory, the results of the experiment should have corresponded to the slits, the impacts on the screen appearing in two vertical lines. Instead, the results showed that the coherent beams of light were interfering, creating a pattern of bright and dark bands on the screen. This contradicted classical particle theory, in which particles do not interfere with each other, but merely collide.
The only possible explanation for this pattern of interference was that the light beams were in fact behaving as waves. Thus, this experiment dispelled the notion that light consisted of corpuscles and played a vital part in the acceptance of the wave theory of light. However subsequent research, involving the discovery of the electron and electromagnetic radiation , would lead to scientists considering yet again that light behaved as a particle too, thus giving rise to wave-particle duality theory.
Electromagnetism and Special Relativity:
Prior to the 19th and 20th centuries, the speed of light had already been determined. The first recorded measurements were performed by Danish astronomer Ole Rømer, who demonstrated in 1676 using light measurements from Jupiter's moon Io to show that light travels at a finite speed (rather than instantaneously).
By the late 19th century , James Clerk Maxwell proposed that light was an electromagnetic wave, and devised several equations (known as Maxwell's equations) to describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents. By conducting measurements of different types of radiation (magnetic fields, ultraviolet and infrared radiation), he was able to calculate the speed of light in a vacuum (represented as c).
In 1905, Albert Einstein published "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", in which he advanced one of his most famous theories and overturned centuries of accepted notions and orthodoxies. In his paper, he postulated that the speed of light was the same in all inertial reference frames, regardless of the motion of the light source or the position of the observer.
Exploring the consequences of this theory is what led him to propose his theory of Special Relativity, which reconciled Maxwell's equations for electricity and magnetism with the laws of mechanics, simplified the mathematical calculations, and accorded with the directly observed speed of light and accounted for the observed aberrations. It also demonstrated that the speed of light had relevance outside the context of light and electromagnetism.
For one, it introduced the idea that major changes occur when things move close the speed of light, including the time-space frame of a moving body appearing to slow down and contract in the direction of motion when measured in the frame of the observer. After centuries of increasingly precise measurements, the speed of light was determined to be 299,792,458 m/s in 1975.
Einstein and the Photon:
In 1905, Einstein also helped to resolve a great deal of confusion surrounding the behavior of electromagnetic radiation when he proposed that electrons are emitted from atoms when they absorb energy from light. Known as the photoelectric effect, Einstein based his idea on Planck's earlier work with "black bodies" – materials that absorb electromagnetic energy instead of reflecting it (i.e. white bodies).
At the time, Einstein's photoelectric effect was attempt to explain the "black body problem", in which a black body emits electromagnetic radiation due to the object's heat. This was a persistent problem in the world of physics, arising from the discovery of the electron, which had only happened eight years previous (thanks to British physicists led by J.J. Thompson and experiments using cathode ray tubes).
At the time, scientists still believed that electromagnetic energy behaved as a wave, and were therefore hoping to be able to explain it in terms of classical physics. Einstein's explanation represented a break with this, asserting that electromagnetic radiation behaved in ways that were consistent with a particle – a quantized form of light which he named "photons". For this discovery, Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1921.
Wave-Particle Duality:
Subsequent theories on the behavior of light would further refine this idea, which included French physicist Louis-Victor de Broglie calculating the wavelength at which light functioned. This was followed by Heisenberg's "uncertainty principle" (which stated that measuring the position of a photon accurately would disturb measurements of it momentum and vice versa), and Schrödinger's paradox that claimed that all particles have a " wave function ".
In accordance with quantum mechanical explanation, Schrodinger proposed that all the information about a particle (in this case, a photon) is encoded in its wave function, a complex-valued function roughly analogous to the amplitude of a wave at each point in space. At some location, the measurement of the wave function will randomly "collapse", or rather "decohere", to a sharply peaked function. This was illustrated in Schrödinger famous paradox involving a closed box, a cat, and a vial of poison (known as the "Schrödinger's Cat" paradox).
According to his theory, wave function also evolves according to a differential equation (aka. the Schrödinger equation). For particles with mass, this equation has solutions; but for particles with no mass, no solution existed. Further experiments involving the Double-Slit Experiment confirmed the dual nature of photons. where measuring devices were incorporated to observe the photons as they passed through the slits.
When this was done, the photons appeared in the form of particles and their impacts on the screen corresponded to the slits – tiny particle-sized spots distributed in straight vertical lines. By placing an observation device in place, the wave function of the photons collapsed and the light behaved as classical particles once more. As predicted by Schrödinger, this could only be resolved by claiming that light has a wave function, and that observing it causes the range of behavioral possibilities to collapse to the point where its behavior becomes predictable.
The development of Quantum Field Theory (QFT) was devised in the following decades to resolve much of the ambiguity around wave-particle duality. And in time, this theory was shown to apply to other particles and fundamental forces of interaction (such as weak and strong nuclear forces). Today, photons are part of the Standard Model of particle physics, where they are classified as boson – a class of subatomic particles that are force carriers and have no mass.
So how does light travel? Basically, traveling at incredible speeds (299 792 458 m/s) and at different wavelengths, depending on its energy. It also behaves as both a wave and a particle, able to propagate through mediums (like air and water) as well as space. It has no mass, but can still be absorbed, reflected, or refracted if it comes in contact with a medium. And in the end, the only thing that can truly slow down or arrest the speed of light is gravity (i.e. a black hole).
What we have learned about light and electromagnetism has been intrinsic to the revolution which took place in physics in the early 20th century, a revolution that we have been grappling with ever since. Thanks to the efforts of scientists like Maxwell, Planck, Einstein, Heisenberg and Schrodinger, we have learned much, but still have much to learn.
For instance, its interaction with gravity (along with weak and strong nuclear forces) remains a mystery. Unlocking this, and thus discovering a Theory of Everything (ToE) is something astronomers and physicists look forward to. Someday, we just might have it all figured out!
Source: Universe Today
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Unraveling an ancient European extinction mystery: Disappearance of dwarf megafauna on paleolithic Cyprus
9 hours ago

Highly-sensitive beaks could help albatrosses and penguins find their food

'Scuba-diving' lizards use bubble to breathe underwater and avoid predators

Pollen affects cloud formation and precipitation patterns, researchers find
12 hours ago

Freshwater oysters could be key to developing stronger, 'greener' adhesives

Nuclear theorists turn to supercomputers to map out matter's building blocks in 3D

Study discovers that fruit flies' visual navigation tactics differ by environment

Zirconium metals under extreme conditions found to deform in surprisingly complex ways

Astronomers discover new feature in exoplanet distribution that's between the Neptunian Desert and Savanna

Computational tool can pinpoint causal relationships from complex biological data
Relevant physicsforums posts, how does output voltage of an electric guitar work.
Sep 16, 2024
Electromagnetic Skrymion Created
Sep 15, 2024
Looking for info on old, unlabeled Geissler tubes
Sep 13, 2024
Why does my ceiling glow in the dark?
Sep 8, 2024
Brownian Motions and Quantifying Randomness in Physical Systems
Sep 2, 2024
Container in an MRI room
Sep 1, 2024
More from Other Physics Topics
Related Stories

Experiment suggests it might be possible to control atoms entangled with the light they emit by manipulating detection
May 12, 2016
The 'great smoky dragon' of quantum physics
Mar 10, 2016

