

Different levels of tourism policy and planning
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
What are the different levels of tourism policy and planning? Tourism policy and planning is a very complex issue involving a number of stakeholders and bodies. Research in this area can often be overwhelming and confusing for the untrained eye.
This post, therefore, intends to provide a basic introduction to tourism policy and planning, outlining the different levels of involvement by different organisations. At the end of the post I have included some recommend texts for further reading suitable for tourism industry stakeholders (those working in or interested in the industry) and those studying the tourism industry.
What is tourism policy and planning?
These two terms are largely interchangeable. Tourism policy can be defined as;
‘ A set of rules, regulations, guidelines, directives, and development/promotion objectives and strategies that provide framework within which the collective, as well as individual decisions directly affecting long-term tourism development and the daily activities within a destination are taken ’
Planning can be defined as;
‘the process of making decisions for the future , and not simply the physical preparation of a ‘plan’. Planning involves implementing decisions and monitoring the outcomes.’
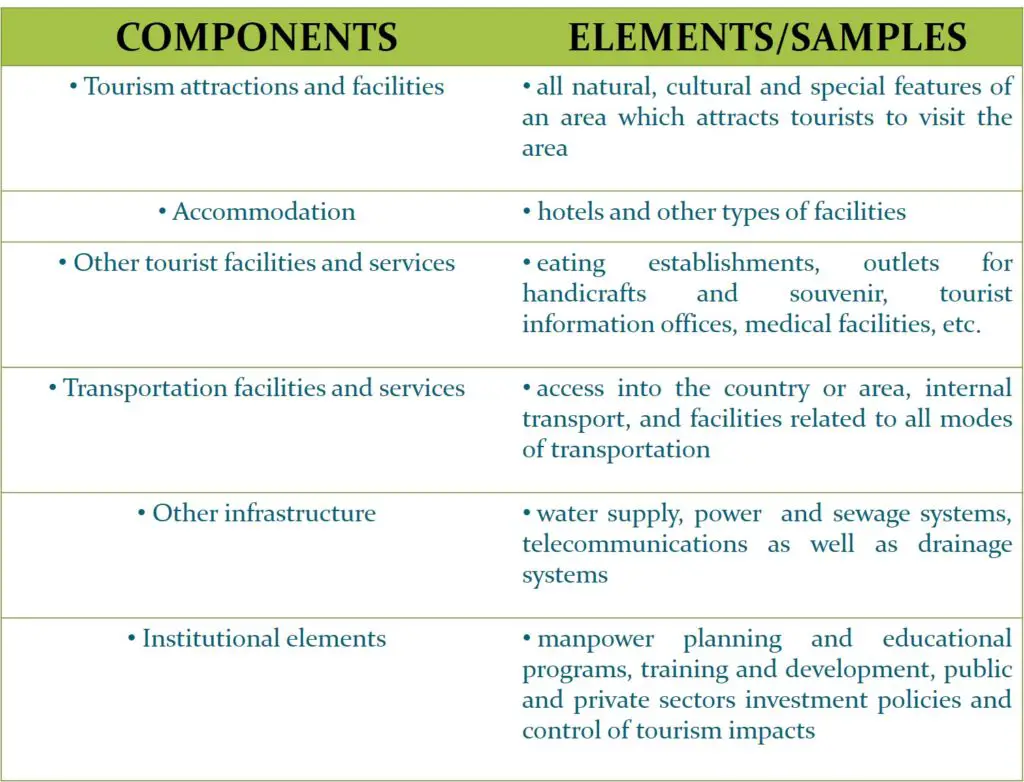
Components of tourism
Tourism policy and planning typically involves a number of components, namely:
- Tourism attractions and activities
- Accommodation
- Other tourist facilities and services
- Transportation facilities and services
- Other infrastructure
- Institutional elements
You may also be interested in my post- ‘ Why tourism planning is important ‘
Levels of tourism planning
Tourism policy and planning takes place on different levels. This can take a top-down approach, for example by international or national bodies, or a bottom-up approach, from a local level.

International tourism planning
At the international level tourism planning typically involves; international transportation services; the movement and scheduling of the tours of tourists among different countries; the development of major tourist attractions and facilities in neighbouring countries and the working strategies and promotional programs of many countries.
Examples of international level participation groups include:
- International Government and Intra-government Org’s: g. World Tourism Organisation ; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- International Producer Organisations: g. World Travel and Tourism Council
- International Non-Producer Organisations: g. Tourism Concern ; World Wildlife Fund (WWF); Greenpeace;
- International Single Interest Organisations: g. World Congress Against the Commercial Sexual Exploitation of Children
You may also be interested in my post- ‘ What is tourism? A definition of tourism ‘
The following organisations will consider similar issues, but not limited by the concerns or boundaries of a single nation. Decisions and influences from this level can be significant for tourism at a national and local level
- European Union
- of Caribbean States (ACS)
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
- The South Pacific Tourism Organization (SPTO)
- The “Tourism Program” of the Organization of American States (OAS)
National tourism planning
The national level of tourism planning is concerned with: tourism policy; infrastructure facilities and a physical structure plan which includes important tourist attractions, selected tourism development regions, international entry points, facilities, and services. It is also concerned with: the amount, kinds, and quality of accommodation and other required tourist facilities and services; the important tour routes in the country and their regional connections; tourism organisational entitles, laws and investment policies; tourism marketing strategies and promotion; education and training programs and environmental, economic, and socio-cultural analysis.
Examples of national level participation groups include:
- National Government and Intra-government Organisations- e.g. Visit Britain, Tourism New Zealand
- National Producer Organisations- e.g. Visit Scotland, ABTA, The Association of Independent Tour Operators (AITO)
- National Non-Producer Organisations- e.g. National Trust; The British Association for Nature Conservationists
- National Single Interest Organisations- e.g. The Wilderness Society; Society for the Protection of Birds
You may also be interested in my post- ‘ Volunteer tourism: The reasons why people volunteer ‘
Regional tourism planning
Regional planning looks at aspects including; regional policy: regional entry points and transportation facilities and services; kinds of tourist attractions and their locations; the amount, kinds, and location of tourist accommodation and other tourist facilities, and services and location of tourist development areas including resort areas.
