Skip to content

Well Child Visits: Bright Futures Parent Education
Primary care locations.
Parent and patient handouts from the Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit address key information for health supervision care from infancy through adolescence. You may receive print outs of this, or similar, information following well visits at a CHOP Primary Care location.
First week visit (3 to 5 days)
1 month visit, 2 month visit, 4 month visit, 6 month visit, 9 month visit, 12 month visit, 15 month visit, 18 month visit, 2 year visit, 2½ year visit, 3 year visit, 4 year visit, 5 and 6 year visits, 7 and 8 year visits.
- English - parent handout
- Spanish - parent handout
- English - patient handout
- Spanish - patient handout
9 and 10 year visits
11-14 year visits, 15-17 year visits, 18-21 year visits.

With our patient portal you can schedule appointments, access records, see test results, ask your care provider questions, and more.

Subscribe to Health Tips
Subscribe to our Health Tips enewsletter to receive health and wellness tips from the pediatric experts at CHOP.

Family Life

AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits

Parents know who they should go to when their child is sick. But pediatrician visits are just as important for healthy children.
The Bright Futures /American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the " periodicity schedule ." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence.
Schedule of well-child visits
- The first week visit (3 to 5 days old)
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months old
- 15 months old
- 18 months old
- 2 years old (24 months)
- 2 ½ years old (30 months)
- 3 years old
- 4 years old
- 5 years old
- 6 years old
- 7 years old
- 8 years old
- 9 years old
- 10 years old
- 11 years old
- 12 years old
- 13 years old
- 14 years old
- 15 years old
- 16 years old
- 17 years old
- 18 years old
- 19 years old
- 20 years old
- 21 years old
The benefits of well-child visits
Prevention . Your child gets scheduled immunizations to prevent illness. You also can ask your pediatrician about nutrition and safety in the home and at school.
Tracking growth & development . See how much your child has grown in the time since your last visit, and talk with your doctor about your child's development. You can discuss your child's milestones, social behaviors and learning.
Raising any concerns . Make a list of topics you want to talk about with your child's pediatrician such as development, behavior, sleep, eating or getting along with other family members. Bring your top three to five questions or concerns with you to talk with your pediatrician at the start of the visit.
Team approach . Regular visits create strong, trustworthy relationships among pediatrician, parent and child. The AAP recommends well-child visits as a way for pediatricians and parents to serve the needs of children. This team approach helps develop optimal physical, mental and social health of a child.
More information
Back to School, Back to Doctor
Recommended Immunization Schedules
Milestones Matter: 10 to Watch for by Age 5
Your Child's Checkups
- Bright Futures/AAP Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care (periodicity schedule)
Your Child’s Well Visit: What Parents Need to Know

In the world of pediatric care, a well visit is the equivalent of what used to be called a check-up or a physical. Once a year, parents typically make an appointment for a well visit with their family physician or pediatrician to make sure all’s well with their child and to voice any concerns. For children 3 and under, though, visits are as frequent as every few weeks in the newborn period to every 2 to 6 months. Well visits are a must for infants, toddlers, school-age children and teens alike.
Understandably, parents tend to have plenty of questions about what’s involved in a well visit : how to prepare for it, what to bring and what to expect once you get called into the doctor’s office. Let’s review all your FAQs in detail with Weill Cornell Medicine pediatrician Dr. Corey Wasserman as your guide.
What is generally included in a well visit?
Depending on your child’s age, a well visit may include immunizations, a complete physical examination, a review of your child’s medical history and a conversation regarding any concerns. The visit will typically take from 15 to 30 minutes.
“We can actually accomplish a great deal during that 15 minutes, Dr. Wasserman says. “Mainly, the idea is to check on your child’s vital signs and developmental milestones, and to listen to any concerns you may have. Most of the time, your children are indeed well, not sick, so we start out with that assumption. And if there is reason for concern, you can follow up with a separate appointment to investigate what may be happening with your child’s health.”
How should I prepare for my child’s well visit?
First, check in via Connect up to 5 days before your child’s visit to make sure we have your most up-to-date information, including your pharmacy and insurance , along with a list of your child’s medications , if any . Y ou can also review and update your responses to your health questionnaire.
When it comes to blood work and other medical r ecords, instead of uploading them to Connect , it may be preferable to email them to the Medical Records Department at [email protected] .
On the day of your appointment, please arrive 10 minutes before your scheduled time, which will allow you t o complete and submit any additional forms beforehand.
As a matter of policy, we require at least one parent or guardian to be present for the duration of the well visit. That will facilitate the best possible communication between provider and parent and allow us to secure your permission for any necessary immunizations.
If you can’t be present, you’ll need to reschedule the appointment.
What should I bring?
Please b ring :
- Your insurance card and ID
- School or camp forms as needed
- Records of medical visits elsewhere (with a different provider or institution), if you weren’t able to submit these electronically
“ Keep in mind that your doctor may not be able to fill out school or camp forms on the day of your appointment . If they have the time to complete the form during your visit, they will do so. But it’s just as likely that the information from your child’s well visit will be entered afterwards and sent to you at a later date ,” Dr. Wasserman says.
What, exactly, will take place during the visit?
Your doctor will:
- Review your child’s height, weight, and BMI (body mass index).
- Check your child’s blood pressure, heart rate and breathing.
- Perform a head-to-toe physical exam.
- Administer any needed immunizations.
- Address your concerns and offer advice regarding your child’s growth and development.
Additionally, your doctor will assess your child based on their age.
At an infant well visit, your doctor will:
- Look for developmental milestones.
- Measure your baby’s weight, length and head circumference.
- Look at her ears, eyes, mouth and skin.
- Press on his belly to detect any problems.
- Inspect your baby’s genitals for tenderness, lumps or other signs of infection.
If your child is a toddler , your doctor will also:
- Conduct a vision and hearing check.
- Ask questions to get a sense of your child’s mental, emotional and social development.
During a school-age well check , your doctor will ask questions about the following:
- Behavioral changes, if any
- Physical activity
- Sleeping habits
- Motor, language and problem-solving skills
During a teen well visit , your doctor— optimally, someone your teenager feels comfortable with—will :
- Look for indications of alcohol, tobacco or drug use, as well as anxiety or depression.
- Discuss your teenager’s sexual health and provide guidance on birth control, the risk of contracting an STI (sexually transmitted infection) and other pertinent issues.
What if I need to ask the doctor about a specific medical issue?
Specific issues are considered part of a follow up or “sick” visit. These will be billed to your insurance, and you may be responsible for copayments, coinsurance or deductible payments, based on the terms of your policy.
If you’d like to address non-routine concerns during your child’s annual well visit, let your doctor ’s office know about these issues when you schedule your appointment. Depending on their complexity, your doctor may need to deal with them at a later time.
What does a follow-up or “sick” visit entail?
- Any new problems or complaints
- Your child’s need for new medications or tests
- Referrals to a specialist
- Additional treatment options for an already-existing condition
Can I combine my child’s well visit with a non-routine or sick office visit?
Combining your child’s well visit with a non-routine office visit will save you time by eliminating an extra appointment, but doing so may affect your costs. Your doctor will bill your visit based on the reason you originally gave for scheduling the appointment, plus the specific issues you raised during the appointment. Anything more than a check-up may result in unplanned out-of-pocket costs to you. For these reasons, we recommend that you schedule your child’s annual well visit and any follow-up or sick office visits separately.
The most i mportant points to remember
- When scheduling your child’s well visit, clearly state the purpose of the visit.
- A parent or guardian must accompany all patients under 18 to their well visit.
- Arrive 10 minutes before your appointment time.
- Bring all relevant information and documentation, including any forms you need filled out.
- The well visit will take 15 minutes.
- Review your insurance plan’s summary of benefits to clarify what will and won’t be covered during your child’s well visit.
To make an appointment with a pediatrician at Weill Cornell Medicine, go to https://weillcornell.org/services/pediatrics
Related Links
Back to News
In This Article
Clinical service.
Catch Up on Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations

Many children missed check-ups and recommended childhood vaccinations over the past few years. CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend children catch up on routine childhood vaccinations and get back on track for school, childcare, and beyond.

Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread.
Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations Are Essential

Well-child visits and recommended vaccinations are essential and help make sure children stay healthy. Children who are not protected by vaccines are more likely to get diseases like measles and whooping cough . These diseases are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children. In recent years, there have been outbreaks of these diseases, especially in communities with low vaccination rates.
Well-child visits are essential for many reasons , including:
- Tracking growth and developmental milestones
- Discussing any concerns about your child’s health
- Getting scheduled vaccinations to prevent illnesses like measles and whooping cough (pertussis) and other serious diseases

It’s particularly important for parents to work with their child’s doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines.
Routinely Recommended Vaccines for Children and Adolescents
Getting children and adolescents caught up with recommended vaccinations is the best way to protect them from a variety of vaccine-preventable diseases . The schedules below outline the vaccines recommended for each age group.
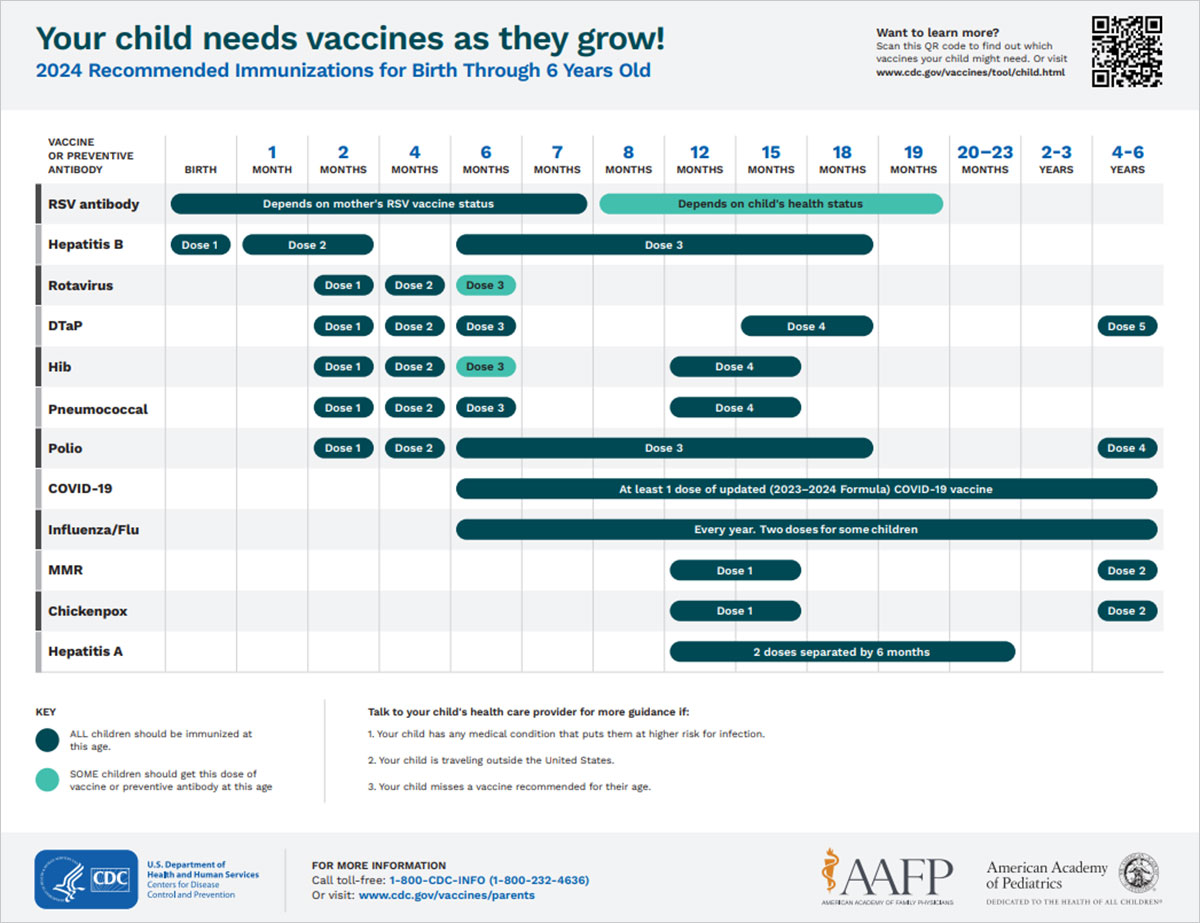
See which vaccines your child needs from birth through age 6 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
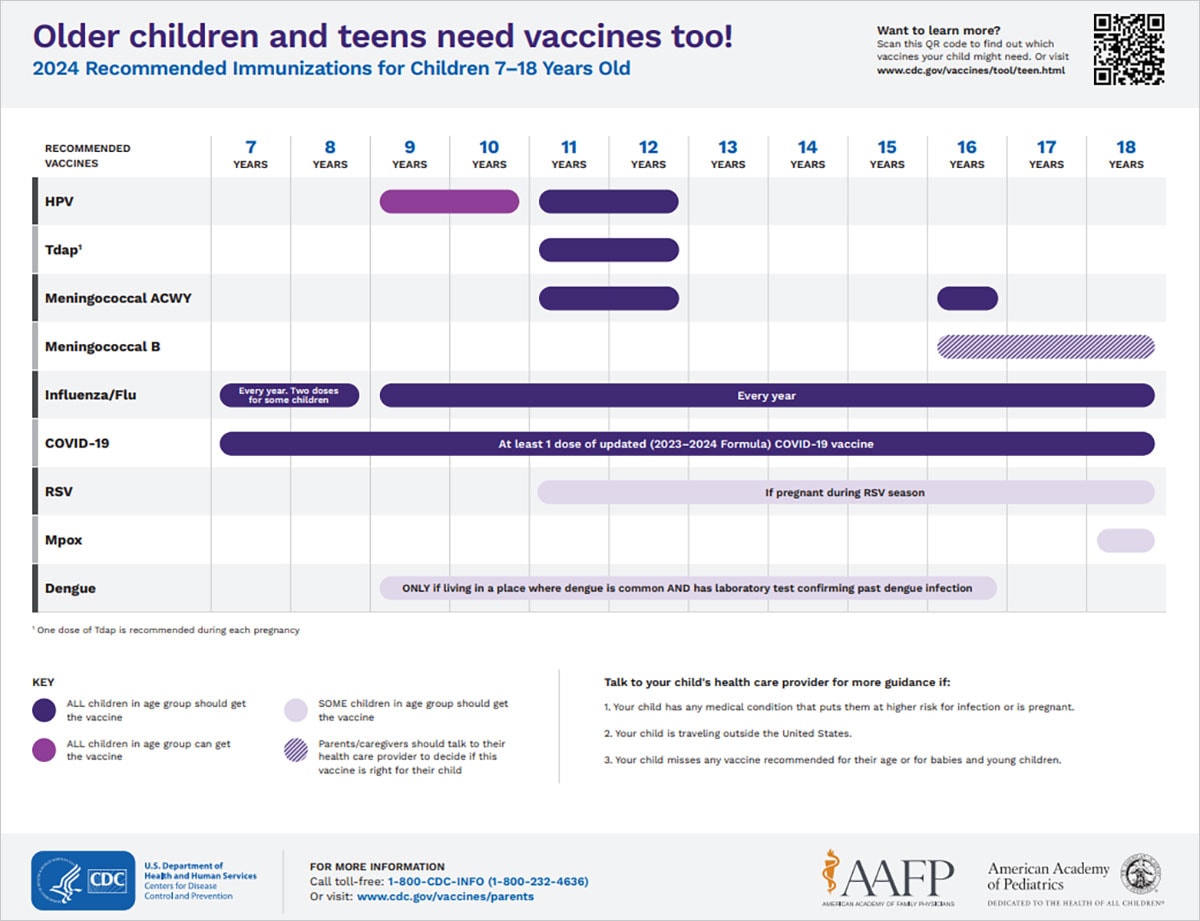
See which vaccines your child needs from ages 7 through 18 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program’s requirements and talk to your child’s doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider. You can also find a VFC provider by calling your state or local health department or seeing if your state has a VFC website.

COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens
Everyone aged 6 months and older can get an updated COVID-19 vaccine to help protect against severe illness, hospitalization and death. Learn more about making sure your child stays up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Primary Care Patient Education

Featured Topics and Education

Constipation

Mental Health

Well-Child Visits: Ages and Stages
11-14 years, 15-18 years.

Browse Our Full Health Library

Connect With Us
3333 Burnet Avenue, Cincinnati, Ohio 45229-3026
© 1999-2024 Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. All rights reserved.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(9); 2023 Sep
- PMC10576162

Analyzing Best Practices for Pediatric Well-Child Clinic Visits in the United States for Children Aged Three to Five Years: A Review
Okelue e okobi.
1 Family Medicine, Larkin Community Hospital Palm Springs Campus, Miami, USA
2 Family Medicine, Medficient Health Systems, Laurel, USA
3 Family Medicine, Lakeside Medical Center, Belle Glade, USA
Patience F Akahara
4 Family Medicine, Inglewood Medical Centre, Edmonton, CAN
Onyinyechukwu B Nwachukwu
5 Neurosciences and Psychology, California Institute of Behavioral Neurosciences & Psychology, Fairfield, USA
6 Family Medicine, American International School of Medicine Georgetown, Guyana, USA
Thelma O Egbuchua
7 Pediatrics and Neonatology, Delta State University Teaching Hospital, Oghara, NGA
Olamide O Ajayi
8 Internal Medicine, Obafemi Awolowo College of Health Sciences, Olabisi Onabanjo University, Sagamu, NGA
Kelechukwu P Oranu
9 Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kenechukwu Specialist Hospital and Maternity Enugu, Enugu, NGA
Ifreke U Ibanga
10 Pediatrics, Thompson General Hospital, Manitoba, CAN
Inadequate routine healthcare check-up visits for children aged three to five years impose substantial economic and social burdens due to morbidity and mortality. The absence of regular well-child visits and vaccinations leads to avoidable diseases, underscoring the need for a renewed emphasis on childhood immunizations and check-ups. Out of 160 articles initially screened after removing duplicates, 45 were chosen for full-text review following initial title and abstract screening by two independent reviewers. Afterward, 20 studies met the predefined inclusion criteria during the final assessment of full-text articles, and data were systematically extracted from these selected studies using standardized forms to ensure accuracy and consistency. Well-child visits promote holistic development, health, and well-being in children aged three to five years. Following established guidelines and evidence-based practices, healthcare professionals provide assessments, vaccinations, and guidance for a healthy future. Despite challenges, well-child visits are vital for preventive care, empowering informed decisions for children's growth and development. The benefits of well-child visits encompass growth monitoring, anticipatory guidance, and preventive measures, crucial for children with chronic illnesses. Key components include comprehensive assessments, developmental screenings, vision and hearing evaluations, immunizations, health education, and counseling. In the case of juvenile diabetes, parental education is paramount. Parents need to understand the intricacies of insulin administration, including proper dosage calculation based on glucose measurements, meal planning, and the importance of timing insulin injections. Implementing guidelines and principles by organizations such as Bright Futures and the American Academy of Pediatrics ensures holistic care, parent involvement, and evidence-based practices. This review explores best practices and guidelines for such visits, emphasizing their role in monitoring and promoting children's development.
Introduction and background
Pediatric-associated morbidity and mortality resulting from inadequate routine healthcare check-up visits impose a considerable national economic and social burden worldwide, including in the United States. The data collected from medical check-up records from January 2019 to December 2020 revealed that the risk of disease-related adverse outcomes in a population is higher if routine non-healthcare check-up visits are ignored [ 1 - 4 ]. For example, missed vaccinations have been identified as a significant contributor to the rise of pediatric vaccine-preventable illnesses in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), millions of children in the United States are under-vaccinated or unvaccinated against preventable diseases [ 1 - 5 ]. The CDC website provides a recommended immunization schedule for children from birth through 18 years of age, and parents can check with their child's healthcare provider to ensure that their child is up to date on vaccinations [ 1 - 3 ]. However, missed well-child visits (WCVs) have resulted in significant declines in vaccination coverage in children at all milestone ages [ 1 ]. The decline in vaccination coverage has markedly increased the risk of vaccine-preventable diseases in children, including measles, polio, and pertussis [ 1 , 2 ]. Re-prioritizing childhood immunizations and well-visits can prevent the re-emergence of vaccine-preventable diseases, and it is essential that parents and care providers prioritize children's well-child schedule to prevent the rise of pediatric-preventable illnesses in the United States. In addition to that, re-prioritizing childhood immunizations has a far-reaching impact beyond the prevention of vaccine-preventable diseases. This, in turn, can help prevent non-vaccine-preventable diseases by alleviating the burden on healthcare systems, reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections, and improving overall population health [ 1 - 5 ].
Also, these absences of regular and full body healthcare check-ups for children aged three to five years can lead to undetected health issues, delayed interventions, and potentially fatal consequences [ 2 - 6 ]. This translates into increased medical costs, reduced productivity, and an emotional toll on families. The economic impact encompasses direct medical expenses for treating preventable illnesses, emergency care, and hospitalization, often straining healthcare resources. Moreover, the long-term consequences of inadequate health supervision during these critical developmental years can lead to reduced educational attainment, hindered workforce participation, and a perpetuated cycle of health disparities [ 5 - 8 ]. As a result, investing in and promoting routine healthcare check-up visits for pediatric populations is essential not only for safeguarding the well-being of the younger generation but also for alleviating the economic and social ramifications that arise from preventable disease burdens and loss of life [ 1 - 9 ].
Pediatric WCVs are marked by significant changes in speech and language proficiency, as well as the refinement of fine and gross motor skills. Their burgeoning social interactions and cognitive abilities further underscore the importance of this developmental phase. Regular WCVs during this stage assume a vital role in assessing a child's progress, offering a valuable chance to identify any potential deviations from the expected trajectory and intervene promptly if necessary [ 8 - 10 ].
Moreover, the preschool years witness the emergence of emotional and behavioral skills in children, a domain equally crucial to their holistic development. Within this context, WCVs serve as a platform for healthcare providers to engage with parents, addressing concerns related to behavior, furnishing strategies for managing behavioral obstacles, and discerning subtle signs of emotional or psychological challenges that might warrant attention. Adding to the array of advantages inherent in these WCVs, it is noteworthy that this age range coincides with a critical juncture for immunizations. The routine check-ups between three and five years of age routinely encompass pivotal immunizations that bolster a child's immunity, safeguarding them against a spectrum of severe diseases, and forging a shield of protection that will serve them well into the future [ 3 - 6 , 11 - 14 ].
This comprehensive review analyzes the best practices and guidelines for pediatric WCVs in children aged three to five years. We will explore the importance and benefits of these visits and the components that make up a successful visit. Additionally, we will examine the best practices and potential challenges associated with implementing them and review the guidelines and principles that should be followed during these visits. By doing so, we hope to provide a thorough understanding of the importance of these visits and the relationship between continuity, quality of care, and long-term health outcomes that can guide healthcare providers in delivering the most effective care to pediatric patients, ultimately leading to improved health and well-being in the years to come.
Methods and Materials, and Literature Search
For the present systematic review, an in-depth and comprehensive literature search was conducted on various online databases, including PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, Embase, and Cochrane Library, for peer-reviewed and English-language articles published between 2000 and 2023. The search used various combinations of MeSh terms: “Well child visit,” “well child clinic,” “pediatric healthcare check-up visit,” and “well-baby care,” “preventive care,” and “primary care,” and Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and parentheses to specify various combinations of operations in PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, Embase, Cochrane Library, and HINARI: (1) PubMed (All terms with OR): (“Well child visit” OR “well child clinic” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) AND (“preventive care” OR “primary care”); (2) Science Direct (Well-child visit and preventive care): (“Well-child visit” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) AND “preventive care”; (3) Google Scholar (primary care and well-child visit): (Well child visit” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) AND “primary care”; (4) Embase (Well-child visit and NOT primary care): (“Well child visit” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) NOT “primary care”; (5) Cochrane Library (Well-child visit OR well-child clinic): (“Well child visit” OR “well-child clinic”) AND (“preventive care” OR “primary care”). We also used exact phrase search, and these combinations allowed us to specify different search criteria related to child healthcare visits, preventive care, and primary care. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA; Figure Figure1) 1 ) was then used as the preferred guideline for consistency. To locate the articles, we employed keywords that included “well child clinic,” “pediatric healthcare check-up visit,” and “well-baby care,” alongside MeSH terms “preventive care” and “primary care.” The references of the included studies were searched to identify additional articles. The articles sought for were mainly those that analyzed the best practices related to well-child clinic visits, those that explored the significance of such clinical visits, and those that reviewed the components making up successful and effective well-child clinic visit, as well as the best practices and challenges linked to execution of best practices guidelines and principles. The present systematic review has focused on the best practices and guidelines for well-child clinic visit for children aged three to five years. To attain the objectives, the interventions are to be practice-based and applicable to well-child clinic care delivery.

PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
For the current systematic review, we excluded studies that had focused on the evaluation of the process of quality improvement in best practices in well-child clinic visits without acknowledging specific practice changes to child care delivery; articles that focused on one topic in well-child care as opposed to tackling the different aspects of well-child clinic practices more generally; articles that were published before 2010 and those that were published in languages other than English, and studies that focused on tackling changes in well-child clinic without tackling the issue of changes in service delivery.
A total of 160 articles were screened for primary screening (title and abstract review) after removing duplicates. Two independent reviewers conducted the initial screening of titles and abstracts to identify potentially relevant articles. After the initial screening, a total of 45 studies were included for secondary screening or full-text review. Full-text articles were obtained for studies that met the initial screening criteria or where there was uncertainty. The full-text articles were then assessed for final inclusion based on the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, and, finally, 20 studies were included in this review for data extraction. Data were systematically extracted from the selected studies and assessed using standardized forms to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Consequently, the studies included in this review (Table (Table1) 1 ) were observational studies, randomized controlled trials, and systematic reviews, which included child participants aged zero to five years (with focus on three to five years), and whose findings are directly related to delivery and reception of well-child clinic services, care quality, and child health and development outcomes. We also independently screened the studies and titles with the objective of excluding articles that were duplicated and were irrelevant to the study objectives. The abstracts of studies were also screened using a brief and structured screening tool with the objective of establishing if the selected article satisfied the inclusion criteria, including the topic being studied, the study design, target population, sample size, and study location. We also reviewed the abstract screening outcomes, even as disagreements were solved through general consensus. For the accepted abstracts, retrieval of full texts was conducted, even as a structured form was employed in the extraction of data pertaining to the study design, methodology, results, and findings.
EPDS, Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale; PPD, postpartum depression; PRO, patient-reported outcome; RCT, randomized controlled trial; WCC, well-child clinic; WCV, well-child visit
Quality assessment
The assessment of the included studies’ quality was evaluated using the Joanna Briggs Institute quality assessment tool. The tool scores every publication using the frequency scales that were accorded yes, no, unclear, and not applicable responses. The overall quality score of every study was aptly calculated based on the total amount of positive scores received.
An overview of the importance of pediatric well-child visits for children aged three to five years
The importance of a pediatric WCV for children aged three to five years should not be underestimated. These visits provide an opportunity for the physician to screen for medical issues, provide anticipatory guidance, and promote good health for the child [ 6 ]. They also allow primary care physicians to establish a bond with the parents or caregivers and to prioritize interventions with the strongest evidence for good patient-oriented outcomes, such as family social-economic dynamics, assessment and support, and other health-related goals [ 6 ]. Following the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines, immunizations should be updated if necessary, and a one-time vision screening should be carried out between three and five years of age [ 6 ]. Additionally, a head-to-toe examination should be performed, including a review of growth [ 6 ]. During the visit, the physician can answer any questions the parents or caregivers might have and provide age-appropriate guidance [ 6 ]. Furthermore, if any abnormalities are detected, the visit offers the opportunity for further evaluation [ 6 ]. Pediatricians are often parents' main formal counseling source for their children's development and education. Their anticipatory guidance can help improve outcomes in various areas such as infant vocal behavior, parenting skills, infant sleep patterns, parental use of discipline, language development, prevention of falls, home accidents, and auto-passenger injuries [ 7 ]. The WCV is also a chance to use the CDC-recommended growth charts for assessment and to review parent/caregiver-child interactions [ 6 ]. Furthermore, potential signs of abuse should be assessed, and interval growth should be reviewed using appropriate growth charts for height, weight, head circumference, and body mass index [ 6 - 7 ]. Moreover, primary care providers are well-positioned to engage parents and provide referrals to community services during WCVs [ 8 ]. Table Table2 2 shows an overview of the main components of a WCV.
Benefits of a well-child visit for young children
The benefits of WCVs for young children are numerous [ 8 , 9 ]. WCVs enable pediatricians to review a patient's health history, track a child's growth and development, and provide guidance for parents around topics such as nutrition, sleep, and behavioral development [ 10 , 11 ]. Furthermore, studies have shown that the length of a WCV is linked to the amount of unmet needs experienced by a family [ 12 , 13 ]. This is especially pertinent for children with chronic illnesses or special healthcare needs [ 12 ], as pediatric visits are more likely to result in hospital admission than adults [ 14 ]. Additionally, WCVs provide an opportunity to discuss prevention, as in the case of childhood obesity [ 15 ]. To ensure that WCVs are valuable, there should be an agreement between parents and medical professionals about the visit's goals [ 7 ]. Furthermore, physicians should discuss topics such as when to introduce solid foods [ 6 ], as this has implications for a child's long-term health. As a result, WCVs can be incredibly beneficial to young children and their families.
Components of a well-child visit for children aged three to five years
This analysis also provided details of the topics discussed during the visits. These topics were classified into seven categories: secondary prevention, primary prevention, health promotion, development, education, and those focused on the parents and family relationship [ 7 ]. The study was based on 49 visits to five pediatricians for children aged three to five years [ 7 ]. The results showed that the major topics discussed during the visits were illness prevention and education, followed by physical examination and development. Other topics such as health promotion, safety, nutrition, and emotional and mental health were also discussed but in lesser amounts. These results suggest that pediatric providers focus on the primary aspects of a child's physical and mental health, although other topics are often included in the visit. However, this study did not provide specific information about the components of a WCV for children aged three to five years [ 7 ]. This means that it is still necessary to understand the specific topics discussed during a WCV to effectively assess a child's health. Therefore, further studies are needed to provide more information about the components of a WCV for children aged three to five years.
Best practices for pediatric well-child visits