The first ever photograph of light as both a particle and wave
Mar 2, 2015
'One real mystery of quantum mechanics': Physicists devise new experiment
Nov 1, 2012

Quantum physics inside a drop of paint

Will we have to rewrite Einstein's theory of general relativity?
Nov 25, 2015
Recommended for you

Black hole pairs may unveil new particles
15 hours ago

CMS experiment at CERN weighs in on the W boson mass
17 hours ago

Theoretical physicists develop method to model a central theory of quantum gravity in the laboratory

Energy-saving computing with magnetic whirls

A fundamental magnetic property of the muon measured to unprecedented precision
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
The Nature of Light
Introduction.
Light is a transverse, electromagnetic wave that can be seen by the typical human. The wave nature of light was first illustrated through experiments on diffraction and interference . Like all electromagnetic waves, light can travel through a vacuum. The transverse nature of light can be demonstrated through polarization .
- In 1678, Christiaan Huygens (1629–1695) published Traité de la Lumiere , where he argued in favor of the wave nature of light. Huygens stated that an expanding sphere of light behaves as if each point on the wave front were a new source of radiation of the same frequency and phase.
- Thomas Young (1773–1829) and Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) disproved Newton's corpuscular theory.
Light is produced by one of two methods…
- Incandescence is the emission of light from "hot" matter (T ≳ 800 K).
- Luminescence is the emission of light when excited electrons fall to lower energy levels (in matter that may or may not be "hot").
Just notes so far. The speed of light in a vacuum is represented by the letter c from the Latin celeritas — swiftness. Measurements of the speed of light.
Veramente non l'ho sperimentata, salvo che in lontananza piccola, cioè manco d'un miglio, dal che non ho potuto assicurarmi se veramente la comparsa del lume opposto sia instantanea; ma ben, se non instantanea, velocissima…. In fact I have tried the experiment only at a short distance, less than a mile, from which I have not been able to ascertain with certainty whether the appearance of the opposite light was instantaneous or not; but if not instantaneous it is extraordinarily rapid …. Galileo Galilei, 1638 Galileo Galilei, 1638
Ole Rømer (1644–1710) Denmark. "Démonstration touchant le mouvement de la lumière trouvé par M. Roemer de l'Académie des Sciences." Journal des Scavans . 7 December 1676. Rømer's idea was to use the transits of Jupiter's moon Io to determine the time. Not local time, which was already possible, but a "universal" time that would be the same for all observers on the Earth, Knowing the standard time would allow one to determine one's longitude on the Earth — a handy thing to know when navigating the featureless oceans.
Unfortunately, Io did not turn out to be a good clock. Rømer observed that times between eclipses got shorter as Earth approached Jupiter, and longer as Earth moved farther away. He hypothesized that this variation was due to the time it took for light to travel the lesser or greater distance, and estimated that the time for light to travel the diameter of the Earth's orbit, a distance of two astronomical units, was 22 minutes.
- The speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant in all reference frames.
- The speed of light in a vacuum is fixed at 299,792,458 m/s by the current definition of the meter.
- The speed of light in a medium is always slower the speed of light in a vacuum.
- The speed of light depends upon the medium through which it travels.The speed of anything with mass is always less than the speed of light in a vacuum.

other characteristics
The amplitude of a light wave is related to its intensity.
- Intensity is the absolute measure of a light wave's power density.
- Brightness is the relative intensity as perceived by the average human eye.
The frequency of a light wave is related to its color.
- Color is such a complex topic that it has its own section in this book.
- Laser light is effectively monochromatic.
- There are six simple, named colors in English (and many other languages) each associated with a band of monochromatic light. In order of increasing frequency they are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet .
- Light is sometimes also known as visible light to contrast it from "ultraviolet light" and "infrared light"
- Other forms of electromagnetic radiation that are not visible to humans are sometimes also known informally as "light"
- Nearly every light source is polychromatic.
- White light is polychromatic.
A graph of relative intensity vs. frequency is called a spectrum (plural: spectra ). Although frequently associated with light, the term can be applied to any wave phenomena.
- Blackbody radiators emit a continuous spectrum.
- The excited electrons in a gas emit a discrete spectrum.
The wavelength of a light wave is inversely proportional to its frequency.
- Light is often described by it's wavelength in a vacuum .
- Light ranges in wavelength from 400 nm on the violet end to 700 nm on the red end of the visible spectrum.
Phase differences between light waves can produce visible interference effects. (There are several sections in this book on interference phenomena and light.)
Leftovers about animals.
- Falcon can see a 10 cm. object from a distance of 1.5 km.
- Fly's Eye has a flicker fusion rate of 300/s. Humans have a flicker fusion rate of only 60/s in bright light and 24/s in dim light. The flicker fusion rate is the frequency with which the "flicker" of an image cannot be distinguished as an individual event. Like the frame of a movie… if you slowed it down, you would see individual frames. Speed it up and you see a constantly moving image. Octopus' eye has a flicker fusion frequency of 70/s in bright light.
- Penguin has a flat cornea that allows for clear vision underwater. Penguins can also see into the ultraviolet range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Sparrow Retina has 400,000 photoreceptors per square. mm.
- Reindeer can see ultraviolet wavelengths, which may help them view contrasts in their mostly white environment.
It’s a wonderful world — and universe — out there.
Come explore with us!
Science News Explores
Understanding light and other forms of energy on the move.
This radiation includes visible light, radio signals — even medical X-rays