In addition, they will manage: socio-cultural, environmental, economic, and impact analysis’s; education and training programs on the regional level; marketing techniques and promotion; organisational establishments, laws, regulations and investment policies and implementation methods which include project plans and regional zoning regulations.
Examples of regional level participation groups include:
- Regional Government and Intra-government Organisations – g. Caricom, Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS)
- Regional Producer Organisations – e.Caribbean Hotel & Tourism Association
- Regional Non-Producer Organisations – e.g. European Environmental Bureau (EEB), Regional Environmental Centre for Central and Eastern Europe
- Regional Single Interest Organisations- e.g. Coastwatch Europe, Climate Action Network Europe
Local tourism planning
Local level participants will consider tourism planning goals/objectives, analysis, plan preparation, outputs, outcomes, and evaluation at grass roots level.
Examples of local level participation groups include:
- Local Government and Intra-government Organisations- e.g. local government involvement in leisure and tourism provision, e.g. Visit Cornwall , Tourism South East
- Local Producer Organisations- e.g. local chambers of commerce and industry associations; local sporting clubs and private sport and leisure centres
- Local Non-Producer Organisations- e.g. ratepayers and resident associations,
- Single Interest Organisation – e.g. organisations such as ‘friends of a park’ or a group which has been formed in order to prevent particular developments such as a hotel or airport
The approach and implementation of tourism policy and planning differs considerably between destinations. It may, for example, be well organised and regulated in a developed country (or even over-regulated in some cases), and less resourced in developing countries.
Tourism Policy and Planning
To conclude, this post has demonstrated that tourism policy and planning takes place on different levels and in many different regards. For more information on tourism planning I recommend that you take a look at this post- ‘ Why tourism planning is important ‘
I also recommend that you consult some of the following texts, which are beneficial both to tourism practitioners and those who are studying the travel and tourism industry.
Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing
Leisure, Sport and Tourism, Politics, Policy and Planning
Tourism Planning: Policies, Processes and Relationships
Do you have any views on this topic? Please leave any comments in the box below.
If you wish to cite any of the content in the post please use reference ‘Stainton, Hayley. (2018) Lifeasabutterfly.’
Liked this article? Click to share!
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

TOURISM PLANNING APPROACHES

Related Papers
Kelly Bricker
Predicated on socio-economic changes in the more developed countries, international tourism in less developed countries has become an attractive option for economic development. As international tourism continued to grow however, it became apparent that a range of negative impacts was affected. As a result, sustainable development became a focus for tourism as a development tool. There are several inherent challenges in applying the principles of sustainable development at an operational level in tourism. These include the nature of the tourism industry and product, the fragmented fashion in which critical decisions about tourism are made, and the diverse and often conflicting interests in tourism development held by a broad range of stakeholders. Sustainability under these conditions is an elusive concept and even more of a challenge to implement within the tourism system. This paper considers the pragmatic implications of operationalizing sustainable practices in tourism developme...
Tourism International Scientific Conference Vrnjačka Banja - TISC
Biljana Pejoska Risteska
European Scientific Journal
Rezarta Brokaj
Theodosia Christhe Nathalia
Purpose: Tourism is becoming increasingly more important in economic development. Aware of this potential, organizations, governments, professionals, and scholars that are involved in tourism development recognize the need and right for stakeholders to be included and involved in the tourism development process. The focus on more stakeholder participation emphasizes its ability to handles multiple perceived issues. The purpose of the paper is to identify stakeholders of Central Sumba who is responsible for the development of a tourism destination and how they have been applied in relation to sustainable tourism development. Design/methodology/approach: A qualitative research method was chosen. The data are based on the interviews of tourism stakeholders in Central Sumba. Data were collected via semi-structured, in-depth interviews with 25 representatives. In order to capture the widest variety of local, regional and national viewpoints on the implementation of sustainable tourism development situation, local residents, governmental, non-governmental and private sectors were included. Findings: The level of leadership among the stakeholders in Central Sumba varied, yet still depends on the public sectors which is local government. The public sectors seem to have a greater role and more responsibility in developing the destinations. Originality/value: The paper discusses the roles of tourism stakeholders.
Proceedings of the International Conference on Tourism (ICOT 2013). Trends, Impacts and Policies on Sustainable Tourism Development
Valentina Della Corte , Alessandra Iavazzi
The aim of the paper is to deeply understand the different strategic choices a destination management organization (DMO) can make with a managerial approach in order to ensure the development of the destination by systematizing local resources according to a long run vision. Once the “sustainable tourism” is identified, it is necessary to understand which are the main strategic initiatives a DMO can put in place taking into account the stakeholders directly or indirectly involved in tourism activities, according to a responsible tourism approach. In order to identify common procedures and successful policies, the paper uses a comparative case study analysis in order to describe several existent best practices with some possible generalizations. The findings of this research highlight strategic governance choices, as well as the role of public and private actors, in facilitating destinations sustainable development.
Sustainable Development
Maria Partidario
mahmood ziaee
Extended Abstract Sustainable tourism development recently as a management strategy for destinations has got special significant. However, there is Discontinuities between concept of sustainable tourism development (STD) and original paradigm that STD derived from it, means sustainable development, in terms of theoretical and practical viewpoints. The main goal of paper discusses and analyze around the most important practical and theoretical challenges that sustainable tourism development has face with them. The research method is literature content review of this field. This paper, Also, review different frameworks of sustainable tourism development. Dynamics of tourism destination development during the three Separate ways that according one environmental pragmatism move to sustainable mass tourism and finally converge will be discussed. Finding of this paper is identifying the most important theoretical and practical challenges and critics of sustainable tourism development form...
Morena Mičetić Fabić
The purpose of this paper is to establish how and to what extent local self-governments(towns) in tourism destinations are involved in sustainable development. The aim is to identify the types of activities undertaken by local self-government units to promote sustainable development and the main problems they are faced with in undertaking and implementing these activities. The paper also investigates whether the towns possess plans containing activities for promoting sustainable development, whether they have defined indicators to measure progress in sustainable growth and whether they use them, whether they have made the necessary organisational adjustments to planning and promoting sustainable development and whether they are equally concerned with ecological, economic and socio-cultural sustainability. Two primary studies were conducted, one on a sample of experts on sustainable development and/or tourism and the other on a sample of towns in Croatian coastal counties. The study ...