A recent study assessed the effectiveness of the Improved Care for Moms and Babies (ICC) model on maternal depression screening and other health behaviors discussed during pediatric WCVs. The study gathered information from mothers who had accompanied their children to WCVs at ages 12 and 24 months [ 15 ]. The survey included questions about health history, behaviors, and whether the physician discussed maternal depression, tobacco use, family planning, and folic acid supplementation [ 16 ]. The results of the study showed that the ICC model had improved the way maternal depression was being addressed during WCVs. However, best practices for screening, referral processes, and documentation related to PPD screening during WCVs still require further study [ 17 ]. This is especially important, as screening for postpartum depression in mothers is recommended during WCVs for young children [ 17 ].
Best practices implemented in a well-child visit
Best practices for WCVs are those that provide the most patient-oriented outcomes, such as immunizations, postpartum depression screening, and vision screening [ 18 ]. The American Academy of Pediatrics has created guidelines for WCVs, known as the periodicity schedule, and they recommend scheduled WCVs [ 19 ]. A study was conducted to determine the impact of the intervention on illness visits between WCVs [ 10 ]. The results showed that there were few differences between the two study arms, but a chart review showed that intervention children had fewer illness visits [ 10 ]. Pediatric WCVs also provide an opportunity to address psychosocial issues and developmental assessments [ 20 , 21 ], and there is wide variation in practice patterns regarding screening [ 22 ]. As far as the duration of WCVs, they are usually short; therefore, strategies for addressing the time devoted to WCVs must be considered [ 23 ]. Finally, it is important to understand the best practice of screening, education, and referral processes for addressing psychosocial issues during WCVs [ 16 ], as they are a significant part of pediatric office visits [ 24 ].
Potential challenges to implementing these best practices in a well-child visit
Additionally, the potential challenges to implementing best practices in a WCV must be acknowledged [ 18 ]. For instance, the lack of evidence-based practices can lead to uncertainty about how best to use the limited time available [ 23 ]. Furthermore, the Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine of the American Academy of Pediatrics has offered a periodicity schedule to recommend scheduled WCVs [ 19 ]. In a study to assess the differences between the interventions and the control arms, it was found that children in the intervention group had fewer illness visits between WCVs than control children [ 10 ]. This points to the importance of further understanding best practices for screening, education, and referral during the WCVs [ 16 ]. In this regard, research has revealed that 11.6% of the 483 WCVs were with children between 18 and 36 months of age [ 24 ]. Moreover, wide variations in practice patterns have been observed with some using a parent questionnaire for all WCVs and some using formal screens only at specific ages [ 22 ]. In addition, there is growing interest in understanding the practices of pediatric well-child care internationally [ 21 ] and exploring promising strategies for screening during WCVs [ 17 ]. Finally, there is a need to consider the ethical and legal dimensions of the boundaries of pediatric care [ 20 ].
Guidelines and principles for pediatric well-child visits
The subject of pediatric WCVs has been studied, and a number of guidelines have been developed to ensure that young children receive the best care. Studies have looked into adherence to pediatric WCV recommendations [ 25 ], and the standards and principles of Bright Futures [ 26 ]. In addition, similarities in approach to child health with periodic visits and anticipatory guidance have been seen abroad [ 21 ]. Guidelines recommend scheduled WCVs, detailing the schedule and content of care [ 19 ]. This includes preventive care such as guidance directed by a physician [ 27 ], and screening tests such as hearing screening [ 28 ]. However, further work is needed to optimize well child care [ 29 ], and a study found that a schedule with fewer visits had no detrimental effect on child health [ 30 ]. Pediatric WCVs are essential for the health and well-being of children, and research has been conducted to ensure that these visits are up-to-date and provide the best possible care.
Implementing guidelines and principles in a well-child visit
Therefore, the implementation of established guidelines and principles for WCVs is necessary [ 25 ]. The standards and principles of Bright Futures and the American Academy of Pediatrics [ 26 ] are similar in their approach of providing periodic visits and anticipatory guidance [ 21 ]. These guidelines and principles are used to define the schedule and content of well-child care [ 19 ], which includes guidance directed by a physician and preventive issues [ 17 ]. For example, screening tests for children who cannot fully participate are recommended [ 28 ]. Furthermore, research has shown that a schedule with fewer visits has no detrimental effect on child health [ 30 ]. Even though these articles provide a proof of principle, additional work is necessary to optimize well-child care [ 20 ]. Table Table3 3 shows an overview of the basic principles fostering a WCV.
Potential challenges to implementing these guidelines and principles in a well-child visit
Challenges to implementing effective WCV guidelines and principles arise from multiple areas [ 25 ]. For instance, the adherence rate of WCV recommendations may be lower for certain children [ 26 ]. Various countries have a similar approach to child health, focusing on periodic visits and anticipatory guidance [ 21 ]. The principles of prevention that shape WCV can vary depending on the country [ 19 ]. WCV is the most common type of physician visit for children, and it typically involves guidance from a physician [ 27 ]. For example, some children may have difficulty participating in screening tests [ 28 ]. In addition, further work is needed to optimize WCV, and research has suggested that a schedule with fewer visits may not have a detrimental effect on child health [ 29 ]. While there are suggested approaches for WCV programs, these are intended to be illustrative principles rather than specific programs [ 30 ]. As such, there are multiple potential challenges to implementing WCV guidelines and principles that must be carefully considered.
Study strengths and limitations
The research conducted in this study possesses several strengths. Firstly, the systematic review follows the PRISMA guidelines, ensuring a rigorous and transparent approach to study selection, data extraction, and synthesis. The search strategy utilized a range of global databases, including Web of Science, EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane Library, HINARI, and Google Scholar, as well as reference list searches, minimizing the risk of missing relevant studies and enhancing the comprehensiveness of the review. The use of Boolean operators and specific keywords contributes to the thoroughness of the search process; however, the debate surrounding the replication of search results using mesh terms, Boolean combinations, and parentheses for precise literature retrieval stems from concerns about sensitivity and specificity. This debate continues due to factors such as the publication rate, retractions in online scholarly articles, and limitations in search algorithms. Additionally, the focus on studies published within a specific timeframe (2000-2023) enables the inclusion of recent and up-to-date evidence, relevant to the current landscape of acute gout treatment. The evolution and progression of best practices in pediatric well-child clinic visits from 2000 to 2023 have been influenced by advancements in healthcare, changes in technology, evolving clinical guidelines, and a growing understanding of child development and preventive care. The systematic approach to data extraction and quality assessment, including the use of the Joanna Briggs Institute quality assessment tool, enhances the credibility of the findings and the overall reliability of the review. Moreover, the analysis of both monotherapy and combination therapy approaches provides a comprehensive understanding of their respective impacts on serum urate levels, gout symptoms, and overall management. By evaluating various outcomes such as serum urate levels, tophi, gout flare rates, and urinary uric acid, the study contributes a holistic perspective on the effectiveness of the different treatment strategies. Overall, these methodological strengths support the reliability and validity of the conclusions drawn from the research.