Light is a form of energy created by the movement of electrons. Different wavelengths appear as different colors, although most wavelengths are not visible to the human eye.
Natasha Hartano/Flickr ( CC BY-NC 2.0 ); adapted by L. Steenblik Hwang
Share this:
- Google Classroom
By Jennifer Look
July 16, 2020 at 6:30 am
Light is a form of energy that travels as waves. Their length — or wavelength — determines many of light’s properties. For instance, wavelength accounts for light’s color and how it will interact with matter. The range of wavelengths, from super short to very, very long, is known as the light spectrum. Whatever its wavelength, light will radiate out infinitely unless or until it is stopped. As such, light is known as radiation.
Light’s formal name is electromagnetic radiation. All light shares three properties. It can travel through a vacuum. It always moves at a constant speed, known as the speed of light, which is 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second in a vacuum. And the wavelength defines the type or color of light.
Just to make things interesting, light also can behave as photons , or particles. When looked at this way, quantities of light can be counted, like beads on a string.
Humans have evolved to sense a small part of the light spectrum. We know these wavelengths as “visible” light. Our eyes contain cells known as rods and cones. Pigments in those cells can interact with certain wavelengths (or photons) of light. When this happens, they create signals that travel to the brain. The brain interprets the signals from different wavelengths (or photons) as different colors.
The longest visible wavelengths are around 700 nanometers and appear red. The range of visible light ends around 400 nanometers. Those wavelengths appear violet. The whole rainbow of colors falls in between.
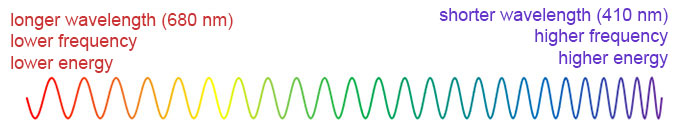
Most of the light spectrum, however, falls outside that range. Bees, dogs and even a few people can see ultraviolet (UV) light . These are wavelengths a bit shorter than violet ones. Even those of us without UV vision can still respond to UV light, however. Our skin will redden or even burn when it encounters too much.
Many things emit heat in the form of infrared light. As that name suggests, infrared wavelengths are somewhat longer than red’s. Mosquitoes and pythons can see in this range. Night-vision goggles work by detecting infrared light.
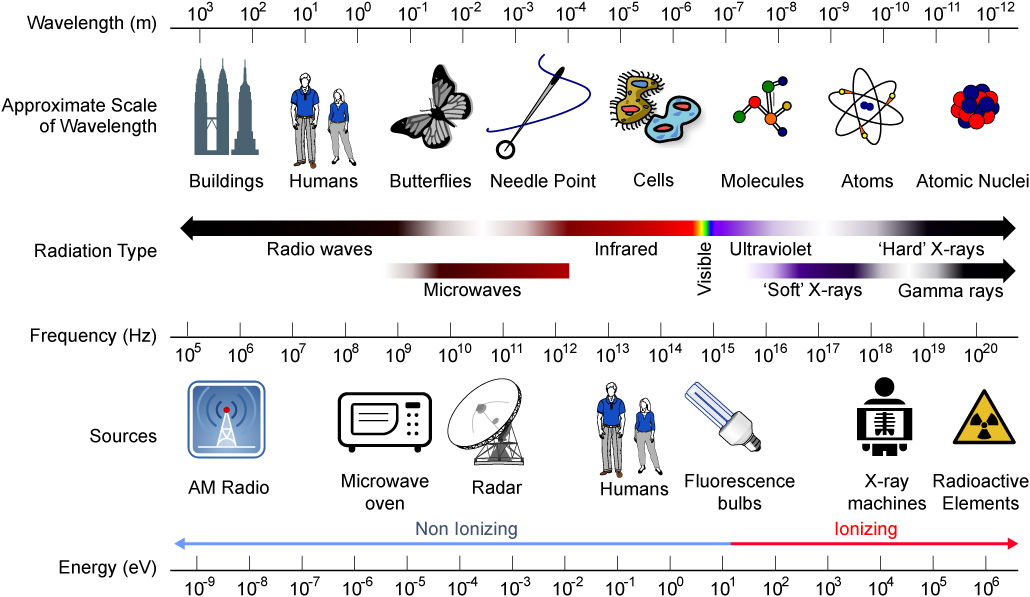
Light also comes in many other types. Light with really short, high-energy waves can be gamma rays and X-rays (used in medicine). Long, low-energy waves of light fall in the radio and microwave part of the spectrum.
Desiré Whitmore is a physics educator at the Exploratorium in San Francisco, Calif. Teaching people about light as radiation can be difficult, she says. “People are afraid of the word ‘radiation.’ But all it means is that something is moving outward.”
The sun emits lots of radiation in wavelengths that span from X-rays to infrared. Sunlight provides almost all of the energy required for life on Earth. Small, cool objects release much less radiation. But every object emits some. That includes people. We give off small amounts of infrared light generally referred to as heat.
Whitmore points to her cell phone as a common source of many types of light. Smartphones use visible wavelengths to light up the screen display. Your phone talks to other phones via radio waves. And the camera has the ability to detect infrared light that human eyes cannot see. With the right app, the phone transforms this infrared light into visible light that we can see on the phone’s screen.
“This is fun to try out with your cell phone’s front-facing camera,” Whitmore says. Use a remote control for a television or other device. Its light is infrared, she notes, “so we cannot see it. But when you point the controller at your phone’s camera and press a button, “you can see a bright pink light appear on the screen!”
“All these different types of radiation help improve our lives,” Whitmore says. They “have been shown to be safe when used in reasonable amounts,” she notes — but can be “dangerous when you use too much of it.”
More Stories from Science News Explores on Physics

Science reveals the reasons behind painful paper cuts

Scientists Say: Kugelblitz

Experiment: Making music with bottles

Scientists Say: Magnetosphere

Scientists Say: Cosmic rays

The periodic table might soon have a new element

Lasers help put the cork on spilled oil

Scientists Say: Goldene
Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE
Sciencing_icons_biology biology, sciencing_icons_cells cells, sciencing_icons_molecular molecular, sciencing_icons_microorganisms microorganisms, sciencing_icons_genetics genetics, sciencing_icons_human body human body, sciencing_icons_ecology ecology, sciencing_icons_chemistry chemistry, sciencing_icons_atomic & molecular structure atomic & molecular structure, sciencing_icons_bonds bonds, sciencing_icons_reactions reactions, sciencing_icons_stoichiometry stoichiometry, sciencing_icons_solutions solutions, sciencing_icons_acids & bases acids & bases, sciencing_icons_thermodynamics thermodynamics, sciencing_icons_organic chemistry organic chemistry, sciencing_icons_physics physics, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-physics fundamentals, sciencing_icons_electronics electronics, sciencing_icons_waves waves, sciencing_icons_energy energy, sciencing_icons_fluid fluid, sciencing_icons_astronomy astronomy, sciencing_icons_geology geology, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geology fundamentals, sciencing_icons_minerals & rocks minerals & rocks, sciencing_icons_earth scructure earth structure, sciencing_icons_fossils fossils, sciencing_icons_natural disasters natural disasters, sciencing_icons_nature nature, sciencing_icons_ecosystems ecosystems, sciencing_icons_environment environment, sciencing_icons_insects insects, sciencing_icons_plants & mushrooms plants & mushrooms, sciencing_icons_animals animals, sciencing_icons_math math, sciencing_icons_arithmetic arithmetic, sciencing_icons_addition & subtraction addition & subtraction, sciencing_icons_multiplication & division multiplication & division, sciencing_icons_decimals decimals, sciencing_icons_fractions fractions, sciencing_icons_conversions conversions, sciencing_icons_algebra algebra, sciencing_icons_working with units working with units, sciencing_icons_equations & expressions equations & expressions, sciencing_icons_ratios & proportions ratios & proportions, sciencing_icons_inequalities inequalities, sciencing_icons_exponents & logarithms exponents & logarithms, sciencing_icons_factorization factorization, sciencing_icons_functions functions, sciencing_icons_linear equations linear equations, sciencing_icons_graphs graphs, sciencing_icons_quadratics quadratics, sciencing_icons_polynomials polynomials, sciencing_icons_geometry geometry, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geometry fundamentals, sciencing_icons_cartesian cartesian, sciencing_icons_circles circles, sciencing_icons_solids solids, sciencing_icons_trigonometry trigonometry, sciencing_icons_probability-statistics probability & statistics, sciencing_icons_mean-median-mode mean/median/mode, sciencing_icons_independent-dependent variables independent/dependent variables, sciencing_icons_deviation deviation, sciencing_icons_correlation correlation, sciencing_icons_sampling sampling, sciencing_icons_distributions distributions, sciencing_icons_probability probability, sciencing_icons_calculus calculus, sciencing_icons_differentiation-integration differentiation/integration, sciencing_icons_application application, sciencing_icons_projects projects, sciencing_icons_news news.
- Share Tweet Email Print
- Home ⋅
- Science ⋅
- Physics ⋅
- Sound & Light (Physics): How are They Different?
How Does Light Travel?