Vanessa GB Gowreesunkar
Few businesses are subjected to negative criticism as tourism does. In early stages, it was considered a passport to development, later around the last quarter of 20th century, it touched the zenith, bringing in its wake, myriad negative consequences that it consumes places, cultures, creates acculturation, degrades the environment and suffers from leakages. Tourism destroys tourism become a bye-word. Serious thinkers came forward with two mantras of redemption: Ecological Tourism and Sustainable Development (SD). Both models were a promise of conservation of resources, and assured well-being of the local community and of the visitors. Both were the outcomes of the world’s best brains; they asked for the parsimonious use of finite resources, promote localism, and act in line with the laws of nature with sustainable policy. Ecotourism fell prey to human greed and green washed many splendid ecosystems and SD got entangled with definitional irk. This paper reviews the tourism scenario critically and indicate possible barriers that hamper the fruition of the concept of sustainability. Critics of SD argue that, it needs new knowledge to operate effectively. It does not have strong database on the present world tourism situation, let alone future generation. SD is based on the science of ecology, we may have theoretical knowledge, but the deeper understanding of overall ecosphere is wanting. ‘Evenmoreism’ seems not to be compatible with SD such as anthropocentrism, resourcism, modernism. The myth of endless growth that promotes over-consumerism, over production, ineffective policy and poor governance are some of the drivers of unsustainability. One of the sad facts is that most stakeholders are averse to tourism research that relegates them to archaic methods. For attaining sustainable development, stakeholders have to foster a culture of sustainability. The paper illustrates the factors responsible for unsustainability with the help of a case study which demonstrates ‘how a sustainable resort declines without effective policy and guidelines.
Tourism is a vital component of the Welsh economy and the need to incorporate sustainability principles into new and more responsible forms of tourism development is now widely accepted. Sustainability in a tourism context is multi-faceted, involving consideration of the economic, sociocultural and environmental impacts of tourism on all of the people and places impacted by it, including tourism and non-tourism businesses, residents and guests. Planning for sustainable tourism is therefore complex, requiring integration with other relevant planning processes; wide-ranging stakeholder participation; and, an integrative, iterative and strategic approach. This study assessed the extent to which Wales’ regional tourism entities have to date incorporated a stakeholder-driven, sustainability-focused mindset into their planning activities. Evaluation of 22 recent destination management plans revealed that there are many opportunities for improvement in the extent to which the desires of th...
RELATED PAPERS
Marián Fabian
Alexandre Corso
Ahmad almogren
Teguh Priatin
suparna bantul
Journal of the South African Veterinary Association
Alaster Samkange
Advances in Economics and Business
Wojciech Bieńkowski
Geophysical Journal International
Bernhard Steinberger
Laurence Zerafa
Firas Safadi
Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz
Fidel OSPINA SARAY
Hira Batool
Biophysical Journal
Kirsten von Hagen
International Journal of Plasticity
Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry
Andreas Zahn
Il vizio funzionale utile ex art. 1669 C.C.
Micaela Lopinto
Colleen A . Sheehan
IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation
Alexander I. Nosich
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
Behnam Rasekh
Información tecnológica
Gilmar Santafé
Christine Moffitt
Free Radical Biology and Medicine
Javier Escobar
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Wait you forgot to try your Luck
Enter your email and get details on how you can win Prizes/ Shopping Vouchers

- Business Courses How to start a travel agency 4Ps of Tourism Marketing Interpersonal Skills Training Mastering in AIRBNB Travel Consultant Course Travel Photography Travel Agent Essentials Tourism Marketing Course International Tourism Course View All
- Destinations Alpines of Graubunden Lakshadweep Oman Andaman Manali Hampi Hawaii Hungary Saudi Arabia Ooty View All
- Hotels Centara Ras Fushi Resort Maldives Centara Grand Maldives Courtyard By Marriott Bangkok JW Marriott Bangkok FIVE Zurich Hyatt Ziva Los Cabos Hyatt Ziva Puerto Vallarta Sinner Paris Kandima Maldives View All
- Experiences ARTECHOUSE Kennedy Space Center An out of this world adventure SUMMIT One Vanderbilt Phillip Island Nature Park Trans Studio Bali Theme Park Zoos Victoria Vana Nava The Wheel at ICON Park View All

- Register with us
- Webinar Registration
- Destinations
- Experiences
- Business Courses
- TBO Portal Training
- Strategic Alliance
Existing Agents Login Here

Reset Password
Tourism planning: importance, benefits, types & levels.
Planning is to prepare a Road Map to achieve goals.
Faludi, in 1973, defined tourism planning as "Planning is a very important part of the process by which governments manage tourism at the national, local and organizational levels".
What is Tourism Planning?
The upkeep and expansion of the tourism sector in a particular area is referred to as tourism planning. Planning for tourism is, of course, a crucial component.
Creating strategies and plans to increase, develop, and stimulate tourism for/in a destination may be summed up as tourism planning. The primary motivation behind establishing and implementing strategies for the tourist industry is to generate money, which will eventually raise the GDP of a nation or region.
What is the need for Tourism Planning?
For the expansion of the sector important to plan tourism activities for the following reasons:
- It is necessary to plan tourism activities on different levels and in various manners to promote tourism and boost the economy.
- To provide quality to both tourists and residents.
- It involves making major decisions which cannot be taken spontaneously.
What are the components of Tourism Planning
- Exploration phase/ Preparatory
- Planning phase/Feasibility/
- Zoning phase/Formal planning
- Design and implementation phase
- Operational phase
Most nations that have successfully planned their tourism can be found online and are regarded as incredible holiday destinations. People go to these nations hoping their travel vlogs will increase their subscriber count on YouTube. That is an indication of success in the modern day.
Benefits of Tourism Planning
Tourism destination planning should be a vital component of every destination's tourism development plan to get the best outcomes and please all stakeholders. While some places do a great job of maintaining sustainable tourism, others (typically developing countries) need to recognize the significance of comprehensive tourism development planning.
Tourism planning can benefit various parties involved from the industry in the following ways:
- It boosts revenue and employment thanks to tourist spending.
