
Electricalterminology
Best Blog for Basic Electrical Knowledge

Difference Between Shunt Trip, Undervoltage Release and Closing Coil

Shunt trip, Undervoltage release, and closing coil are the accessories of circuit breakers . Let’s have a look at their definitions and differences. After reading the article you will fully understand their differences.
The shunt trip is an electrical accessory used for the instantaneous opening of the circuit breaker. It is generally controlled through normally open contact. It is also referred to as an opening coil or shunt release. By energizing the shunt trip you can open the circuit breaker remotely.
The range of shunt trips proposes various supply voltages. (For example from 24 V to 415 V)
Q1 selenoid of a circuit breaker that actuates a release mechanism when voltage is applied. When de-energized the system is in the rest position. A normally open contact actuates the system. Tripping does not occur in the event of wire breakage, loose contacts , or Undervoltage.
Undervoltage release
The Undervoltage release is an electrical accessory used for triggering the instantaneous opening of the circuit breaker if the supply voltage drops below a certain level and in particular if the control contact opens. It is generally controlled by normally closed contact.
A passive electromagnetic relay (Q1) actuates a release mechanism when the supply voltage drops or is interrupted. (For example To prevent the automatic restarting of motors) The system is in the rest position when energized. Actuation is produced by a normally closed contact. Undervoltage releases are always designed for uninterrupted operation.
Time-delayed Undervoltage release
Time-delayed Undervoltage release is equipped with an electronic device that delays its operation for around 3 or 4 seconds. It is designed to be used in unstable supplies, where the supply voltage of the release may be subject to variations or micro-breaks, to avoid unwanted opening of the circuit breaker.
Delayed Undervoltage release (Q1) is a combination of a separate delay unit and the respective release. This release is used to prevent brief interruptions in power leading to disconnection of the circuit breaker. The delay time can be set between approximately 0,06…..16 seconds.
Closing coil
The closing coil is an electrical accessory used for controlling the closing of the power contacts of the circuit breaker. The springs of the circuit breaker are to be loaded before the action of the closing coils. It is controlled by NO contact.
In conclusion, understanding the accessories of circuit breakers, such as shunt trip, undervoltage release, and closing coil, is essential for proper circuit breaker operation. Shunt trip is used for remote opening of the circuit breaker, undervoltage release triggers the instantaneous opening of the circuit breaker if the supply voltage drops below a certain level, and the closing coil controls the closing of the power contacts of the circuit breaker. Time-delayed undervoltage release is designed for unstable supplies and prevents unwanted opening of the circuit breaker due to variations or micro-breaks. Knowing the differences and connections of these accessories can help ensure the safety and efficiency of circuit breaker systems.
“If you’re an electrical engineer or know someone who is, check out this hilarious TIIMG Engineer keychain on Amazon! Click here to buy it now!”
Related Stories

Best Electrical Tapes for Outdoor Use: Buying Guide

What is an Arc Flash Relay? How Does it Work?

What is a Dual Function Circuit Interrupter? And Its Function

Advantages and Disadvantages of Incandescent Lamps

VFD Parts: A Guide to Their Essential Functions

Applications of 3-Phase Induction Motors in Industries
- You have no items in your shopping cart.
- Wishlist (0)
Notification

Preset Color

Frequency Converters
Variable Frequency Drives
Power Inverters
Voltage Converters
Soft Starters
1) Modify GoHz Single Phase 240v Converter to Split Phase 120v/240v
2) 3 Phase Motor Running on Single Phase Power Supply
3) How to convert 60Hz to 50Hz?
4) What does a frequency converter do?
5) Can I run a 50Hz motor on 60Hz power supply?
6) Wiring a VFD to control single phase motor speeds
7) Difference between 50Hz and 60Hz frequency
8) Impact of 60Hz (50Hz) motor being used on 50Hz (60Hz) power supply
Difference between Shunt Trip and Undervoltage Trip
Wednesday, july 1, 2015.