Sound & Light (Physics): How are They Different?
The question of how light travels through space is one of the perennial mysteries of physics. In modern explanations, it is a wave phenomenon that doesn't need a medium through which to propagate. According to quantum theory, it also behaves as a collection of particles under certain circumstances. For most macroscopic purposes, though, its behavior can be described by treating it as a wave and applying the principles of wave mechanics to describe its motion.
Electromagnetic Vibrations
In the mid 1800s, Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell established that light is a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in waves. The question of how it manages to do so in the absence of a medium is explained by the nature of electromagnetic vibrations. When a charged particle vibrates, it produces an electrical vibration that automatically induces a magnetic one -- physicists often visualize these vibrations occurring in perpendicular planes. The paired oscillations propagate outward from the source; no medium, except for the electromagnetic field that permeates the universe, is required to conduct them.
A Ray of Light
When an electromagnetic source generates light, the light travels outward as a series of concentric spheres spaced in accordance with the vibration of the source. Light always takes the shortest path between a source and destination. A line drawn from the source to the destination, perpendicular to the wave-fronts, is called a ray. Far from the source, spherical wave fronts degenerate into a series of parallel lines moving in the direction of the ray. Their spacing defines the wavelength of the light, and the number of such lines that pass a given point in a given unit of time defines the frequency.
The Speed of Light
The frequency with which a light source vibrates determines the frequency -- and wavelength -- of the resultant radiation. This directly affects the energy of the wave packet -- or burst of waves moving as a unit -- according to a relationship established by physicist Max Planck in the early 1900s. If the light is visible, the frequency of vibration determines color. The speed of light is unaffected by vibrational frequency, however. In a vacuum, it is always 299,792 kilometers per second (186, 282 miles per second), a value denoted by the letter "c." According to Einstein's Theory of Relativity, nothing in the universe travels faster than this.
Refraction and Rainbows
Light travels slower in a medium than it does in a vacuum, and the speed is proportional to the density of the medium. This speed variation causes light to bend at the interface of two media -- a phenomenon called refraction. The angle at which it bends depends on the densities of the two media and the wavelength of the incident light. When light incident on a transparent medium is composed of wave fronts of different wavelengths, each wave front bends at a different angle, and the result is a rainbow.
Related Articles
What is the formula for velocity of a wave, the famous physicist who discovered photons, how to convert hertz to nanometers, what happens to a white light when it passes through..., how does light travel from the sun to earth, why is the discovery of gravitational waves important, what is light measured in, what causes the dispersion of white light, how to convert photons to joules, how to calculate a wavenumber, how to calculate frequency in hertz, how to find resonant frequencies, what affects the angle of refraction of light, how to calculate oscillation frequency, what is the difference between radio waves & cell phone....
- Boundless.com: Planck's Quantum Theory
About the Author
Chris Deziel holds a Bachelor's degree in physics and a Master's degree in Humanities, He has taught science, math and English at the university level, both in his native Canada and in Japan. He began writing online in 2010, offering information in scientific, cultural and practical topics. His writing covers science, math and home improvement and design, as well as religion and the oriental healing arts.
Photo Credits
Marcochow/iStock/Getty Images
Find Your Next Great Science Fair Project! GO
Does Light Travel Forever?
Most recent answer: 01/23/2013
Hi Raja, Good question. First, let's think about why sound does not travel forever. Sound cannot travel through empty space; it is carried by vibrations in a material, or medium (like air, steel, water, wood, etc). As the particles in the medium vibrate, energy is lost to heat, viscous processes, and molecular motion. So, the sound wave gets smaller and smaller until it disappears. In contrast, light waves can travel through a vacuum, and do not require a medium. In empty space, the wave does not dissipate (grow smaller) no matter how far it travels, because the wave is not interacting with anything else. This is why light from distant stars can travel through space for billions of light-years and still reach us on earth. However, light can also travel within some materials, like glass and water. In this case, some light is absorbed and lost as heat, just like sound. So, underwater, or in our atmosphere, light will only travel some finite range (which is different depending on the properties of the material it travels through). There is one more aspect of wave travel to consider, which applies to both sound and light waves. As a wave travels from a source, it propagates outward in all directions. Therefore, it fills a space given approximately by the surface area of a sphere. This area increases by the square of the distance R from the source; since the wave fills up all this space, its intensity decreases by R squared. This effect just means that the light/sound source will appear dimmer if we are farther away from it, since we don't collect all the light it emits. For example, light from a distant star travels outward in a giant sphere. Only one tiny patch of this sphere of light actually hits our eyes, which is why stars don't blind us! David Schmid
(published on 01/23/2013)
Follow-Up #1: How far does light go?
Light just keeps going and going until it bumps into something. Then it can either be reflected or absorbed. Astronomers have detected some light that has been traveling for more that 12 billion years, close to the age of the universe.
Light has some interesting properties. It comes in lumps called photons. These photons carry energy and momentum in specific amounts related to the color of the light. There is much to learned about light. I suggest you log in to our website and type LIGHT into the search box. Lots of interesting stuff there.
To answer your previous question "Can light go into a black hole?" , the answer is yes.
(published on 12/03/2015)
Follow-Up #2: less than one photon?
Certainly you can run the ouput of a single-photon source through a half-silvered mirror, and get a sort of half-ghost of the photon in two places. If you put ordinary photon detectors in those places, however, each will either detect zero or one. For each source photon, you'll get at most one of the detectors to find it. How does the half-ghost at the other one know whether it's detectably there or not? The name of that mystery is "quantum entanglement". At some level we don't really know the answer.
(published on 02/04/2016)
Follow-Up #3: stars too far away to see?
Most stars are too far for us to see them as individual stars even with our best telescopes. Still, we can get light from them, mixed with light from other stars. If our understanding of the universe is at all right, there are also stars that once were visible from here but now are outside our horizon so no light from them reaches us. It's probable that there are many more stars outside our horizon than inside, maybe infinitely more. It's hard to check, however, what's happening outside our horizon! It's even hard to define what we mean by "now" for things outside the horizon.
(published on 07/22/2016)
Follow-Up #4: light going out to space
Certainly ordinary light travels out to space. That's how spy cameras and such can take pictures of things here on the Earth's surface.
(published on 09/01/2016)
Follow-Up #5: end of the universe?
We don't think there's any "end" in the sense of some spatial boundary. Unless something changes drastically, there also won't be an end in time. The expansion looks like it will go on forever. So that wouldn't give a maximum range.
(published on 03/26/2017)
Follow-Up #6: seeing black holes
In principle a well-aimed beam would loop around the outside of the black hole and return to Earth. There aren't any black holes close enough to make this practical. Instead the bending of light by black holes is observed by their lensing effect on light coming from more distant objects.
The amazing gravitational wave signals observed from merging black holes provide even more direct and convincing proof that black holes exist and follow the laws of General Relativity.
(published on 01/29/2018)
Follow-up on this answer
Related Questions
- Can you use light to attract or repel an item?
- Absorption of short light pulses
- light from Hiroshima
- light dependent switches
- Would a tin-can phone work in space?
- refraction and reflection
- light reflection from glass
- light from old sources
- Seeing reflected and emitted light
- Speed of light in various directions
Still Curious?
Expore Q&As in related categories
- Properties of Light
- Properties of Sound
February 12, 2013
Something from Nothing? A Vacuum Can Yield Flashes of Light
"Virtual particles" can become real photons--under the right conditions
By Charles Q. Choi
A vacuum might seem like empty space, but scientists have discovered a new way to seemingly get something from that nothingness, such as light. And the finding could ultimately help scientists build incredibly powerful quantum computers or shed light on the earliest moments in the universe's history.
Quantum physics explains that there are limits to how precisely one can know the properties of the most basic units of matter—for instance, one can never absolutely know a particle's position and momentum at the same time. One bizarre consequence of this uncertainty is that a vacuum is never completely empty, but instead buzzes with so-called “ virtual particles ” that constantly wink into and out of existence.
These virtual particles often appear in pairs that near-instantaneously cancel themselves out. Still, before they vanish, they can have very real effects on their surroundings. For instance, photons—packets of light—can pop in and out of a vacuum. When two mirrors are placed facing each other in a vacuum, more virtual photons can exist around the outside of the mirrors than between them, generating a seemingly mysterious force that pushes the mirrors together.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
This phenomenon, predicted in 1948 by the Dutch physicist Hendrick Casimir and known as the Casimir effect , was first seen with mirrors held still . Researchers also predicted a dynamical Casimir effect that can result when mirrors are moved, or objects otherwise undergo change. Now quantum physicist Pasi Lähteenmäki at Aalto University in Finland and his colleagues reveal that by varying the speed at which light can travel, they can make light appear from nothing.
The speed of light in a vacuum is constant, according to Einstein's theory of relativity, but its speed passing through any given material depends on a property of that substance known as its index of refraction. By varying a material's index of refraction, researchers can influence the speed at which both real and virtual photons travel within it. Lähteenmäki says one can think of this system as being much like a mirror, and if its thickness changes fast enough, virtual photons reflecting off it can receive enough energy from the bounce to turn into real photons. "Imagine you stay in a very dark room and suddenly the index of refraction of light [of the room] changes," Lähteenmäki says. "The room will start to glow."
The researchers began with an array of 250 superconducting quantum-interference devices, or SQUIDs—circuits that are extraordinarily sensitive to magnetic fields. They inserted the array inside a refrigerator. By carefully exerting magnetic fields on this array, they could vary the speed at which microwave photons traveled through it by a few percent. The researchers then cooled this array to 50 thousandths of a degree Celsius above absolute zero. Because this environment is supercold, it should not emit any radiation, essentially behaving as a vacuum. "We were simply studying these circuits for the purpose of developing an amplifier, which we did," says researcher Sorin Paraoanu, a theoretical physicist at Aalto University. "But then we asked ourselves—what if there is no signal to amplify? What happens if the vacuum is the signal?"
The researchers detected photons that matched predictions from the dynamical Casimir effect. For instance, such photons should display the strange property of quantum entanglement—that is, by measuring the details of one, scientists could in principle know exactly what its counterpart is like, no matter where it is in the universe, a phenomenon Einstein referred to as "spooky action at a distance." The scientists detailed their findings online February 11 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences .
"This work and a number of other recent works demonstrate that the vacuum is not empty but full of virtual photons," says theoretical physicist Steven Girvin at Yale University, who did not take part in the Aalto study.
Another study from physicist Christopher Wilson and his colleagues recently demonstrated the dynamical Casimir effect in a system mimicking a mirror moving at nearly 5 percent of the speed of light. "It's nice to see further confirmation of this effect and see this area of research continuing," says Wilson, now at the University of Waterloo in Ontario, who also did not participate in the Aalto study. "Only recently has technology advanced into a new technical regime of experiments where we can start to look at very fast changes that can have dramatic effects on electromagnetic fields," he adds.
The investigators caution that such experiments do not constitute a magical way to get more energy out of a system than what is input. For instance, it takes energy to change a material's index of refraction.
Instead, such research could help scientists learn more about the mysteries of quantum entanglement, which lies at the heart of quantum computers—advanced machines that could in principle run more calculations in an instant than there are atoms in the universe. The entangled microwave photons the experimental array generated "can be used for a form of quantum computation known as 'continuous variable' quantum information processing,” Girvin says. “This is a direction which is just beginning to open up.”
Wilson adds that these systems “might be used to simulate some interesting scenarios. For instance, there are predictions that during cosmic inflation in the early universe, the boundaries of the universe were expanding nearly at light-speed or faster than the speed of light. We might predict there'd be some dynamical Casimir radiation produced then, and we can try and do tabletop simulations of this."
So the static Casimir effect involves mirrors held still; the dynamical Casimir effect can for instance involve mirrors that move.
How Does Light Travel Through Space? Facts & FAQ
Last Updated on Mar 15 2024