- It safeguards cultural and natural assets so that visitors can enjoy them.
- It broadens the comprehension of cultural diversity
- It constructs new infrastructure, such as sewage systems, roads, etc., for the community.

Impacts of Tourism Planning
The impacts of tourism destination planning can be sorted into seven general categories:
- Environmental
- Social and cultural
- Crowding and congestion
- Community attitude
According to Inskeep, six "golden standards" should be followed when creating a strategy for tourist planning and policy (1991).
1. Goal Oriented: Tourism Planning should be oriented to achieve broad national and community goals.
2. Integrative: Integrating tourist policy and planning into the economy, land use and infrastructure, conservation, and environmental planning.
3. Market Driven: Planning for successful tourism growth in a cutthroat international market.
4. Resource Driven: Developing tourism that capitalizes on the location's inherent advantages while preserving and improving the features and experiences of existing tourism resources.
5. Consultative: Considering broader community attitudes, needs, and desires to determine what the population will accept.
6. Systematic: utilizing primary or secondary information to support planners conceptually or predictably, incorporating knowledge from other tourist locations
Levels of Tourism Planning
Planning and policy for the tourism industry occur at several levels. This can be done in a top-down approach, with international or national bodies, or a bottom-up approach from a local level.
1. International Tourism Planning: Tourism planning at the international level typically involves international transportation services, the movement and scheduling of tourist tours between different countries, the development of significant tourist attractions and facilities in neighboring countries, as well as the working strategies and promotional programs of many nations.
2. National Tourism Planning: Tourism policy, infrastructural facilities, and a physical structure plan, which includes significant tourist attractions, chosen tourism development regions, international entrance points, facilities, and services, are all addressed at the national level of tourism planning. Additionally, it is concerned with the quantity, types, and quality of lodging and other essential tourist facilities and services; the country's major travel routes and their regional connections; tourism organization
rights, laws, and investment policies; marketing and promotion strategies for the industry; education and training initiatives; and environmental, economic, and sociocultural analysis.
3. Regional Tourism Planning: Regional planning considers factors such as regional policy, regional entrance points, transportation facilities, and services; the types and locations of tourism attractions; the quantity, varieties, and places of lodging and other tourist facilities and services; and the sites of tourist development regions, such as resort areas.
They will also oversee sociocultural, environmental, economic, and impact analyses, regional education and training programmes, marketing strategies, investment policies, organizational structures, legal frameworks, and implementation strategies, including project plans and zoning ordinances.
4. Local Tourism Planning: Participants at the local level will think about the analyses, outputs, outcomes, and assessment of tourism planning at the ground level.
Types of Tourism Planning
Before creating a comprehensive plan to market the destination, the following types of tourism planning are taken into account:
Spatial Tourism Planning: Spatial tourism planning attempts to thoroughly process social, environmental, and economic change to bring about certain ends. Drawing plans, maps or diagrams are put together to decide where socio-spatial activities can occur.
Sectoral Tourism Planning: In this kind of planning, the regions are divided into sections, and each section is called a sector. It concentrates on a manageable area and takes into account the specific infrastructure, land use, transportation, and environmental requirements of that region. Depending on the nature of the products or services provided, economic, social, and administrative activities are grouped into sectors.
Complex Tourism Planning: When various regions are considered for the purpose of tourism planning, it is known as complex tourism planning. These regions are to be developed comprehensively because of the significant interest shown by international tourists. There is a possibility that these regions are located far away from one another.
Integrated Tourism Planning: Integrated tourism refers to making tourism the primary industry in a given area by systematically and comprehensively promoting all available economic, social, and tourism resources.
Sustainable Tourism Planning: Sustainable tourism planning involves striking the correct balance between the requirements of people and the environment. It entails stating the community's mission, vision, and unique selling point or identity in clear terms. With the help of this type of destination planning in our local communities, we are better equipped to plan for the long term, and respond to changing target markets, trends, and emergencies like the Covid-19 outbreak. Additionally, it guarantees that resources are allocated properly while ethically and sustainably establishing local communities. This method of tourism planning benefits people and places in positive ways on all fronts—socially, economically, culturally, and environmentally—puts sustainability at its core.
Centralized Tourism Planning: Centralized tourism planning is done by a single authority, usually the state or central government.
Decentralized Tourism Planning: Organizations are interested in developing tourist spots and planning the various activities visitors can enjoy. (Joint Venture).
They take assistance from government. Suggested Read: Sustainable Tourism
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. why is tourism planning important.
A1. Destination development plans should include tourism planning since it promotes a destination's long-term viability and encourages cooperation among important stakeholders..
Q2. What are the features of tourism planning?
A2. Three general principles of planning for tourism can be specified as anticipation, regulation and monitoring.
Q3. What are the barriers to tourism planning?
A3. A3. According to earlier research conducted in several nations, a common pattern of issues has emerged. For instance, financial constraints, a lack of knowledge, an insufficient amount of time, and other issues have prevented local governments from incorporating tourism into their development plans.
- Exploring Sigatoka Sand Dunes: The Crowned Jewel of Fiji
- 10 Most Beautiful Places to visit in Istanbul
- Things to do in Phillip Island: For an Incredible trip to Melbourne, Victoria
- Top 15 Things to Do in Victoria: Exploring Melbourne and Beyond
- Top 6 Places to Visit in Muscat: Top Attractions & Hidden Gems
- 10 Things to Do in Saudi Arabia Beyond a Spiritual Experience
- 8 Adventures in Oman: You shouldn’t be missing
- 8 Tourist Places to Visit in Lakshadweep: India’s Island Paradise
- 8 Best Things to do in Oman for a Holiday to Remember
- Full Proof Guide to 13 Top New Attractions in Dubai
- Top Things to Do at Katara Cultural Village, Doha, Qatar
- Exploring the Breathtaking Beaches of Tanzania: A Coastal Paradise
- Discovering Willy’s Rock: Boracay's Hidden Gem
- 10 Top Places to Visit in Oman, Tourist Places & Tourist Attractions
- Camping in Riyadh: A Recreational Escapade in the Desert

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Tourism Policy, Planning, and Development
General overview.