However, there are some limitations. Firstly, the scope of included studies is limited to those published between 2000 and 2023, potentially excluding relevant earlier studies that could contribute valuable insights to the topic. Moreover, the inclusion criteria focus on observational studies with specific designs and geographic restrictions, which might omit relevant experimental or international studies that could provide a more comprehensive perspective on the subject matter. Secondly, the diversity in methodologies, patient populations, and study quality across the included studies introduces heterogeneity, which can lead to inconsistencies in findings and complicate direct comparisons between the studies. Despite the use of the Joanna Briggs Institute quality assessment tool, variations in study quality could influence the reliability and robustness of the conclusions drawn from the review. Finally, the search for studies was confined to a selection of global databases and conducted exclusively in English. This approach may introduce publication bias; favoring studies with significant findings and excluding studies published in other languages may limit the representation of findings from non-English-speaking regions, ultimately affecting the generalizability of the conclusions derived from the research.
Conclusions
Pediatric WCV for children aged three to five years is a vital part of preventive healthcare, addressing physical, emotional, cognitive, and social development. Evidence-based practices ensure comprehensive assessments, vaccinations, developmental screenings, and guidance, thus nurturing a healthy future. These visits benefit immediate and long-term well-being, enhancing individual and community health.
This review emphasizes the importance of WCVs in screening for medical issues, providing guidance, and promoting health. It underlines bonding between physicians, parents, and caregivers, prioritizing evidence-based interventions. Immunizations and socio-dynamic support are highlighted, emphasizing their relevance in WCVs. These visits also offer opportunities for answering parental questions and giving age-appropriate advice. However, challenges exist in implementing guidelines, especially for children with chronic conditions. Primary care providers are essential in engaging parents and linking them to community services, improving outcomes in areas such as vocal behavior, parenting, and language development.
Further research is required to assess individual components' effectiveness in these visits and address implementation challenges, especially for children aged three to five years. In conclusion, policy changes are crucial to underscore the significance of WCVs and ensure that best practices are consistently followed. These changes can lead to better health outcomes, increased vaccination coverage, improved parental education, and reduced healthcare disparities, ultimately benefiting children and communities as a whole.
Acknowledgments
O.E.O. contributed to the conceptualization of this project and the acquisition of the pieces of literature, played several roles in analyzing the collated works of literature, carefully reviewed them for the correctness of the intellectual content, agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the integrity of the work, and approved the final version. P.F.A. contributed to the design of this work, played a role in the interpretation of the collated literature and writing parts such as the introduction, discussion, and other parts, reviewed it for intellectual accuracy, agreed to be accountable for its integrity and will answer any question that may arise, and provided final approval of the final draft. O.B.N. played a role in creating the manuscript design, collating the works of literature used, analyzing the kinds of literature used, drafting parts of the body and conclusion, agreeing to be responsible for the intellectual accuracy and validity of the work, answering the ensuing questions, and authorizing the final version. T.O.E. substantially contributed to this study concept, was involved in analyzing the collated literature that was reviewed, reviewed its scientific content for correctness, drafted part of the abstract and body, agreed to be accountable for its integrity and to resolve any unfolding issues, and then approved its final version. O.O.A. significantly contributed to the creation of this manuscript by playing a role in the conceptualization, ensuring it was critically reviewed for intellectual content and accuracy, agreeing to resolve any unfolding queries about the work and its integrity, and finally approving the final draft. KPO: played a role in conceptualizing this study; reviewed, analyzed, and drafted parts of the body of the work; ensured its intellectual content is worthy of publication; agreed to be accountable for its integrity and to resolve any queries that may arise; and finally approved the final version. IUI: In addition to conceptualizing and designing the manuscript, this author played a role in synthesizing the works of literature, analyzing the content, creating parts of the original drafts, reviewing subsequent drafts for their intellectual validity and content, agreeing to be accountable for all aspects of the work, and finally approving its final version.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Disclaimer » Advertising
- HealthyChildren.org
How You are Doing
Your daily life, your feelings, healthy behavior choices, staying safe, bright futures patient handout: 15-17 year visits.
- Split-Screen
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- CME Quiz Close Quiz
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Get Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
- Search Site
Bright Futures Patient Handout: 15-17 Year Visits. Pediatric Patient Education 2021; 10.1542/peo_document266
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Here are some suggestions from Bright Futures experts that may be of value to you and your family.
Enjoy spending time with your family. Look for ways you can help at home.
Find ways to work with your family to solve problems. Follow your family’s rules.
Form healthy friendships and find fun, safe things to do with friends.
Set high goals for yourself in school and activities and for your future.
Try to be responsible for your schoolwork and for getting to school or work on time.
Find ways to deal with stress. Talk with your parents or other trusted adults if you need help.
Always talk through problems and never use violence.
If you get angry with someone, walk away if you can.
Call for help if you are in a situation that feels dangerous.
Healthy dating relationships are built on respect, concern, and doing things both of you like to do.
When you’re dating or in a sexual situation, “No” means NO. NO is OK.
Don’t smoke, vape, use drugs, or drink alcohol. Talk with us if you are worried about alcohol or drug use in your family.
Visit the dentist at least twice a year.
Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss once a day.
Be a healthy eater. It helps you do well in school and sports.
Have vegetables, fruits, lean protein, and whole grains at meals and snacks.