Light is such a fundamental part of our lives. From the moment we’re born, we are showered with all kinds of electromagnetic radiation, both colorful, and invisible. Light travels through the vacuum of space at 186,828 miles per second as transverse waves , outside of any material or medium, because photons—the particles that make up light—also behave as waves. This is referred to as the wave-particle duality of light.
- What Is Light?
The wave-particle duality of light simply means that light behaves as both waves and particles . Although this has been long accepted as fact, scientists only managed to observe both these properties of light ¹ simultaneously for the first time in 2015.
As a wave, light is electromagnetic radiation—vibrations, or oscillations, of the electric and magnetic fields. As particles, light is made up of little massless packets of energy called photons ¹ .
- What Are Light Waves?
Waves are the transference of energy from one point to another. If we dropped a pebble into a small pond, the energy that the impact creates would transfer as a ripple, or a wave, that travels through the surface of the water, from one water particle to another, until eventually reaching the edge of the pond.
This is also how sound waves work—except that, with sound, it’s the pressure or vibrations of particles in the air that eventually reach our ears.
Unlike water and sound, light itself is electromagnetic radiation—or light waves—so it doesn’t need a medium to travel through.
- What Are Transverse Waves?
Light propagates through transverse waves. Transverse waves refer to a way in which energy is transferred.
Transverse waves oscillate at a 90-degree angle (or right angle) to the direction the energy is traveling in. An easy way to picture this is to imagine an S shape flipped onto its side. The waves would be going up and down, while the energy would be moving either left or right.
With light waves ¹ , there are 2 oscillations to consider. If the light wave is traveling on the X axis, then the oscillations of the electric field would be at a right angle, either along the Y or Z axes, and the oscillations of the magnetic field would be on the other.
- Can Anything Travel Faster Than Light?
The simple answer to this question is no, as far as we know at this time, nothing can go faster than the speed of light ¹ . Albert Einstein’s special theory of relativity states that “no known object can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum.”
Space and time don’t yet exist beyond the speed of light—if we were to travel that fast, the closer we get to the speed of light, the more our spatial dimension would shrink, until eventually collapsing.
Beyond this, the laws of physics state that as an object approaches the speed of light , its mass would become infinite, and so would the energy it would need to propel it. Since it’s probably impossible to create an infinite amount of energy, it would be difficult for anything to travel faster than light.
Tachyon, a hypothetical particle, is said to travel faster than the speed of light. However, because its speed would not be consistent with the known laws of physics, physicists believe that tachyon particles do not exist.
- Final Thoughts
Light travels through space as transverse, electromagnetic waves. Its wave-particle duality means that it behaves as both particles and waves. As far as we know, nothing in the world travels as fast as light.
- https://phys.org/news/2015-03-particle.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms7407
- https://www.wtamu.edu/~cbaird/sq/2017/07/20/is-the-reason-that-nothing-can-go-faster-than-light-because-we-have-not-tried-hard-enough/
- https://www.physics.brocku.ca/PPLATO/h-flap/phys6_1f_1.png
- https://science.nasa.gov/ems/02_anatomy
Featured Image Credit: NASA, Unsplash
Table of Contents
About the Author Cheryl Regan
Cheryl is a freelance content and copywriter from the United Kingdom. Her interests include hiking and amateur astronomy but focuses her writing on gardening and photography. If she isn't writing she can be found curled up with a coffee and her pet cat.
Related Articles:
15 Crucial Facts About Ultraviolet Rays & the Sun
What Constellation Is Spica In? The Interesting Answer!
10 Interesting Leo Constellation Facts, Myths, and FAQs
15 Interesting Pegasus Constellation Facts, Myths, and FAQs
6 Interesting Sagittarius Constellation Facts, Myths, and FAQs in 2024!
What Are Constellations? Where Did They Come From?
8 Interesting Libra Constellation Facts, Myths, and FAQs
What Is Infrared Radiation? Science-Based Facts & FAQ

Why is the speed of light the way it is?
It's just plain weird.

Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute, host of Ask a Spaceman and Space Radio , and author of " How to Die in Space ." He contributed this article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights .
We all know and love the speed of light — 299,792,458 meters per second — but why does it have the value that it does? Why isn't it some other number? And why do we care so much about some random speed of electromagnetic waves? Why did it become such a cornerstone of physics?
Well, it's because the speed of light is just plain weird.
Related: Constant speed of light: Einstein's special relativity survives a high-energy test
Putting light to the test
The first person to realize that light does indeed have a speed at all was an astronomer by the name of Ole Romer. In the late 1600s, he was obsessed with some strange motions of the moon Io around Jupiter. Every once in a while, the great planet would block our view of its little moon, causing an eclipse, but the timing between eclipses seemed to change over the course of the year. Either something funky was happening with the orbit of Io — which seemed suspicious — or something else was afoot.
After a couple years of observations, Romer made the connection. When we see Io get eclipsed, we're in a certain position in our own orbit around the sun. But by the next time we see another eclipse, a few days later, we're in a slightly different position, maybe closer or farther away from Jupiter than the last time. If we are farther away than the last time we saw an eclipse, then that means we have to wait a little bit of extra time to see the next one because it takes that much longer for the light to reach us, and the reverse is true if we happen to be a little bit closer to Jupiter.
The only way to explain the variations in the timing of eclipses of Io is if light has a finite speed.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Making it mean something
Continued measurements over the course of the next few centuries solidified the measurement of the speed of light, but it wasn't until the mid-1800s when things really started to come together. That's when the physicist James Clerk Maxwell accidentally invented light.
Maxwell had been playing around with the then-poorly-understood phenomena of electricity and magnetism when he discovered a single unified picture that could explain all the disparate observations. Laying the groundwork for what we now understand to be the electromagnetic force , in those equations he discovered that changing electric fields can create magnetic fields, and vice versa. This allows waves of electricity to create waves of magnetism, which go on to make waves of electricity and back and forth and back and forth, leapfrogging over each other, capable of traveling through space.
And when he went to calculate the speed of these so-called electromagnetic waves, Maxwell got the same number that scientists had been measuring as the speed of light for centuries. Ergo, light is made of electromagnetic waves and it travels at that speed, because that is exactly how quickly waves of electricity and magnetism travel through space.
And this was all well and good until Einstein came along a few decades later and realized that the speed of light had nothing to do with light at all. With his special theory of relativity , Einstein realized the true connection between time and space, a unified fabric known as space-time. But as we all know, space is very different than time. A meter or a foot is very different than a second or a year. They appear to be two completely different things.
So how could they possibly be on the same footing?
There needed to be some sort of glue, some connection that allowed us to translate between movement in space and movement in time. In other words, we need to know how much one meter of space, for example, is worth in time. What's the exchange rate? Einstein found that there was a single constant, a certain speed, that could tell us how much space was equivalent to how much time, and vice versa.
Einstein's theories didn't say what that number was, but then he applied special relativity to the old equations of Maxwell and found that this conversion rate is exactly the speed of light.
Of course, this conversion rate, this fundamental constant that unifies space and time, doesn't know what an electromagnetic wave is, and it doesn't even really care. It's just some number, but it turns out that Maxwell had already calculated this number and discovered it without even knowing it. That's because all massless particles are able to travel at this speed, and since light is massless, it can travel at that speed. And so, the speed of light became an important cornerstone of modern physics.
But still, why that number, with that value, and not some other random number? Why did nature pick that one and no other? What's going on?
Related: The genius of Albert Einstein: his life, theories and impact on science
Making it meaningless
Well, the number doesn't really matter. It has units after all: meters per second. And in physics any number that has units attached to it can have any old value it wants, because it means you have to define what the units are. For example, in order to express the speed of light in meters per second, first you need to decide what the heck a meter is and what the heck a second is. And so the definition of the speed of light is tied up with the definitions of length and time.
In physics, we're more concerned with constants that have no units or dimensions — in other words, constants that appear in our physical theories that are just plain numbers. These appear much more fundamental, because they don't depend on any other definition. Another way of saying it is that, if we were to meet some alien civilization , we would have no way of understanding their measurement of the speed of light, but when it comes to dimensionless constants, we can all agree. They're just numbers.
One such number is known as the fine structure constant, which is a combination of the speed of light, Planck's constant , and something known as the permittivity of free space. Its value is approximately 0.007. 0.007 what? Just 0.007. Like I said, it's just a number.
So on one hand, the speed of light can be whatever it wants to be, because it has units and we need to define the units. But on the other hand, the speed of light can't be anything other than exactly what it is, because if you were to change the speed of light, you would change the fine structure constant. But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be approximately 0.007, and nothing else. That is simply the universe we live in, and we get no choice about it at all. And since this is fixed and universal, the speed of light has to be exactly what it is.
So why is the fine structure constant exactly the number that it is, and not something else? Good question. We don't know.
Learn more by listening to the episode "Why is the speed of light the way it is?" on the Ask A Spaceman podcast, available on iTunes and on the Web at http://www.askaspaceman.com. Thanks to Robert H, Michael E., @DesRon94, Evan W., Harry A., @twdixon, Hein P., Colin E., and Lothian53 for the questions that led to this piece! Ask your own question on Twitter using #AskASpaceman or by following Paul @PaulMattSutter and facebook.com/PaulMattSutter.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute in New York City. Paul received his PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2011, and spent three years at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, followed by a research fellowship in Trieste, Italy, His research focuses on many diverse topics, from the emptiest regions of the universe to the earliest moments of the Big Bang to the hunt for the first stars. As an "Agent to the Stars," Paul has passionately engaged the public in science outreach for several years. He is the host of the popular "Ask a Spaceman!" podcast, author of "Your Place in the Universe" and "How to Die in Space" and he frequently appears on TV — including on The Weather Channel, for which he serves as Official Space Specialist.
The bubbling surface of a distant star was captured on video for the 1st time ever
Just how dark is the universe? NASA's New Horizons probe gives us best estimate yet
Could we turn the sun into a gigantic telescope?
- voidpotentialenergy This is just my opinion but i think L speed is it's speed because the particle part of it is the fastest it can interact with the quanta distance in quantum fluctuation. Light is particle and wave so the wave happens in the void between quanta. Gravity probably travels in that void and why gravity seems instant. Reply
- rod The space.com article wraps up the discussion with, "So on one hand, the speed of light can be whatever it wants to be, because it has units and we need to define the units. But on the other hand, the speed of light can't be anything other than exactly what it is, because if you were to change the speed of light, you would change the fine structure constant. But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be approximately 0.007, and nothing else. That is simply the universe we live in, and we get no choice about it at all. And since this is fixed and universal, the speed of light has to be exactly what it is. So why is the fine structure constant exactly the number that it is, and not something else? Good question. We don't know." It seems that the *universe* made this decision, *But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be...* I did not know that the universe was capable of making decisions concerning constants used in physics. E=mc^2 is a serious constant. Look at nuclear weapons development, explosive yields, and stellar evolution burn rates for p-p chain and CNO fusion rates. The report indicates why alpha (fine structure constant) is what it is and c is what it is, *We don't know*. Reply
Admin said: We all know and love the speed of light, but why does it have the value that it does? Why isn't it some other number? And why did it become such a cornerstone of physics? Why is the speed of light the way it is? : Read more
rod said: The space.com article wraps up the discussion with, "So on one hand, the speed of light can be whatever it wants to be, because it has units and we need to define the units. But on the other hand, the speed of light can't be anything other than exactly what it is, because if you were to change the speed of light, you would change the fine structure constant. But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be approximately 0.007, and nothing else. That is simply the universe we live in, and we get no choice about it at all. And since this is fixed and universal, the speed of light has to be exactly what it is. So why is the fine structure constant exactly the number that it is, and not something else? Good question. We don't know." It seems that the *universe* made this decision, *But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be...* I did not know that the universe was capable of making decisions concerning constants used in physics. E=mc^2 is a serious constant. Look at nuclear weapons development, explosive yields, and stellar evolution burn rates for p-p chain and CNO fusion rates. The report indicates why alpha (fine structure constant) is what it is and c is what it is, *We don't know*.
- rod FYI. When someone says *the universe has chosen*, I am reminded of these five lessons from a 1982 Fed. court trial. The essential characteristics of science are: It is guided by natural law; It has to be explanatory by reference to natural law; It is testable against the empirical world; Its conclusions are tentative, i.e., are not necessarily the final word; and It is falsifiable. Five important points about science. Reply
- Gary If the universe is expanding , how can the speed of light be constant ( miles per second , if each mile is getting longer ) ? Can light's velocity be constant while the universe expands ? So, with the expansion of the universe , doesn't the speed of light need to increase in order to stay at a constant velocity in miles per second ? Or, do the miles in the universe remain the same length as the universe 'adds' miles to its diameter ? Are the miles lengthening or are they simply being added / compounded ? Reply
- Gary Lets say we're in outer space and we shoot a laser through a block of glass. What causes the speed of the laser light to return to the speed it held prior to entering the block of glass ? Is there some medium in the vacuum of space that governs the speed of light ? Do the atoms in the glass push it back up to its original speed. If so, why don't those same atoms constantly push the light while it travels through the block of glass ? Reply
Gary said: Lets say we're in outer space and we shoot a laser through a block of glass. What causes the speed of the laser light to return to the speed it held prior to entering the block of glass ? Is there some medium in the vacuum of space that governs the speed of light ? Do the atoms in the glass push it back up to its original speed. If so, why don't those same atoms constantly push the light while it travels through the block of glass ?
Gary said: If the universe is expanding , how can the speed of light be constant ( miles per second , if each mile is getting longer ) ? Can light's velocity be constant while the universe expands ? So, with the expansion of the universe , doesn't the speed of light need to increase in order to stay at a constant velocity in miles per second ? Or, do the miles in the universe remain the same length as the universe 'adds' miles to its diameter ? Are the miles lengthening or are they simply being added / compounded ?
- View All 31 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 SpaceX's private Polaris Dawn astronauts splash down to end historic spacewalk mission (video)
- 3 SpaceX's private Polaris Dawn astronauts will return to Earth early Sunday. Here's how to watch live online
- 4 Astronauts 3D-print 1st metal part while on ISS
- 5 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 128 — Starliner is Back! What Now?