Tourism policy, planning, and development are all very connected and do not just occur when a geographic area decides to be a tourism destination. Policy, planning, and development are included in numerous aspects of communities.
continue but from different perspectives. An example would be the use of the destination/product lifecycle, discussed later. It is important to understand what tourism planning and development are individually as well as collectively. Planning is essential to effective development. Tourism is not always a beneficial industry for a geographical area, but without planning tourism can damage the area, including natural and cultural resources (Morrison et al., 2018). A destination might consider “Who, What, When, Where, Why” when working on a tourism plan. The same can be considered for tourism development, as well as other topics included in this alternative textbook (e.g., marketing and promotion).
Tourism Policy
A policy is essentially a course of action taken by some organization or institution (e.g., government, business, educational institution). A tourism policy as defined by Edgell et al. (2008) “is a progressive course of actions, guidelines, directives, principles, and procedures set in an ethical framework that is issues-focused and best represents the intent of a community (or nation) to effectively meet its planning, development, product, service, marketing, and sustainability goals and objectives for the future grown of tourism” (p. 7). Stated more simply, Hall and Jenkins (1995) suggest “tourism public policy is whatever governments choose to do nor not to do with respect to tourism” (p. 7-8). A tourism policy is essentially a framework including guidelines, goals, and initiatives to work toward achieving the goals. Where as an act by government, such as the Travel Promotion Act of 2009 establishing Brand USA, is a law or statute.
A policy for international travel is having a current passport and for many countries a Visa. The application for a Visa to visit a foreign country allows countries to approve who may visit the country and not allow individuals for a variety of reasons (e.g., security threat). The U.S also has the Visa Waiver Program, which is an agreement with 40 countries allowing citizens of those countries to visit the U.S. for business or leisure travel purposes for up to 90 days without a Visa, provided they meet other requirements (U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs, n.d.). The countries with the Visa Waiver Program also allows U.S. residents to travel to the respective countries with fairly similar criteria. The purpose of requiring a Visa is to regulate travel between countries. The Visa Waiver Program is an agreement to allow citizens of certain countries to visit without having to obtain a Visa if certain criteria are met. This essentially makes it easier to travel between the respective countries.
The International Trade Administration includes a Tourism Policy Council (TPC) to ensure national decision-making considers the national interests of travel and tourism (International Trade Administration, n.d.). The TPC provides resources to help with such issues or challenges as recovering from disaster, and links to Center for Disease Control (CDC), and many other potential issues or challenges for travel and tourism in the U.S.
At more local levels, Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism destinations can develop policies for development, marketing, tourist experiences, human resource issues, tourism organizations (e.g., structure), relationships throughout the community, quality assurance, and supporting services (e.g., safety and security).
Policy Setting Process
There are a series of recommended steps for the establishing policy (Morrison et al., 2018). First, identifying and assessing the circumstances related to the issue. This includes understanding contraints that you and/or will face. Constraints can be internal (e.g., locals’ awareness of tourism, training and education of employees in hospitality and tourism, budget) or external (e.g., economy, price of gas, natural disaster). The tourism organization/local industry has more control or ability to do something about internal constraints, while have little or no control over external constraints. For example, nothing can be done about bad weather or if a natural disaster occurs. However, if locals are not aware of tourism in the local community, education and information can be shared to make locals more aware. This step in the process can also make you aware of new opportunities (e.g., an attraction to develop, new target market).
The next step is typically to create a policy statement to provide guidelines, goals, and initiatives to help guide the organization, destination, etc. While not directly a policy statement, most CVB vision statements include something that provides a guideline with somewhat vague goals. For example, it might be to maintain and/or improve the quality of life for residents of the destination by promoting the destination for tourism and conventions, which would include an economic goal. A policy statement for this vision would be more specific with the goals and initiatives identified to fulfill the goals.
Consultation with government, local tourism businesses, and any other stakeholders is next. This step is to get feedback about the policy statement. Following the consultation and depending on the outcome, the policy statement might be rewritten or modified. Next would be another round of consultation and then rewriting until the the policy statement is approved.
Now is time to implement the policy statement. This will include identifying specific roles of individuals, committees, organizations, etc. This step also includes developing the budget and timeline for the initiative(s).
Finally, those involved evaluation the policy. Were the goals achieved? Why or why not? However, you do not wait until the end of the established timeline for the policy to evaluate. There should be constant assessment to identify if you are likely to achieve the goals. Remember there are numerous constraints that are external (e.g., weather, natural disaster) that might dictate the need to adjust the initiatives and other efforts related to the tourism policy.
Tourism Planning
Prior to tourism planning it is important to consider other types of planning for a community or geographic area. Planning is not new. Gunn and Var (2002) indicate physical planning goes back to early Greek and Roman times. Planning is done to manage visual appearance and land use. However, planning incorporates many disciplines and perspectives: “Planning is a multidimensional activity and seeks to be integrative. It embraces social, economic, political, psychological, anthropological, and technology factors. It is concerned with the past, present, and future” (Rose, 1984, p. 45).
Gunn and Var (2002) suggest when plans (not only tourism, but community, etc.) are created they often include very high or lofty goals and it is difficult to actually achieve such goals for numerous reasons. Planning is very vague and has no real theory behind it. For community plans the general goal is a better place to live. For tourism planning the goal might be to provide visitors with a good experience. As stated earlier, an effective tourism plan can also maintain or even improve the quality of life of residents, not just economically but the attractions provide activities for local residents as well as tourists.
Morrison et al. (2018) offer three primary reasons for tourism planning. The first two are related to impacts, to maximize the economic benefits and minimize damage to resources (i.e., natural, environmental, cultural). Another reason for a tourism plan is that tourism is constantly changing for many reasons (e.g., visitor expectations, needs, motives; politics; economy; technology). As a result, the plan needs to be adaptable.
Not all destinations have a tourism plan. Some reasons for not having a tourism plan include (Morrison et al., 2018):
- Objections – it should be taken care of by the private sector and there is no need for a formal plan.
- Cost – includes market research, consultations, and a lot of time.
- Complex – tourism is affected by numerous things, such as government policies, dynamic of the community and stakeholders.
- Diversity – various sectors involved directly or indirectly in tourism.