Limit fatty, sugary, and salty foods that are low in nutrients, such as candy, chips, and ice cream.
Eat when you’re hungry. Stop when you feel satisfied.
Eat with your family often.
Eat breakfast.
Drink plenty of water. Choose water instead of soda or sports drinks.
Make sure to get enough calcium every day.
Have 3 or more servings of low-fat (1%) or fat-free milk and other low-fat dairy products, such as yogurt and cheese.
Aim for at least 1 hour of physical activity every day.
Wear your mouth guard when playing sports.
Get enough sleep.
Be proud of yourself when you do something good.
Figure out healthy ways to deal with stress.
Develop ways to solve problems and make good decisions.
It’s OK to feel up sometimes and down others, but if you feel sad most of the time, let us know so we can help you.
It’s important for you to have accurate information about sexuality, your physical development, and your sexual feelings toward the opposite or same sex. Please consider asking us if you have any questions.
Choose friends who support your decision to not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Support friends who choose not to use.
Avoid situations with alcohol or drugs.
Don’t share your prescription medicines.
Don’t use other people’s medicines.
Not having sex is the safest way to avoid pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Plan how to avoid sex and risky situations.
If you’re sexually active, protect against pregnancy and STIs by correctly and consistently using birth control along with a condom.
Protect your hearing at work, home, and concerts. Keep your earbud volume down.
Always be a safe and cautious driver.
Insist that everyone use a lap and shoulder seat belt.
Limit the number of friends in the car and avoid driving at night.
Avoid distractions. Never text or talk on the phone while you drive.
Do not ride in a vehicle with someone who has been using drugs or alcohol.
If you feel unsafe driving or riding with someone, call someone you trust to drive you.
Wear helmets and protective gear while playing sports. Wear a helmet when riding a bike, a motorcycle, or an ATV or when skiing or skateboarding. Wear a life jacket when you do water sports.
Always use sunscreen and a hat when you’re outside.
Fighting and carrying weapons can be dangerous. Talk with your parents, teachers, or doctor about how to avoid these situations.
The information contained in this handout should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. Original handout included as part of the Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit , 2nd Edition.
Listing of resources does not imply an endorsement by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). The AAP is not responsible for the content of external resources. Information was current at the time of publication.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) does not review or endorse any modifications made to this handout and in no event shall the AAP be liable for any such changes.
© 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics. All rights reserved.
Recipient(s) will receive an email with a link to "Bright Futures Patient Handout: 15-17 Year Visits" and will not need an account to access the content.
Subject: You have been sent a link from Pediatric Patient Education from the American Academy of Pediatrics
(Optional message may have a maximum of 1000 characters.)
- VIS—HPV (Human Papillomavirus) Vaccine
- Making Healthy Decisions About Sex
- Deciding to Wait
- Meningococcal Disease—Information for Teens and College Students
- VIS—Meningococcal ACWY Vaccine
- Acne: How to Treat and Control It
- Bright Futures Patient Handout: 11-14 Year Visits
- Bright Futures Parent Handout: 11-14 Year Visits
- Expect Respect: Healthy Relationships
- Teen Checkups: A Message From Your Pediatrician
- Bright Futures Parent Handout: 15-17 Year Visits
- Bright Futures Patient Handout: 18-21 Year Visits
Advertising Disclaimer »
Affiliations
- Well-Child Visit Handouts
- Handouts By Collection
- Handouts By Language
- Online ISSN 2156-3012
- Pediatrics Open Science
- Hospital Pediatrics
- Pediatrics in Review
- AAP Grand Rounds
- Latest News
- Pediatric Care Online
- Red Book Online
- Pediatric Patient Education
- AAP Toolkits
- AAP Pediatric Coding Newsletter
First 1,000 Days Knowledge Center
Institutions/librarians, group practices, licensing/permissions, integrations, advertising.
- Privacy Statement | Accessibility Statement | Terms of Use | Support Center | Contact Us
- © Copyright American Academy of Pediatrics
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
Internet Explorer Alert
It appears you are using Internet Explorer as your web browser. Please note, Internet Explorer is no longer up-to-date and can cause problems in how this website functions This site functions best using the latest versions of any of the following browsers: Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, or Safari . You can find the latest versions of these browsers at https://browsehappy.com
- Publications
- HealthyChildren.org
Shopping cart
Order Subtotal
Your cart is empty.
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart.
- Career Resources
- Philanthropy
- About the AAP
- The Role of the Pediatrician in the Promotion of Healthy, Active Living
- How Can You Support Patients in Healthy, Active Living? Check Out Updated Report
- Helping Kids Build Healthy Active Lives: AAP Policy Explained
- Climate Change & Children’s Health: AAP Policy Explained
- News Releases
- Policy Collections
- The State of Children in 2020
- Healthy Children
- Secure Families
- Strong Communities
- A Leading Nation for Youth
- Transition Plan: Advancing Child Health in the Biden-Harris Administration
- Health Care Access & Coverage
- Immigrant Child Health
- Gun Violence Prevention
- Tobacco & E-Cigarettes
- Child Nutrition
- Assault Weapons Bans
- Childhood Immunizations
- E-Cigarette and Tobacco Products
- Children’s Health Care Coverage Fact Sheets
- Opioid Fact Sheets
- Advocacy Training Modules
- Subspecialty Advocacy Report
- AAP Washington Office Internship
- Online Courses
- Live and Virtual Activities
- National Conference and Exhibition
- Prep®- Pediatric Review and Education Programs
- Journals and Publications
- NRP LMS Login
- Patient Care
- Practice Management
- AAP Committees
- AAP Councils
- AAP Sections
- Volunteer Network
- Join a Chapter
- Chapter Websites
- Chapter Executive Directors
- District Map
- Create Account
- Early Relational Health
- Early Childhood Health & Development
- Safe Storage of Firearms
- Promoting Firearm Injury Prevention
- Mental Health Education & Training
- Practice Tools & Resources
- Policies on Mental Health
- Mental Health Resources for Families
Well Baby Visit, 12 Months
Topics to discuss with patients during their well baby visit at 12 months.
- anthropometric measurements (link to Optimizing Nutrition for Newborns and Infants/Nutrition Assessment Tools/Term Infant Growth Tools/WHO Growth Charts for Infants 0 to 24 Months)
- physical examination
- screen for iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia
- babies who are breastfeeding beyond one year may need addition iron screening if iron intake is inadequate
- overweight babies >12 months may be given 2% milk but not skim milk
- continue vitamin D at 400 IU/day
Consider Referral
- Growth faltering (failure to thrive)
Additional Information
- Gastroesophageal reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease: Parent FAQs , American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Parent’s Guide to GER (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) and GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Solid Food (Baby Foods) (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Tips for Introducing Solid Foods (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Food Allergy (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Food Allergy and Your Child (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Anaphylaxis (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Common Food Allergies , American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Lactose Intolerance and Your Child (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics.