Can anything travel faster than the speed of light?
Does it matter if it's in a vacuum?

In 1676, by studying the motion of Jupiter's moon Io, Danish astronomer Ole Rømer calculated that light travels at a finite speed. Two years later, building on data gathered by Rømer, Dutch mathematician and scientist Christiaan Huygens became the first person to attempt to determine the actual speed of light, according to the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. Huygens came up with a figure of 131,000 miles per second (211,000 kilometers per second), a number that isn't accurate by today's standards — we now know that the speed of light in the "vacuum" of empty space is about 186,282 miles per second (299,792 km per second) — but his assessment showcased that light travels at an incredible speed.
According to Albert Einstein 's theory of special relativity , light travels so fast that, in a vacuum, nothing in the universe is capable of moving faster.
"We cannot move through the vacuum of space faster than the speed of light," confirmed Jason Cassibry, an associate professor of aerospace engineering at the Propulsion Research Center, University of Alabama in Huntsville.
Question answered, right? Maybe not. When light is not in a vacuum, does the rule still apply?
Related: How many atoms are in the observable universe?
"Technically, the statement 'nothing can travel faster than the speed of light' isn't quite correct by itself," at least in a non-vacuum setting, Claudia de Rham, a theoretical physicist at Imperial College London, told Live Science in an email. But there are certain caveats to consider, she said. Light exhibits both particle-like and wave-like characteristics, and can therefore be regarded as both a particle (a photon ) and a wave. This is known as wave-particle duality.
If we look at light as a wave, then there are "multiple reasons" why certain waves can travel faster than white (or colorless) light in a medium, de Rham said. One such reason, she said, is that "as light travels through a medium — for instance, glass or water droplets — the different frequencies or colors of light travel at different speeds." The most obvious visual example of this occurs in rainbows, which typically have the long, faster red wavelengths at the top and the short, slower violet wavelengths at the bottom, according to a post by the University of Wisconsin-Madison .
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
When light travels through a vacuum, however, the same is not true. "All light is a type of electromagnetic wave, and they all have the same speed in a vacuum (3 x 10^8 meters per second). This means both radio waves and gamma rays have the same speed," Rhett Allain, a physics professor at Southeastern Louisiana University, told Live Science in an email.
So, according to de Rham, the only thing capable of traveling faster than the speed of light is, somewhat paradoxically, light itself, though only when not in the vacuum of space. Of note, regardless of the medium, light will never exceed its maximum speed of 186,282 miles per second.
Universal look
According to Cassibry, however, there is something else to consider when discussing things moving faster than the speed of light.
"There are parts of the universe that are expanding away from us faster than the speed of light, because space-time is expanding," he said. For example, the Hubble Space Telescope recently spotted 12.9 billion year-old light from a distant star known as Earendel. But, because the universe is expanding at every point, Earendel is moving away from Earth and has been since its formation, so the galaxy is now 28 billion light years away from Earth.
In this case, space-time is expanding, but the material in space-time is still traveling within the bounds of light speed.
Related: Why is space a vacuum?
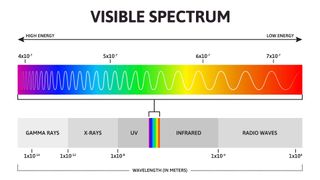
So, it's clear that nothing travels faster than light that we know of, but is there any situation where it might be possible? Einstein's theory of special relativity, and his subsequent theory of general relativity, is "built under the principle that the notions of space and time are relative," de Rham said. But what does this mean? "If someone [were] able to travel faster than light and carry information with them, their notion of time would be twisted as compared to ours," de Rham said. "There could be situations where the future could affect our past, and then the whole structure of reality would stop making sense."
This would indicate that it would probably not be desirable to make a human travel faster than the speed of light. But could it ever be possible? Will there ever be a time when we are capable of creating craft that could propel materials — and ultimately humans — through space at a pace that outstrips light speed? "Theorists have proposed various types of warp bubbles that could enable faster-than-light travel," Cassibry said.
But is de Rham convinced?
"We can imagine being able to communicate at the speed of light with systems outside our solar system ," de Rham said. "But sending actual physical humans at the speed of light is simply impossible, because we cannot accelerate ourselves to such speed.
"Even in a very idealistic situation where we imagine we could keep accelerating ourselves at a constant rate — ignoring how we could even reach a technology that could keep accelerating us continuously — we would never actually reach the speed of light," she added. "We could get close, but never quite reach it."
Related: How long is a galactic year?
This is a point confirmed by Cassibry. "Neglecting relativity, if you were to accelerate with a rate of 1G [Earth gravity], it would take you a year to reach the speed of light. However, you would never really reach that velocity because as you start to approach lightspeed, your mass energy increases, approaching infinite. "One of the few known possible 'cheat codes' for this limitation is to expand and contract spacetime, thereby pulling your destination closer to you. There seems to be no fundamental limit on the rate at which spacetime can expand or contract, meaning we might be able to get around this velocity limit someday."
— What would happen if the speed of light were much lower?
— What if the speed of sound were as fast as the speed of light?
— How does the rubber pencil illusion work?
Allain is similarly confident that going faster than light is far from likely, but, like Cassibry, noted that if humans want to explore distant planets, it may not actually be necessary to reach such speeds. "The only way we could understand going faster than light would be to use some type of wormhole in space," Allain said. "This wouldn't actually make us go faster than light, but instead give us a shortcut to some other location in space."
Cassibry, however, is unsure if wormholes will ever be a realistic option.
"Wormholes are theorized to be possible based on a special solution to Einstein's field equations," he said. "Basically, wormholes, if possible, would give you a shortcut from one destination to another. I have no idea if it's possible to construct one, or how we would even go about doing it." Originally published on Live Science.
Joe Phelan is a journalist based in London. His work has appeared in VICE, National Geographic, World Soccer and The Blizzard, and has been a guest on Times Radio. He is drawn to the weird, wonderful and under examined, as well as anything related to life in the Arctic Circle. He holds a bachelor's degree in journalism from the University of Chester.
A long-lost moon could explain Mars' weird shape and extreme terrain
The moon might still have active volcanoes, China's Chang'e 5 sample-return probe reveals
Fall equinox 2024: When it is, why it happens and what to look for
Most Popular
- 2 A long-lost moon could explain Mars' weird shape and extreme terrain
- 3 Greenhouse gas 80 times more potent than CO2 is rising in the atmosphere — and fast
- 4 China plans to build moon base at the lunar south pole by 2035
- 5 'Space trash' will lead us to intelligent aliens, Harvard astrophysicist Avi Loeb says