In this pursuit, I would like to begin with the understanding of the different word "TRIP or RELEASE", which is in fact a combined "ELECTROMECHANICAL MODULE or MECHANISM that comprises of a "mechanical latch" and a "Electrical Relay / Release" which can OPEN THE SWITCHING DEVICE e.g. a circuit breaker , by electrical "energisation" or "de-energisation", according to their characteristics. Now coming back to our main subject, i.e.; "SHUNT RELEASE" & "UNDER_VOLTAGE RELEASE", How they DIFFER IN THEIR FEATURES & CHARACTERISTICS and, what are the VARIATION IN APPLICATIONS & USAGE. Both have got their individual characteristics and are used according to the specific circuit requirements, that I describe here below: SHUNT RELEASE: This Electrical Device operates by momentary energisation and opens the "Switching Device / Circuit Breaker" by activating the Mechanical Latch. Since, this require energisation hence you NEED A CONTROL SUPPLY either of "it's own inherent" or an "Independent" one, and the other important thing, that this "Release is wired through its NO (Normally open Contact" that ensures supply cessation immediately after OPENING / TRIPPING the "Switching Device. SHUNT Release is generally used for "REMOTE OPENING OF THE SWITCHING DEVICE" but, you can also use it for LOCAL OPENING / TRIPPING of the SWITCHING DEVICE through local Push Button OR through any number of parallel Control Signals. Further this is a MOMENTARY DUTY type Release whose Power supply needs to be interrupted after opening / Tripping the "Switching Device / Circuit Breaker". NOTE: SHUNT RELEASE does not provide the feature of TRIPPING THE "Switching Device / Circuit Breaker" upon Power supply failure OR Voltage dips UNDER VOLTAGE RELEASE: This Electrical Device always NEED ENERGISATION to initially "Closing the SWITCHING DEVICE / Circuit Breaker ", OR to KEEP IT IN CLOSED condition. The SWITCHING DEVICE immediately TRIPS / SWITCHES "OFF" as soon as the Control supply is interrupted through "Local Push Button" or through interlocking Auxiliary Contacts that are wired in Series of its circuit path. Further, this is CONSTANT DUTY Type Release. NOTE: 1. UNDER VOLTAGE RELEASE offers the feature of TRIPPING THE "Switching Device / Circuit Breaker " upon Power supply failure OR Voltage dips below its "Drop-out Voltage Design", which is generally 80 % of its rated Voltage. This is the reason "Under-voltage Release" is also used as an "UNDER-VOLTAGE RELAY" and most of the "Under-voltage sensitive Circuits", like Motor Feeders are incorporated with this "Release". 2. To avoid nuisance / undesired Tripping of the "Switching Device / Circuit Breaker " on the Voltage Dips OR needing to keep an operator to Re-closing same, a Different Variation of "Under-voltage Release" is available that is fitted with a Capacitor element across its terminals, which prevents the "De-energisation" of "Under-voltage Release" and "Tripping / Opening" of the "Switching Device", and the energy stored in the Capacitive unit is used while the Circuit is deprived of OR drops below the operating Control Voltage range.
Leave your comment ( Registered user only )
Information.
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Notice
- Conditions of Use
Customer service
- Recently viewed products
- Shopping cart
Sign up for our newsletter:
Login/Register
Welcome back! Access your account here.
Sign up to an account that suits your needs and take advantage of a customised Clipsal experience.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between a shunt and undervoltage trip for the breaker.
20 June 2022
- Site Search Search Posts Find A Forum Thread Number Threads by Name Search FAQs
- ENGINEERING.com
- Eng-Tips Forums
- Tek-Tips Forums

Join Eng-Tips ® Today!
Join your peers on the Internet's largest technical engineering professional community. It's easy to join and it's free.
Here's Why Members Love Eng-Tips Forums:
- Notification Of Responses To Questions
- Favorite Forums One Click Access
- Keyword Search Of All Posts, And More...
Register now while it's still free!
Already a member? Close this window and log in.
Join Us Close
- Semiconductors
- $2 for 1-8 layer PCBs
What Is A Shunt Trip Breaker & How Does It Work? Detailed Guide
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What Is A Shunt Trip Breaker & How Does It Work. The shunt trip breaker is a combination of a shunt trip accessory and a main circuit breaker. it connects to the main breaker for the protection of the electrical system. it also added security to the system since it manually or automatically cut the supply in the circuit. In this post, we will discuss the all details shunt trip breaker and other parameters. So let’s get started What is a shunt trip
Table of Contents
What is a Shunt Trip Breaker?
If the circuit breaker trips it finds faults condition and automatically shuts off the current flow to prevent the circuit from overheating. The shunt trip breaker is an optional device for a circuit breaker that helps to trip the breaker remotely in any instant or automatically in case of surge saving any damage and instrument damage.
There are 2 main types of shunt trip breakers first one is manual and the second one is automatic.
Manual witches help to off the breaker externally with the use of the remote button. Automatic switch off power when detecting surges from the external power supply.