- Seasonality – in many destinations the jobs related to tourism can be seasonal (e.g., beach destinations, snow skiing destinations).
- Unpredictability – keep in mind the numerous things that affect and make tourism complex (e.g., natural disasters, crises, politics, economy).
Gunn and Var (2002) add the following tourism planning barriers:
- Lack of awareness of tourism impacts – which is ironic because it is a reason for a tourism plan.
- Do not understand tourism development – there needs to be a plan for developing tourism and then maintaining and even upgrading tourism (e.g., attractions, facilities, etc.).
- Inadequate infrastructure – might have deteriorated attractions, facilities, etc.
- Unorganized – no leadership to guide the process.
- Politics – usually various opinions among stakeholders (e.g., businesses, government, other stakeholders).
- Lack of hospitality training.
However, there can be serious consequences of unplanned tourism. In general, unplanned tourism is not likely to be sustainable tourism economically, environmentally, socially/culturally.
Tourism Planning Models or Approaches
Morrison et al. (2018) provide a seven step tourism destination planning model:
- Background analysis – including a SWOT analysis and assessments of government policies that affect tourism, inventory analysis (e.g., attractions, accommodations, restaurants, etc.), current demand for tourism at the destination.
- Research and analyses – identify/map locations of the inventory analysis, market survey of current visitors (e.g., motivations, what they like to do) and non-visitors (e.g., why have they not visited?, awareness of the destination, image/perception of the destination), competitive analysis (e.g., who are your competitors?, how can you differentiate your destination from competitors? what do and can you work to improve?).
- Where are we now? (position statement).
- Where would we like to be? (vision statement). Then, identify critical success factors or ways to measure and determine if you achieved your vision.
- Setting goals, establishing strategies, and setting objectives – develop a policy or (e.g., stimulate the economy). Set goals or achievable outcomes. Identify alternative strategies to achieve goals and select the most desired of the alternatives given environment or conditions (e.g., economy, resources, politics). Set objectives which are more short term goals to help monitor if you are going to achieve your longer term goals. If not, remember a tourism destination plan should be adaptable, which is the next step.
- Develop a plan – identify organizations and people to be involved and their roles, funding sources and budgets for different aspects of the plan, activities to implement your plan.
- Implement and monitor the plan – While the plan should be developed by input and participation by numerous stakeholders, it is generally implemented by a local tourism agency or organization (e.g., CVB). But, there should be committees derived of various stakeholders to which the agency is accountable. This helps monitor progress of implementing the tourism destination plan and adapt if needed.
- Evaluate the plan – measure performant of the various parts of the plan against the goals (e.g., did you achieve the goals? Why or why not?). Use the evaluation to see if and how you might adapt the plan moving forward.
Tourism Development
The tourism destination plan helps guide development of tourism. Destinations will be at various stages of development. So, it is not that the tourism plan is just for a destination just getting involved in tourism. As suggested by Mason (2003). development and change for destinations occurs as time progresses. The characteristics, motives, preferred activities and attractions, and many other things change over time and destinations redevelop to remain competitive. A fairly common way to view this is commonly referred to as “Butler’s Tourism Area Lifecycle”. There are five main stages to Butler’s Life Cycle (Butler, 1980):
- Exploration – at this stage there might be some tourism but not really an effort to provide traditional or common tourism attractions, facilities, etc. This stage mostly include tourists visiting facilities and local resources used by residents.
- Involvement – this is the beginning of the destination offering some facilities for tourists. The destination begins to more formally organize and provide or improve infrastructure, some attractions, and facilities for tourists at a local level.
- Development – the destination begins marketing and promoting the destination. This stage also begins development from outside organizations and/or businesses. The destination will begin to develop and look more like a noticeable tourist destination. More and more tourists will likely visit the destination as development progresses.
- Consolidation – at this stage the rate of increase in visitors will begin to decline. The rate of development will also begin to decline. Residents may become opposed to tourism with all of the non-locals who are in the community and there is more traffic and congestion. Some of the older attractions, facilities, etc. may also begin showing degradation.
- Decline – number of visitors will be begin to decrease as competitor destinations might have more appealing attractions, infrastructure, etc. The degradation of attractions, infrastructure, and other aspects of the destination will continue and possibly turn into what Butler (1980) refers to as a “veritable tourist slum” (p. 9).
- Rejuvenation – this outcome can occur by development of a new man-made attraction, which is likely to be followed by improvement of surrounding attractions, facilities, and other tourist needs. However, if competitor destinations also rejuvenate, the competition will remain and rejuvenation might be much less or possibly not rejuvenate and potentially decline. Another way Butler (1980) suggest rejuvenation can occur is to utilize natural resources that might not have been part tourism product throughout previous tourism development and marketing and promotion.
Butler (1980), as well as many other tourism scholars, suggest all of these efforts or stages of Tourism Area Life Cycle should be a collaborative effort within the community. For example, the government could offer incentives for private development of a new man-made attraction.
There are a number of potential ways to develop tourism. One way is to develop a “flagship” attraction, which are major attractions like a theme park (e.g., Disney Land, Disney World) and/or utilize natural attractions (e.g., ocean, lake, National Park). Gunn and Var (2002) offer recommendations for tourism destinations to develop destination zones. The zone would have clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) and a corridor connecting the clusters with some form of transportation. Clustering attractions provides tourists with more to do in a closer area so they spend more time at attractions and less traveling between attractions. The destination zone and clustering is a great example of planning and development and how integrated the two initiatives should be.
Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism involvement should be holistic. The holistic view would include consideration of the product (e.g., attractions, events, support facilities, transportation, infrastructure, etc.). Respective destinations could also ensure people (i.e., hosts, guests) are included to ensure there is community awareness and inclusion of local businesses, organizations, and residents. Morrison et al. (2018) also suggest visitor management (e.g., signage) and identifying the visitor mix of the destination. Packages (e.g., all inclusive, hotel and tickets to attraction) and programs (e.g., events, festivals, other activities) could also be developed to attract more tourists. However, destinations should approach tourism development and/or redevelopment from a sustainable approach to avoid overtourism (i.e., too many tourists).
Sustainable Tourism Development
Tourism development should also be sustainable and include the three impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural).
The United Nations (n.d.) proposes 17 goals to consider for economic development, which include economic (e.g., “No Poverty”, “Decent Work and Economic Growth”, environmental (e.g., “Clean Water and Sanitation”, “Affordable and Clean Energy”), and social/cultural (e.g., “Good Health and Well Being”, Quality Education”) goals. The 17th goal is “Partnerships For the Goals”, which are very important for tourism destinations, not only in tourism destination planning and development, but other aspects such as marketing and promotion.
Relating development back to the impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural). Sustainable development should include these impacts. Morrison et al. (2018) through applying the triple bottom line to tourism offers some examples of efforts for sustainable development in each of the three areas:
- Social – include residents, be sure development improves or at least maintains locals’ quality of life.
- Environmental – protect resources, educate visitors and residents of ways to protect resources.
- Economic – new employment opportunities, increase spending of visitors, find ways to have businesses purchase locally to minimize leakage.
Tourism Development Strategies
Various strategies exist to develop tourism. For example, flagship attractions (e.g., large amusement parks, National Parks) can provide something unique to market and promote. Development of clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) provide several attractions near each other so visitors do not have to drive long distances between attractions. Such districts could also include development of a circuit or trail for transportation via hiking or biking. Aside from man-made attractions, events can be developed by destinations to highlight such things as cultural or other unique aspects of a destination.
Considering all of the possible options of tourism development provides a holistic view. Not only the examples of attractions and events, but packages and programs can developed. Destinations need to also consider all of the elements of tourism in development (i.e., attractions, infrastructure, transportation, built/support facilities, service quality/hospitality). Again, not only businesses and organizations directly involved in tourism, but all stakeholders (e.g., residents, other local businesses) should be included and/or given the opportunity to provide feedback regarding the tourism development plan.
The general goals of tourism development should include improving visitors’ experiences, improving the local economy, not damaging natural resources, and integration throughout the destination so that tourism attractions and venues are not isolated from the rest of the community (Gunn & Var, 2002). Such goals of tourism development require all three sectors (i.e., private, non-profit, government) to be involved and collaborate.
Tourism Development Roles
The private sector, non-profit, government, and local community (e.g., residents) should be involved in tourism development. The private sector role is entrepreneurial and operations (Morrison et al., 2018). The entrepreneurial role is to identify investors to develop man-made attractions, accommodations, food and beverage, and other facilities for tourists. Once built their role becomes to hire workers, manage the operation and ensure it is successful. After all, they are taking a risk as entrepreneurs.
As discussed in the Tourism Organizations section, the non-profit organizations include CVBs to market and manage the destination, chambers of commerce, associations such as a local sports association to attract sporting events to the destination. The CVB typically works with all stakeholders and leads the marketing and sales (e.g., conventions, trade shows) for the destination. Chambers of commerce might be the tourism marketing and sales organization in smaller destinations. However, many of these non-profit types of organizations collaborate with each other, as well as with private or for-profit-sector (e.g., members of CVBs) and government (e.g., hotel tax dollars as a funding source). Non-profit organizations might also operate such things as museums and historical attractions, as well as festivals and events. Such organizations might be local cultural organizations.
The government really does not manage tourism attractions. However, there are exceptions, such as National Parks. Government roles are to stimulate development of tourism, as well as establish and enforce procedures, codes, such as zoning (e.g., business, residential). Government might also get involved for the following reasons: bankruptcy of an attraction where the government needs to help the business in some way, ensure cultural aspects of the community are conserved, encouraging private sector development, find ways to work with potential attractions and other elements of tourism provided through the private sector where businesses may have concerns about being profitable (Morrison et al., 2018).
Government might fulfill some of the above reasons for their role in tourism development by offering incentives (e.g., tax breaks) to entice development by the private sector. Government might also offer a piece of land for private sector development, which lowers the businesses cost to develop at attraction, supporting facilities, or other element of tourism.
While the sectors may have relatively unique roles in tourism development, it is also important the cooperate with each other for the good of the destination. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) offer a model whereby there are times each will work independently of the other two sectors, times when two sectors work together (e.g., private sector and government), and times when all three work together. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) call this “coopetition”. For example, while attractions compete within the destination for tourists to visit respective attractions, if all stakeholders cooperate the develop and manage tourism, the destination will do better overall.
Project Development Analyses
Prior to developing an attraction, hotel, or other element of tourism, there should be an assessment or analysis to determine the feasibility of being successful. Private sector developers who need be profitable will typically do feasibility studies. This may start with a pre-feasibility study, which is essentially to see if the project is even viable. For example, does the project make sense given what the destination already offers? Pre-feasibility studies might be conducted by whatever company or organization is interested in the project. If it does, the next step would be a more robust feasibility study to identify such things as potential sites for the product being considered, assess the market demand of the project, projected revenues and expenses, capital costs to develop the project, and will there be enough return on investment (ROI) if the project is developed. The full feasibility study is often conducted by an independent consulting company to minimize biases. The feasibility studies helps the company or organization identify if the project should move forward or not.
The market demand study within the full feasibility study would include secondary and primary research. Secondary research would include existing data, such as hotel metrics (e.g., supply, demand or rooms sold over a given period of time, occupancy, average daily rate (ADR), and revenue per available room (REVPAR) if the project is a hotel. Primary market analysis requires collection of data. This can include surveys (e.g., visitors of the destination to determine if the potential project is of interest), focus groups to get in-depth insight as to the interest of visitors. Surveys can also be conducted to potentially identify potential demand for the project.
If a project is not intended to be profitable, such as one being developed by the government or non-profit organization, a cost-benefit analysis can be conducted. Such a study essentially identifies the potential benefits to society are worth the cost of the investment.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area life cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer, XXIV (1), 5-12.
Draper, J., Woosnam, K. M., & Norman, W. C. (2011). Tourism use history: Exploring a new framework for understanding residents’ attitudes toward tourism. Journal of Travel Research, 50 (1), 64-77.
Edgell, D. L., Allen, M. D., Smith, G., & Swanson, L. E. (2008). Tourism policy and planning: Yesterday, today and tomorrow . Elsevier Inc.
Gunn, C. A., & Var, T. (2002). Tourism planning: Basics, concepts, cases (4th ed.). Routledge.
Hall, C. M., & Jenkins, J. M. (1995). Tourism and public policy . Routledge.
International Trade Administration. (n.d.). Tourism Policy Council (TPC). https://www.trade.gov/tourism-policy-council
Mason, P. (2003). Tourism impacts, planning and management . Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Morrison, A. M., Lehto, X. Y., & Day, J. G. (2018). The tourism system (8th ed.). Kendall Hunt.
Rose, E. A. (1984). Philosophy and purpose in planning. In M. J. Bruton (Ed.), The spirit and purpose of planning (2nd ed., pp. 31-65). Hutchinson.
United Nations. (n.d.). Department of Economic and Social Affairs: Sustainable Development. https://sdgs.un.org/goals
U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs. (n.d.) Visa Waiver Program. https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas/tourism-visit/visa-waiver-program.html
GHL 2365 - Tourism Copyright © 2024 by Jason Draper is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
National tourism planning. The national level of tourism planning is concerned with: tourism policy; infrastructure facilities and a physical structure plan which includes important tourist attractions, selected tourism development regions, international entry points, facilities, and services. It is also concerned with: the amount, kinds, and ...
This publication lays the foundation for tourism development of a country and its regions. It establishes the principal guidelines for preparing tourism development plans at the national and regional levels with emphasis on the integrated approach, balancing economic, environmental, and socio-cultural factors achieving sustainable tourism.
Handbook on Tourism Planning is a comprehensive and timely compilation. that documents progress in research and practice during the half century since the. publication of Gunn's pioneering book ...
tion of the tourism planning process needs to be able to accommodate the different scales or levels at which tourism planning occurs and the con-text of such planning in terms of the linkages and relationships between the various levels. Or, as Mill and Morrison (1985: xix) observed with respect to the concept of a tourism system: 'The
Areas which are detailed in the master plan are: Performing an in-depth marketing study Designation and extent of land uses for tourism Planning infrastructure facilities including roads, airports, walkways, drainage, sewage, water, power and other utilities. Selection of sites for tourist facilities including their sizes and boundaries.
PDF | On Jan 1, 2009, B. King and others published Planning for tourism at local and regional levels: Principles, practices and possibilities | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ...
This publication lays the foundation for tourism development of a country and its regions. It establishes the principal guidelines for preparing tourism development plans at the national and regional levels with emphasis on the integrated approach, balancing economic, environmental, and socio-cultural factors achieving sustainable tourism.
Positive guidelines for better planning are in demand by developers and designers who need new understandings of the breadth of tourism's complexity for their own success. Long considered the seminal work on tourism development, Tourism Planning provides a comprehensive, integrated overview of all aspects of tourism and the planning functions ...
View PDF PDF View EPUB EPUB; ABSTRACT. The purpose of this paper is to further advance the discussion regarding Local Authorities and approaches to facilitate sustainable planning for tourism. Building on previous research into tourism planning at local level in Ireland, this study employed qualitative semi-structured interviews with every ...
It examines tourism planning at all levels fr micro and includes approaches that are applicable to both the more and less countries with case studies from many parts of the world. Divided into five p covers the general background of and approaches to tourism planning, while remainder of the book examines specific aspects of this subject.
Only 24% of the local tourism destinations that is 125 in Queensland had a specific tourism planning document. The majority, 65% did not have a tourism planning document for their area, and the left over minority destinations, 11% were in the process of developing a tourism plan or strategy at the time of sampling.
6.2 LEVELS AND TYPES OF TOURISM PLANNING. Ideally, tourism should be planned as one element in a comprehensive manner. More commonly, however, tourism planning is done independently without recognising it as an integrated sector. Tourism plans are, thus, prepared at various levels. Each of these levels focusses on a different degree of specificity.
at destination level should address issues around embodying not only management approaches, but also planning considerations and local economic concerns. McLoughlin et al. (2018, p. 87), in fact, suggests that evidence-informed planning for tourism is the way forward to help ensure the future sustainability of tourism.
theory built on basic principles, models, and planning techniques was. weak up to the 1990's. At the turn of the century, Costa (2001) sug-. gested that that the growth of tourism planning had not ...
Tourism Planning: Importance, Benefits, Types & Levels. Planning is to prepare a Road Map to achieve goals. In 1987 D.Getz defined tourism planning as "a process, based on research and evaluation, which seeks to optimize the potential contribution of tourism to human welfare and environmental quality". Faludi, in 1973, defined tourism planning ...
After the literature review on development and planning the next two chapters will provide a basis for understanding the development and planning of tourism in Crete, in order the last Chapter to propose the preferred routes for the development of the island. •. the analysis of secondary sources found. in government.
41 6.2.3 Regional Level The regional level of tourism planning is for one region of a country. This can be a state, a province or a tourist circuit (like a group of islands, special areas like the Buddhist circuit, etc). However, regional plans are formulated within the broader framework of the national tourism policy and plan, provided it exists in a country.
A tourism policy is essentially a framework including guidelines, goals, and initiatives to work toward achieving the goals. Where as an act by government, such as the Travel Promotion Act of 2009 establishing Brand USA, is a law or statute. A policy for international travel is having a current passport and for many countries a Visa.
It is important to not single out tourism alone for development. Rather, it should be planned in conjunction with a region's broader development goals; tourism should be one element of broader ...
development, and the incorporation of tourism into urban planning. In particular, this research will contribute to literature by linking urban tourism and urban planning using concepts from sustainability and stakeholder theory, as well as, the specific case study. This study draws upon a case study of Refshaleøen, a repurposed industrial shipyard
Proper planning of the physical, legal, promotion, finance, economic, market, management, social and environmental aspects will help deliver the benefits of tourism development. Good planning ensures desired results and works in a systematic manner to achieve success. This Unit deals with the growth and development of tourism planning.
tourism planning that is more similar and simpler -. (1) defining the system, goals and objectives, (2) gathering of relevant data, (3) analyzing and interpreting the data, (4) preliminary ...
15.2.2 Process of Tourism Planning. Tourism Planning Process involves the following steps: Study recognition and preparation:The first stage in planning process is associated with the recognition of the need for the strategy in order to obtain and/or increase competitive advantage to contribute to long-term growth.