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How can light (or electromagnetic radiation) travel through a vacuum when there is nothing there to act as a medium, and do so forever in all directions? For example the light coming from a star millions of light years away.
Light may seem to be an exception, leading many to say that light is a wave that can travel through a vacuum with no medium. Light doesn't use EM fields as its medium; light IS an EM (electromagnetic) wave.
Light actually "slows down" every time it has to travel through anything but a vacuum. Look up Cherenkov radiation to see what happens when light initially travels faster than it can through a ...
The speed of light in a vacuum is 186,282 miles per second (299,792 kilometers per second), and in theory nothing can travel faster than light.
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted c, is a universal physical constant that is exactly equal to 299,792,458 metres per second (approximately 300,000 kilometres per second; 186,000 miles per second; 671 million miles per hour).
There are at least two ways that we know light can travel through a vacuum. The first is by observation of the Sun and other stars. Astronauts have measured the pressure in outer space and found that there is a very good vacuum, much better in fact than that which we can easily make on earth. The second is through observations on earth.
So how does light travel? Basically, traveling at incredible speeds (299 792 458 m/s) and at different wavelengths, depending on its energy. It also behaves as both a wave and a particle, able to ...
The speed of light in a vacuum is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure scientists finally agreed on in 1975 - but why settle on that figure? And why does it matter? Answering those questions takes us on an amazing journey through space, time, physics and measurement, and the tale hasn't quite been told yet.
introduction Light is a transverse, electromagnetic wave that can be seen by the typical human. The wave nature of light was first illustrated through experiments on diffraction and interference. Like all electromagnetic waves, light can travel through a vacuum. The transverse nature of light can be demonstrated through polarization.
Light's formal name is electromagnetic radiation. All light shares three properties. It can travel through a vacuum. It always moves at a constant speed, known as the speed of light, which is 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second in a vacuum. And the wavelength defines the type or color of light.
In order to propagate, sound requires a medium to travel through. Sound is generated by vibrations, which causes atoms and molecules in the medium to vibrate; that vibration is passed on to adjacent particles. We sense these vibrations via a sensitive membrane in our ears. A perfect vacuum is a complete absence of a medium.
Light travels slower in a medium than it does in a vacuum, and the speed is proportional to the density of the medium. This speed variation causes light to bend at the interface of two media -- a phenomenon called refraction.
The speed of light is 299,792,458 meters per second and that constant tells us much about cause and effect in the universe.
Speed of light, speed at which light waves propagate through different materials. In a vacuum, the speed of light is 299,792,458 meters per second. The speed of light is considered a fundamental constant of nature. Its significance is far broader than its role in describing a property of electromagnetic waves.
In contrast, light waves can travel through a vacuum, and do not require a medium. In empty space, the wave does not dissipate (grow smaller) no matter how far it travels, because the wave is not interacting with anything else. This is why light from distant stars can travel through space for billions of light-years and still reach us on earth.
A Vacuum Can Yield Flashes of Light. A vacuum might seem like empty space, but scientists have discovered a new way to seemingly get something from that nothingness, such as light. And the finding ...
Facts & FAQ. Light is such a fundamental part of our lives. From the moment we're born, we are showered with all kinds of electromagnetic radiation, both colorful, and invisible. Light travels through the vacuum of space at 186,828 miles per second as transverse waves, outside of any material or medium, because photons—the particles that ...
0 I was looking at rockets and stuff and thought about how they move through a vacuum using newtons 3rd law, and then I started thinking of any other ways you could move through a vacuum without using this and then I thought about the photon. I then thought how does the photon move through a vacuum?
Visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared radiation, radio waves, X-rays, gamma rays, microwaves, and radar waves are all made up of electric and magnetic fields wiggling at different rates, and they all travel at the speed of light. Now, I mentioned earlier that light is a complicated phenomenon. Long after the electromagnetic wave theory of ...
Ergo, light is made of electromagnetic waves and it travels at that speed, because that is exactly how quickly waves of electricity and magnetism travel through space. And this was all well and ...
How does an electromagnetic wave travel through for example, the vacuum of space? I usually see that waves are explained using analogies with water, pieces of rope, the strings of a guitar, etc, but it seems to me that all those waves need a medium to propagate.
When light travels through a vacuum, however, the same is not true. "All light is a type of electromagnetic wave, and they all have the same speed in a vacuum (3 x 10^8 meters per second).