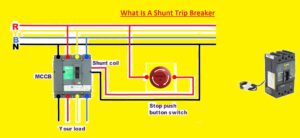
How Does a Shunt Trip Breaker Work?
Normally the current passes through the circuit breaker. But if these currents become high surges, the larger surge of power changes the electromagnet below the breaker switch, tripping the cutting power and switch.
The shunt trip breaker offers extra techniques to charge the electromagnet and trip switch, helping remote or automatic power shutoff. Some hunt trips are connected to an external power supply. When power surges get that source, signal flow from shunt trip to the breaker, mechanical cutting power.
The shunt trip can make a connection with the remote switch outside the building. Pushing the button on the switch sends a surge through shunt trip wiring and off the power.
Components of Shunt Trip Breaker
Read more Top Reasons Why Electric Outlet Stopped Working Breaker Not Tripped?
A shunt trip breaker comes with differnt components:
- The frame of the shunt trip circuit breaker works as an external protective housing and covers all inner components. it is made with the use of durable materials like metallic that help to avoid damage to sensitive inner circuits.
- Contacts are the main part of the circuit breaker that carries electric current. in a shunt trip circuit breaker, there are two types of contacts, main contacts, and auxiliary contacts. The main contact is used for normal power transmission, and auxiliary contacts are used for connecting the external control system
Operating Mechanism:
- The working phenomena in shunt trip circuit breakers help to open and close contacts. it comes with latch releases and trip units. The latch releases are used for maintaining contacts in the closed position until the trip mechanism works. The trip unit detects abnormal electrical conditions and starts the tripping process.
Electromagnet:
- At the core of the shunt trip circuit breaker electromagnet exists, which is important for working. If the external signal gets, the electromagnet activates and produces a magnetic field. This field work on latch releases resulted to open circuit breaker contacts.
- It is the main part of the shunt trip breaker that operates uniformly with an electromagnet. its working is to get an external signal and convert into electrical energy. this energy is used to producing the field needed for tripping breaker.
Why Are Shunt Trip Breakers Important?
irrespective optional nature of the shunt trip breaker, it can be an important safety instrument in a power system. As a result, many engineers use this breaker as a layer of security since they save damage during power surges.
This breaker is good for many fonts but it’s commonly used during fire. By turning off power if a fire breaks out, the electrical hazard is no main risk. Some connections shunt trip to smoke alarm in homes, for power automatically off when detector trigger alarm. It not be good option, since in some conditions smoke alarm gets off due to steam from the shower of smoke from the kitchen
Applications of Shunt Trip Breakers
- In commercial buildings like offices, and shopping malls, shunt trip circuit breakers are connected to ensure sure safety of many components and protect them from electrical faults. It also connected with a building management system to help remote operations
- Industrial facilities mostly work with high-power machines, so electrical safety is needed. Shunt trip breakers are used in such facilities for protection from faults and to reduce the chances of electrical accidents.
- Laboratories and research facilities also use these breakers since they are equipped with sensitive devices.
- There is a need for a regular power supply for critical patient care. Shunt trip breakers help to make sure emergency power is constant without any interruption.
- Data centers come with computing devices and sensitive data. Shunt trip breakers are used to protect these facilities from electrical hazards.
Advantages of Shunt Trip Breakers
- The main benefit of a shunt breaker is that it can remotely shut off in case of any fault. It quickly works and disconnects power in fire which helps to avoid damage in the home and protects people.
- These devices also increase safety levels and security by automating off power to the circuit if there is any fault. it helps to save electrical fires and any other damage.
- The shunt breaker is easily connected and confined with a power system, so it is easy to install the device in the building.
- The shunt breaker is a less cost solution for safety measures in buildings and industries. it is less costly to buy and connect and helps to save homes and buildings in the result of high fault.
- Shunt breakers support many electrical systems and devices so it is versatile devices that are used for the protection of circuits.
Comparison with Other Circuit Protection Devices
Shunt trip breakers vs. standard circuit breakers.
The basic difference between shunt trip breakers and regular circuit breakers is their function. Regular breakers are manually operated and based on a user-to-flip switch if requried or on current overloading that triggers the unlatching process.
While shunt trip breaker provdies more layers of controls. it can be triggered remotely with the use of a switch or automated system. These features allow them to immediately off power in case of fault.
Shunt trip breakers vs. ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs)
GFCI monitors equality between L1 and L2, if there is more than predefined difference in trips. The shunt breaker is a combination type device that combines in regular breaker with its regular function trip it has a remote control to trip breaker.
Ground fault breakers monitor current on neutral wire flowing back to the neutral bar, the four to six-milliampere different trip breakers, and shunt trip breakers can tripled remotely from other switches or points. In industrial uses, it is used to shut off in emergency condtion, when access to an electrical panel is difficult.
Shunt trip breakers vs. arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs)
Shunt Trip Breaker
- It used for overloading and short protection
- its working principle is based on thermal magnetic trip
- Its detection range is 10 to 1000A
- its response time is 10 to 20 milliseconds
- It used for arc fault protections
- It works based on a microprocessor for detecting arcing
- The detection range is 5 to 6000 A
- Response time is 10 to 40 milliseconds
What Are 3 Types Of Shunt Trip Breakers?
- Standard breakers
- Arc fault circuit interrupter circuit breakers
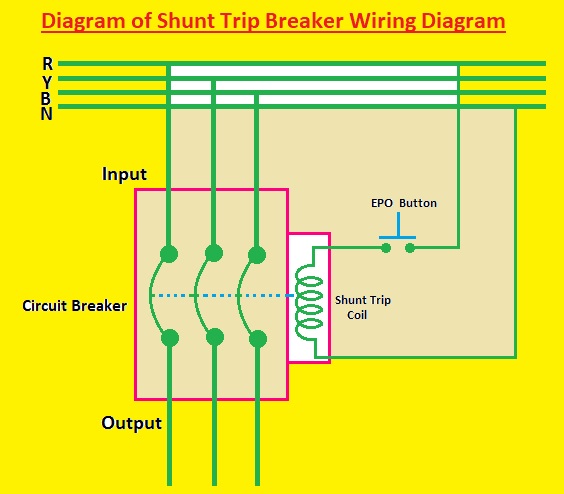
Shunt trip breaker wiring
Follow these steps for shunt trip breaker wiring.
- First of all, see the diagram shown below.
- Arrange requried tools and materials like wire strippers, nuts, and voltage tester.
- Remove the power and wire that shunt the breaker according to instructions.
- Again connect power to the circuit and test breaker to check that working well

Diagram of Shunt Trip Breaker Wiring Diagram
WHICH TYPE OF SHUNT TRIP BREAKER TO USE?
The manual breaker is best to use for small buildings or conditions where any technical staff is available to reset the breaker,. The automatic breaker can be best for larger-size buildings or conditions where there is no option for staff for breaker resetting.
it is also preferred for trigger shunt trip breakers at a distance or remotely. These relays are connected to fire alarm systems and can send a signal to the breaker for tripping if there is any fault.
Read more How Many Outlets on a 15 Amp Circuit Breaker?
How Many Outlets on a 15 Amp Circuit Breaker?
60 Amp Wire Size – Which AWG is Best for 60 Amp Breaker
Difference Between a Single and Double Pole Breaker
Where is the Doorbell Breaker Located? Easy Way to Findout
Difference Between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
How does a shunt trip breaker work?
The shunt trip is a device in the circuit breaker that mechanically trips the breaker when power is given to shunt trip terminals. Power for shunt trip does not come in breakers, so it provided from an external source
How is a shunt trip breaker wiring?
Make the connection of accurate voltage (120V to 240V for the -1021 suffix) with 2 terminals on the shunt trip. Land with a leg from source contact on one terminal and a neutral wire. (L2 , X2 ) to the other terminal
What is the purpose of a shunt with a relay?
Shunt relays are used to bypass normal controls like switches , dimmers, or panel-mounted relays when employed on an emergency circuit.
What is shunt trip and under voltage?
The shunt trip coil is connected to the breaker to offer a remote trip of the breaker but Undervoltage or no voltae coil is connected to offer automatic tripping when power losses occur or when there is a major voltage dip.
Where is shunt trip used?
The shunt trip helps to remotely and fastly turn off the breaker when needed especially in conditions where safety and speed is important, like during a fire or when there is needed to isolate certain areas of the electrical system without physically going to the breaker
What is the difference between shunt and resistance?
The shunt is an electrical device that produces a low resistance path for current. It helps current to flow to another point in cirucit. Shunts are also referred to as ammeter shunts or current shunt resistors.
What is the purpose of a shunt breaker?
its main purpose is to remotely and fastly turn off circuit breaker when necessary
Is the shunt resistor AC or DC?
Shunt provdies DC mV signal for driving moving coil ammeter, overlading protection, and control units for high amper range.
Where are shunt trip breakers required?
These breakers are used in commercial and industrial buildings, also for facilities where safety is a top priority
Why is it called a shunt resistor?
In older circuits, resistors connected in parallel to the ammeter as shunts for expanding the current measuring range called shunt resistors. but now resist used for detection circuit current collectively referred to as shunt resistors
Why is low resistance called shunt?
When a resistor is connected with another resistor of low value, then the equivalent resistance is less the lowest resistor, that is shunt resistors.
What is another name for a shunt resistor?
Shunts also called ammeter shunts or current shunt resistors.
What is a unit of shunt resistance?
The unit of shunt resistance is ohm (Ω).
What is shunt resistance formula?
The shunt resistance formula is:
- Rs is the shunt resistance
- V is the voltage of the shunt resistor
- I is the current passing through the shunt resistor
What is shunt release in a circuit breaker?
The shunt releases is opening coil plus release. Thermal trips and electromagnetic trips also use trip units. use a certain voltage to shunt trip the coil, and the breaker will trip and open.
What is the difference between a shunt trip and series trip?
What are the different types of shunt trip breakers, does a shunt trip breaker need a neutral, what is the difference between shunt trip and a shunt close.
When used as a shunt trip the coils trip breaker when a rated voltage is given. When used as shunt close, coils closes breaker when voltae is provided
Share this:
Wholesale PCBs SMT Stencil & PCBA Service Provider
Special offer:$2 for 1-8 layer PCBs
Sign Up & Get 54$ Coupon
Author: Scott Spencer
I am professional content writer have professional degree in engineering. I have worked in different famous companies and also providing technical and seo based services clients all over the world. With that i am sharing my knowledge to engineering and technical students and new learners to enhance their learning and get new ideas in technical fields. Follow him on Twitter and Facebook .
Related Posts

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post comment
Information
Related articles.
- Number of Views 1
- Number of Views 3
Eaton is an intelligent power management company dedicated to improving the quality of life and protecting the environment for people everywhere. We are guided by our commitment to do business right, to operate sustainably and to help our customers manage power ─ today and well into the future.By capitalizing on the global growth trends of electrification and digitalization, we're accelerating the planet's transition to renewable energy and helping to solve the world's most urgent power management challenges.
About us >
Careers >
Inclusion and Diversity >
Investor relations >
Sustainability >
News and insights >
Slavery and human trafficking statement >
QUICK LINKS
Sign in >
Support >
Policies and statements >
Terms and conditions >
Responsible sourcing of conflict minerals >
Subscribe to emails >
LET'S TALK BIG IDEAS
View all social media >
- Green Premium
- Introduction
- Dual-Break Rotating Contacts
- Reduced Let-Through Currents
- Internal Operating Mechanism
- Handle Position Indication
- Characteristics Indicated on the Faceplate Label
- Codes and Standards
- Circuit Breaker Applications
- PowerPacT B-Frame Circuit Breakers
- Circuit Breaker Ratings
- Reverse Feeding of Circuit Breakers
- Special Ratings
- 400 Hz Applications
- Circuit Breaker Specifications
- Automatic Switch Functions
- Automatic Switch Protection
- Automatic Molded Case Switch Specifications
- AC Magnetic Trip Levels
- DC Magnetic Trip Levels
- Circuit Breaker Mounting Positions
- Catalog Numbering
- I-Line Circuit Breakers
- Trip Unit Options
- Terminations
- Accessory Overview
- Accessory Compatability
- Multiple Types of Power Connections
- EverLink Lug Connector
- Compression Lugs
- Power Distribution Connectors
- Mechanical Lug Kits
- Torque-Limiting Breakaway Bits
- Long Terminal Shields (IP40)
- Interphase Barriers
- Rear Insulating Screens
- Insulation Accessories
- Insulation of Connectors
- Electrical Auxiliaries
- Electrical Accessory Connections
- Auxiliary and Alarm Indication Contacts
- Shunt Trip (MX)
- Undervoltage Release (MN)
- Time Delay Unit for Undervoltage Release
- Class 9421 Type L Door-Mounted Rotary Operators
- Class 9422 Cable Operating Mechanism
- Class 9422 Flange-Mounted Variable-Depth Operating Mechanism
- Direct Rotary Handles
- Extended Rotary Handles
- Side Rotary Handles
- Interlocking of Circuit Breakers with Toggle Control
- Manual Mechanical Interlocking System
- Sealing Accessories
- Environmental Conditions
- Shunt Trip (MX) and Undervoltage Release (MN) Wiring Rules
- Correction Factor
- Calculating Tripping Time
- Installation and Operating Conditions
- PowerPacT B-Frame Circuit Breaker Enclosures
- PowerPacT B Enclosure Hub Accessories
- Enclosures for Special Applications
- PowerPacT B-Frame Enclosure Dimensions
- Clearances and Minimum Distances
- PowerPacT B-frame Clearances, UL Standard
- PowerPacT B-Frame Clearances, IEC Standard
- Circuit Breaker Dimensions
- Connector Dimensions
- Terminal Shield Dimensions
- Interphase Barrier Dimensions
- Insulation Screen Dimensions
- Backplate Dimensions
- DIN Rail Dimensions
- Direct Rotary Handle Dimensions
- Extended Rotary Handle
- Side Rotary Handle Dimensions
- Door-Mounted Operating Mechanism
- NEMA 9422 Cable-Operating Mechanism
- NEMA 9422 Variable Depth Operating Mechanism
- PowerPacT B DC Systems
- PowerPacT B DC Wiring Diagrams
- Grounded B-Phase Systems (Corner-Grounded Delta)
- Indication Contacts
- Remote Operation (MN/MX Voltage Release)
- PowerPacT B-Frame Let-Through Energy Curve
- PowerPacT B-Frame Peak Let-Through Current Curve
- PowerPacT B-Frame 15/20 A Thermal-Magnetic Trip
- PowerPacT B-Frame 25/30 A Thermal-Magnetic Trip
- PowerPacT B-Frame 35/50 A Thermal-Magnetic Trip
- PowerPacT B-Frame 60/100 A Thermal-Magnetic Trip
- PowerPacT B-Frame 110/125 A Thermal-Magnetic Trip
- Busbar Information
- PowerPacT B-Frame 1P Unit-Mount Single Phase Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame 1P I-Line Single Phase Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame 2P Unit-Mount Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame 2P I-Line Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame 3P Unit-Mount Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame 3P I-Line Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame 4P Unit-Mount Circuit Breakers
- PowerPacT B-Frame Switches
- Electrical Accessories
- Connection Accessories
- Insulation Accessories Catalog Numbers
- Rotary Handle Catalog Numbers
- Locking and Sealing Accessories Catalog Numbers
- Adapter/Conversion Kits
- Spare Parts
- Bare-cable connector
- Connection terminals
- Breaking capacity
- Degree of protection (IP) IEC 60529
- Degree of protection against external mechanical impacts (IK)
- Electrical durability
- Insulation class
- Making capacity
- Maximum break time
- Mechanical durability
- Non-tripping time
- Pollution degree of environment conditions IEC 60947–1
- Prospective short-circuit current
- Rated current (In)
- Rated impulse withstand voltage
- Rated insulation voltage (Vi)
- Rated operational current (Ie)
- Rated operational voltage (Ve)
- Rated short-time withstand current (Icw)
- Service breaking capacity (Ics)
- Short-circuit making capacity (Icm)
- Suitability for isolation
- Suitable for isolation with positive contact indication
- Ultimate breaking capacity (Icu)
- CNOMO machine-tool rotary handle
- Direct rotary handle
- Emergency off
- Extended rotary handle
- Remote tripping
- Side rotary handle
- Cascading /Series Ratings
- Current discrimination/Selective coordination
- Discrimination
- Energy discrimination
- Partial discrimination
- Time discrimination
- Total discrimination
- EMC (Electromagnetic compatibility)
- Power loss (Pole resistance)
- Product environmental profile (PEP) LCA: Life-cycle assessment ISO 14040
- RoHS directive (Restriction of Hazardous substances)
- Temperature derating
- Vibration withstand IEC 60068-2-6
- WEEE directive (Waste of Electrical and Electronic Equipment)
- Overvoltage category (OVC - Overvoltage category) IEC 60947-1. Annex H
- Instantaneous protection I (Ii)
- Magnetic protection (Im)
- Neutral protection (IN)
- Thermal protection (Ir)
- Auxiliary contact IEC 60947-1
- Break contact IEC 60947-1
- Make contact IEC 60947-1
- Relay (electrical) IEC 60947-1
- Circuit breaker IEC 60947-2
- Circuit breaker utilisation category IEC 60947-2
- Contactor IEC 60947-1
- Contactor utilisation categories IEC 60947-4-1
- Current-limiting circuit breaker IEC 60947-2
- Disconnector IEC 60947-3
- Magnetic release
- Reflex tripping
- Release IEC 60947-1
- Shunt trip (MX)
- Thermal release
- Thermal-magnetic trip unit
Undervoltage release (MN)
For the best experience of this site, please enable Javascript for the www.productinfo.schneider-electric.com domain.
Show QR code for this page
Was this helpful?
Contact Information
Legal information.
The information provided in this document contains general descriptions, technical characteristics and/or recommendations related to products/solutions.
This document is not intended as a substitute for a detailed study or operational and site-specific development or schematic plan. It is not to be used for determining suitability or reliability of the products/solutions for specific user applications. It is the duty of any such user to perform or have any professional expert of its choice (integrator, specifier or the like) perform the appropriate and comprehensive risk analysis, evaluation and testing of the products/solutions with respect to the relevant specific application or use thereof.
The Schneider Electric brand and any trademarks of Schneider Electric SE and its subsidiaries referred to in this document are the property of Schneider Electric SE or its subsidiaries. All other brands may be trademarks of their respective owner.
This document and its content are protected under applicable copyright laws and provided for informative use only. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), for any purpose, without the prior written permission of Schneider Electric.
Schneider Electric does not grant any right or license for commercial use of the document or its content, except for a non-exclusive and personal license to consult it on an "as is" basis.
Schneider Electric reserves the right to make changes or updates with respect to or in the content of this document or the format thereof, at any time without notice.
To the extent permitted by applicable law, no responsibility or liability is assumed by Schneider Electric and its subsidiaries for any errors or omissions in the informational content of this document, as well as any non-intended use or misuse of the content thereof.
© 2016 – 2021 Schneider Electric
- Get custom product tools and services
- Access training
- Manage support cases
- Create and manage your orders (authorized partners only)
Schneider Electric USA Website
Search FAQs
Can you get both a shunt trip and uvr on a powerpact h, j, l, m, p, or r frame circuit breaker.
- Install a UVR in the breaker
- Supply it from the control power source, going through NC (normally closed) contacts on a relay. This gives you the UVR function plus a means to open the circuit as you would with a shunt trip
- To obtain the shunt trip function, supply the relay coil from a switched control power source as you would a shunt trip. When you activate the switch and energize the relay coil, the NC contacts open, dropping voltage to the UVR, tripping the breaker.
Released for: Schneider Electric USA
Articles that might be helpful
Discuss this topic with experts
Start here!
Find answers now. Search for a solution on your own, or connect with one of our experts.
Contact Support
Reach out to our customer care team to receive more information, technical support, assistance with complaints and more.
Where to buy?
Easily find the nearest Schneider Electric distributor in your location.
Search topic-related frequently asked questions to find answers you need.
Contact Sales
Start your sales inquiry online and an expert will connect with you.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
tripping. The MN release is continuously supplied, i.e. if supply is interrupted: either voluntarily, by the emergency-off button, or accidentally, through loss of power or faulty wiring, the release provokes opening of the circuit breaker. MX shunt release The MX release opens the circuit breaker via an impulse-type (u 20 ms) or maintained order.
The shunt trip is an electrical accessory used for the instantaneous opening of the circuit breaker. It is generally controlled through normally open contact. It is also referred to as an opening coil or shunt release. By energizing the shunt trip you can open the circuit breaker remotely. The range of shunt trips proposes various supply voltages.
Learn how to install and use undervoltage release (UVR) and shunt trip (ST) devices on Power Defense circuit breakers. See ratings, mounting locations, and secondary connector plugs for each accessory.
Learn how an under voltage release (UVR) device automatically trips a circuit breaker when the power falls below a preset level, usually between 70 and 35 percent of the UV rating. Compare UVR with shunt trip, a similar device activated by power outage, and see Eaton's UVR products.
3.6 Shunt-trip and undervoltage releases. Shunt-trip releases enable remote circuit breaking by means of a control signal, for example for electrical interlocking (Figure 8). The undervoltage release switches the circuit breaker OFF when the voltage falls below a (usually fix) certain level of the applied voltage and is used for example for ...
Further, this is CONSTANT DUTY Type Release. 1. UNDER VOLTAGE RELEASE offers the feature of TRIPPING THE "Switching Device / Circuit Breaker " upon Power supply failure OR Voltage dips below its "Drop-out Voltage Design", which is generally 80 % of its rated Voltage. This is the reason "Under-voltage Release" is also used as an "UNDER-VOLTAGE ...
When used as a shunt trip, the coil trips the breaker when the rated voltage (Vn) is applied. When used as a shunt close, the coil closes the breaker when Vn is applied as long as there is nothing preventing the breaker from closing (an open command, the open button being pressed, and engaged padlock attachment, etc.)
I. Shunt Trip: An Overview - Definition and Purpose - Working Principle - Applications. A. Definition and Purpose. A Shunt Trip is an accessory that remotely opens a circuit breaker. It is commonly used in situations where an immediate trip of the circuit breaker is required, such as in emergency shutdowns or for isolation purposes.
MN undervoltage release The MN release opens the circuit breaker when its supply voltage drops to a value below 35% of its rated voltage Un. Undervoltage tripping, combined with an emergency-off button, provides fail-safe tripping. The MN release is continuously supplied, i.e. if supply is interrupted: either voluntarily, by the emergency-off ...
Resolution: A shunt trip device is an optional accessory in a circuit breaker that mechanically trips the breaker when power is applied to the shunt trip terminals. The power for the shunt trip does not come from within the breaker, so it must be supplied from an external source. Released for: Schneider Electric USA. Published on: 8/8/2001 Last ...
Shunt Trip (SHT) This release trips the circuit breaker when the control voltage rises above 0.7 x Un Control signals can be of the impulse type (u 20 ms) or maintained. Under Voltage Release (UVR) This release trips the circuit breaker when the control voltage drops below a tripping threshold of between 0.35 and 0.7 times the rated voltage
The application is the use of tripping means on circuit breakers on an offshore gas platform - there are two commonly used possibilities. 1) a shunt trip coil, which must be energised to trip. 2) a undervoltage coil, which must be energised to allow breaker to close or remain closed. These breakers may be called upon to trip in the event of ...
The shunt trip breaker is a combination of a shunt trip accessory and a main circuit breaker. it connects to the main breaker for the protection of the electrical system. it also added security to the system since it manually or automatically cut the supply in the circuit. In this post, we will discuss the all details shunt trip breaker and ...
Share this Video: play listsVFD -https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLb1LWsNcBcj2Y4tHJjwpnSZx-OjJNz-aiELR- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL...
This release: Trips the circuit breaker when the voltage is less than 0.35 times the rated voltage Un. If the voltage is between 0.35 and 0.7 times the rated voltage Un, tripping is possible but not guaranteed. Above 0.7 times the rated voltage Un, tripping is impossible. Allows to close the circuit breaker again once the voltage reaches 0.85 ...
The shunt trip technology enhances safety by providing a means to open a safety switch electronically. When using an emergency stop, safety interlock or similar means, the remote operation capability of the shunt trip switch no longer requires personnel to manually open the switch with the handle, enhancing safety and improving productivity.
Shunt Close (XF), Shunt Trip (MX), and Undervoltage Release (MN) with Basic Coils. XF Shunt Close and MX Shunt Trip. When signalled, the shunt close (XF) and shunt trip (MX) instantaneously triggers the mechanism to close/open the circuit breaker. The undervoltage trip (MN) also opens the circuit breaker when its supply voltage drops to a value ...
The shunt close (XF), shunt trip (MX), and undervoltage release (MN) are optional accessories mounted inside the device. They can be of standard type or diagnostic and communicating type (standard or with diagnostic function for the undervoltage release [MN]). The standard XF, MX, and MN accessories can have either impulse-type or maintained ...
The undervoltage release and shunt trip can be factory installed into an LA Tri-Pack breaker. It can only be field mounted if the breaker originally had this attachment, because the cover has to be milled to make room for the attachment. To replace the undervoltage release or shunt trip, use the ones for the LA breakers.
Shunt Trip (MX) and Undervoltage Release (MN) Shunt Trip (MX) Undervoltage Release (MN) Time Delay Unit for Undervoltage Release; Rotary Handles. Class 9421 Type L Door-Mounted Rotary Operators; Class 9422 Cable Operating Mechanism; Class 9422 Flange-Mounted Variable-Depth Operating Mechanism; Direct Rotary Handles; Extended Rotary Handles ...
No, Powerpact circuit breakers can accept only one shunt trip or one UVR (undervoltage release). However, you can use an UVR to get both shunt trip and UVR functionality as follows: Install a UVR in the breaker; Supply it from the control power source, going through NC (normally closed) contacts on a relay. This gives you the UVR function plus ...