Last Updated
American Academy of Pediatrics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Beginning at the 7 year visit, there is both a Parent and Patient education handout (in English and Spanish). For the Bright Futures Parent Handouts for well-child visits up to 2 years of age, translations of 12 additional languages (PDF format) are made possible thanks to the generous support of members, staff, and businesses who donate to the ...
Well-Child Visit Handouts. Parent and patient handouts from the Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit, 2nd Edition, address key information for health supervision care from infancy through adolescence.Bright Futures is a national health care promotion and disease prevention initiative that uses a developmentally based approach to address children's health care needs in the context of family ...
Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season ...
Well Child Visits: Bright Futures Parent Education. Parent and patient handouts from the Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit address key information for health supervision care from infancy through adolescence. You may receive print outs of this, or similar, information following well visits at a CHOP Primary Care location.
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the "periodicity schedule." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence. Schedule of well-child visits. The first week visit (3 to 5 ...
Pediatric Patient Education is a comprehensive online library of patient handouts spanning from birth through young adulthood published by the American Academy of Pediatrics. ... Parent and patient handouts from the Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit, 2nd Edition, covering well-child visits from birth to age 21.
When scheduling your child's well visit, clearly state the purpose of the visit. A parent or guardian must accompany all patients under 18 to their well visit. Arrive 10 minutes before your appointment time. Bring all relevant information and documentation, including any forms you need filled out. The well visit will take 15 minutes.
Support a healthy body weight and help your child be a healthy eater. Provide healthy foods. Eat together as a family. Be a role model. Help your child get enough calcium with low-fat or fat-free milk, low-fat yogurt, and cheese. Encourage your child to get at least 1 hour of physical activity every day.
After your child is 2 years old, schedule a well-child visit once a year. Children are sometimes scared of going to the doctor. But you can prepare your child for a doctor's visit. Here's how: Tell your child, or show on a toy, what will happen at the doctor's office. Let your child play with medical toys, such as a toy thermometer.
Make sure you have plenty of time before and after their checkup to avoid any stress. Write down questions or concerns as soon as they come to mind before your kid's well-child visit to ensure they get the proper care. Prepare for common questions covering your kid's mental and physical health. Verify your insurance coverage and get a price ...
Hold and cuddle your baby often. Enjoy playtime with your baby. Put him on his tummy for a few minutes at a time when he is awake. Never leave him alone on his tummy or use tummy time for sleep. When your baby is crying, comfort him by talking to, patting, stroking, and rocking him. Consider offering him a pacifier.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program's requirements and talk to your child's doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider.
In the first year of life, each well-child visit starts with a comprehensive history and physical exam, followed by age-specific interventions and recommendations. Your goal at each well-infant visit is to provide age-appropriate screenings and immunizations; assess development; counsel on nutrition and oral health as indicated; and provide ...
Here are some suggestions from Bright Futures experts that may be of value to your family.We will talk about The information contained in this handout should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. Original handout included as part of ...
Help your child brush his teeth twice a day. Use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste with fluoride. Help your child floss his teeth once a day. Your child should visit the dentist at least twice a year. Help your child be a healthy eater by. Buy fat-free milk and low-fat dairy foods. Encourage 2 to 3 servings each day.
Patient Education. Explore our extensive Cincinnati Children's resources, designed so that you can be as informed as possible when it comes to your child's health. ... Well-Child Visits: Ages and Stages. Learn more about child development milestones through the months and years, parenting tips and possible topics of conversation at check-ups. ...
September 15, 2018 WELL˜CHILD ISITS. -
Patient Education and Counseling Bailey-Davis et al Comparing enhancements to well-child visits in the prevention of obesity: ENCIRCLE cluster-randomized controlled trial ... Well-child visits should be scheduled according to the recommended timeline established by pediatric health organizations, typically occurring annually.
Well-Child Visit Handouts | Pediatric Patient Education | American Academy of Pediatrics Well-Child Visit Handouts Parent and patient handouts from the Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit, 2nd Edition, address key information for health supervision care from infancy through adolescence. Bright Futures is a national health care promotion and disease prevention initiative that uses a ...
Your baby should sleep in your room until she is at least 6 months old. Make sure your baby's crib or sleep surface meets the most recent safety guidelines. If you choose to use a mesh playpen, get one made after February 28, 2013. Swaddling should not be used after 2 months of age. Prevent scalds or burns.
Medical students spend part of their final year in school deciding which specialty field and training program to pursue. They gain patient-care experience at various academic medical centers, hospitals and clinics and attend interviews with residency program directors.
BACKGROUND: Well visits early in childhood are a pivotal part of children's wellbeing, and parents look to physicians for education at these visits. In the current healthcare climate, patient satisfaction scores are becoming an integral part of the system. The aim of this quality improvement project was to increase both the number of guidance topics discussed and parent satisfaction with the ...
Here are some suggestions from Bright Futures experts that may be of value to you and your family. The information contained in this handout should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. Original handout included as part of the Bright ...
Ozempic patients are finding themselves in surprise pregnancies despite being on birth control or struggling with infertility.
What to Expect at Your Baby's 9 Month Visit. We will talk about: Caring for your baby, your family, and yourself. Teaching and playing with your baby. Disciplining your baby. Introducing new foods and establishing a routine. Keeping your baby safe at home and in the car. Helpful Resources: Smoking Quit Line: 800-784-8669.
Topics to discuss with patients during their well baby visit at 12 months. Assess. anthropometric measurements (link to Optimizing Nutrition for Newborns and Infants/Nutrition Assessment Tools/Term Infant Growth Tools/WHO Growth Charts for Infants 0 to 24 Months) physical examination; screen for iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia