

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA Receives 13 Nominations for the 28th Annual Webby Awards

Through Astronaut Eyes, Virtual Reality Propels Gateway Forward

How NASA Spotted El Niño Changing the Saltiness of Coastal Waters
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Altitude Chamber Gets Upgrade for Artemis II, Spacecraft Testing Begins

Media Get Close-Up of NASA’s Jupiter-Bound Europa Clipper
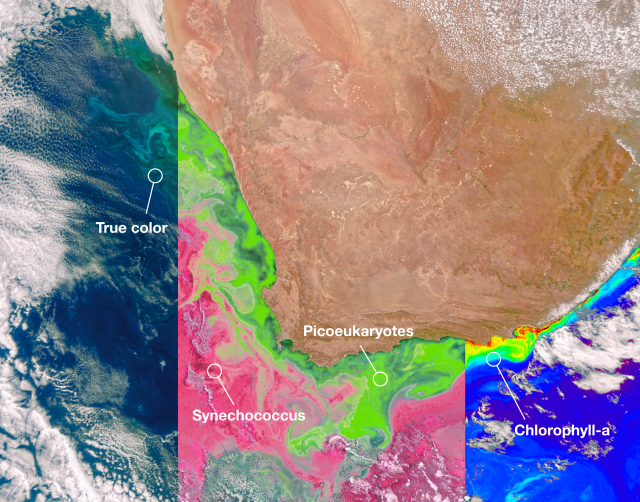
NASA’s PACE Data on Ocean, Atmosphere, Climate Now Available

NASA Shares Medical Expertise with New Space Station Partners

From NASA’s First Astronaut Class to Artemis II: The Importance of Military Jet Pilot Experience

Commercial Space Frequently Asked Questions

NASA’s Lola Fatoyinbo Receives Royal Geographical Society Prize

More Than 36,000 Volunteers Helped Do NASA Eclipse Science

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge

NASA’s TESS Temporarily Pauses Science Observations

NASA’s New Hubble E-Book Spotlights Universe’s Best-Kept Dark Secrets

Accelerating Informatics for Earth Science

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles
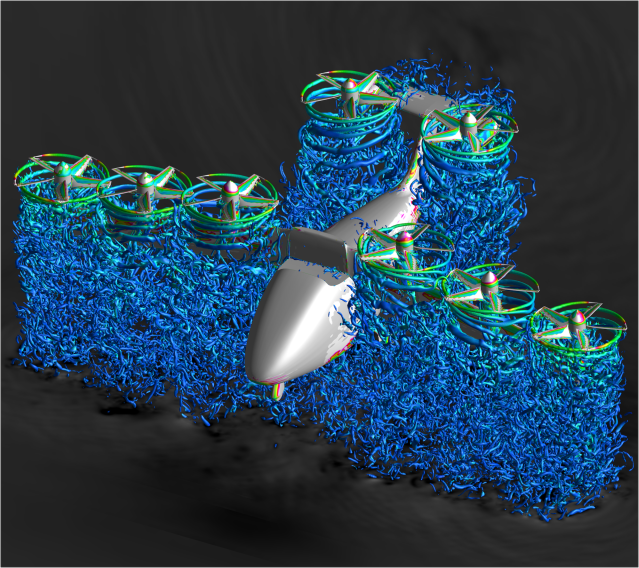
NASA Noise Prediction Tool Supports Users in Air Taxi Industry

ARMD Solicitations
NASA’s SERT II: ‘A Genuine Space Success Story’

Tech Today: Synthetic DNA Diagnoses COVID, Cancer

NASA Partnerships Bring 2024 Total Solar Eclipse to Everyone

Launch Week Event Details

La presentación del X-59 de la NASA personifica la tradición aeronáutica
Voyager, nasa’s longest-lived mission, logs 45 years in space, jet propulsion laboratory, beyond expectations, the long journey, more about the mission.

Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA’s longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space.
NASA’s twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 times slower than a 5G internet connection.
Yet the Voyagers remain on the cutting edge of space exploration. Managed and operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, they are the only probes to ever explore interstellar space – the galactic ocean that our Sun and its planets travel through.
The Sun and the planets reside in the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun’s magnetic field and the outward flow of solar wind (charged particles from the Sun). Researchers – some of them younger than the two distant spacecraft – are combining Voyager’s observations with data from newer missions to get a more complete picture of our Sun and how the heliosphere interacts with interstellar space.
“The heliophysics mission fleet provides invaluable insights into our Sun, from understanding the corona or the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere, to examining the Sun’s impacts throughout the solar system, including here on Earth, in our atmosphere, and on into interstellar space,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the Sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can.”
NASA’s Solar System Interactive lets users see where the Voyagers are right now relative to the planets, the Sun, and other spacecraft. Eyes on the Solar System . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Voyagers are also ambassadors, each carrying a golden record containing images of life on Earth, diagrams of basic scientific principles, and audio that includes sounds from nature, greetings in multiple languages, and music. The gold-coated records serve as a cosmic “message in a bottle” for anyone who might encounter the space probes. At the rate gold decays in space and is eroded by cosmic radiation, the records will last more than a billion years.
Voyager 2 launched on Aug. 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on Sept. 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn, with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system’s two largest planets and their moons. Voyager 2 also became the first and only spacecraft to fly close to Uranus (in 1986) and Neptune (in 1989), offering humanity remarkable views of – and insights into – these distant worlds.
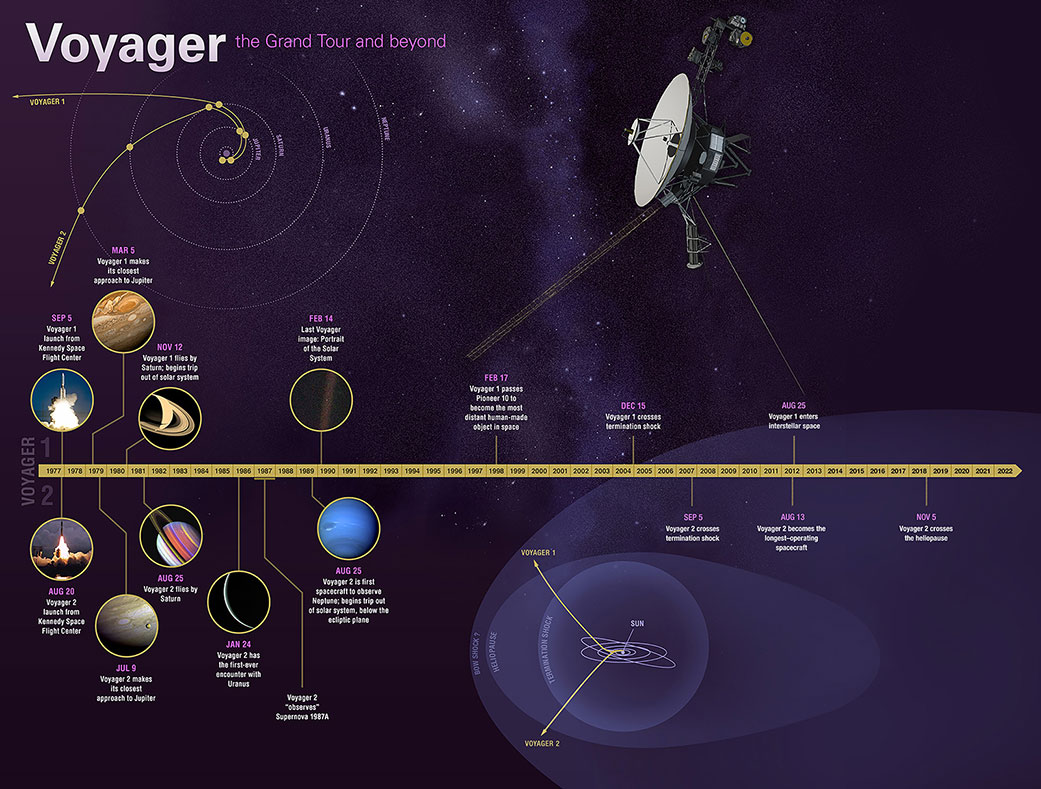
While Voyager 2 was conducting these flybys, Voyager 1 headed toward the boundary of the heliosphere. Upon exiting it in 2012 , Voyager 1 discovered that the heliosphere blocks 70% of cosmic rays, or energetic particles created by exploding stars. Voyager 2, after completing its planetary explorations, continued to the heliosphere boundary, exiting in 2018 . The twin spacecraft’s combined data from this region has challenged previous theories about the exact shape of the heliosphere.
“Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory,” said Linda Spilker, Voyager’s deputy project scientist at JPL. “This is the first time we’ve been able to directly study how a star, our Sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere, helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars, upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions.”
Over the years, the Voyager team has grown accustomed to surmounting challenges that come with operating such mature spacecraft, sometimes calling upon retired colleagues for their expertise or digging through documents written decades ago.
Each Voyager is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator containing plutonium, which gives off heat that is converted to electricity. As the plutonium decays, the heat output decreases and the Voyagers lose electricity. To compensate , the team turned off all nonessential systems and some once considered essential, including heaters that protect the still-operating instruments from the frigid temperatures of space. All five of the instruments that have had their heaters turned off since 2019 are still working, despite being well below the lowest temperatures they were ever tested at.
Recently, Voyager 1 began experiencing an issue that caused status information about one of its onboard systems to become garbled. Despite this, the system and spacecraft otherwise continue to operate normally, suggesting the problem is with the production of the status data, not the system itself. The probe is still sending back science observations while the engineering team tries to fix the problem or find a way to work around it.
“The Voyagers have continued to make amazing discoveries, inspiring a new generation of scientists and engineers,” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager at JPL. “We don’t know how long the mission will continue, but we can be sure that the spacecraft will provide even more scientific surprises as they travel farther away from the Earth.”
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
Some hope —
Finally, engineers have a clue that could help them save voyager 1, a new signal from humanity's most distant spacecraft could be the key to restoring it..
Stephen Clark - Mar 15, 2024 11:23 pm UTC

It's been four months since NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft sent an intelligible signal back to Earth, and the problem has puzzled engineers tasked with supervising the probe exploring interstellar space.
But there's a renewed optimism among the Voyager ground team based at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. On March 1, engineers sent a command up to Voyager 1—more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away from Earth—to "gently prompt" one of the spacecraft's computers to try different sequences in its software package. This was the latest step in NASA's long-distance troubleshooting to try to isolate the cause of the problem preventing Voyager 1 from transmitting coherent telemetry data.
Cracking the case
Officials suspect a piece of corrupted memory inside the Flight Data Subsystem (FDS), one of three main computers on the spacecraft, is the most likely culprit for the interruption in normal communication. Because Voyager 1 is so far away, it takes about 45 hours for engineers on the ground to know how the spacecraft reacted to their commands—the one-way light travel time is about 22.5 hours.
The FDS collects science and engineering data from the spacecraft's sensors, then combines the information into a single data package, which goes through a separate component called the Telemetry Modulation Unit to beam it back to Earth through Voyager's high-gain antenna.
Engineers are almost entirely certain the problem is in the FDS computer. The communications systems onboard Voyager 1 appear to be functioning normally, and the spacecraft is sending a steady radio tone back to Earth, but there's no usable data contained in the signal. This means engineers know Voyager 1 is alive, but they have no insight into what part of the FDS memory is causing the problem.
But Voyager 1 responded to the March 1 troubleshooting command with something different from what engineers have seen since this issue first appeared on November 14.
"The new signal was still not in the format used by Voyager 1 when the FDS is working properly, so the team wasn’t initially sure what to make of it," NASA said in an update Wednesday. "But an engineer with the agency’s Deep Space Network, which operates the radio antennas that communicate with both Voyagers and other spacecraft traveling to the Moon and beyond, was able to decode the new signal and found that it contains a readout of the entire FDS memory."
Now, engineers are meticulously comparing each bit of code from the FDS memory readout to the memory readout Voyager 1 sent back to Earth before the issue arose in November. This, they hope, will allow them to find the root of the problem. But it will probably take weeks or months for the Voyager team to take the next step. They don't want to cause more harm.
"Using that information to devise a potential solution and attempt to put it into action will take time," NASA said.
This is perhaps the most serious ailment the spacecraft has encountered since its launch in 1977. Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn before getting a kick from Saturn's gravity to speed into the outer solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 entered interstellar space when it crossed the heliopause, where the solar wind, the stream of particles emanating from the Sun, push against a so-called galactic wind, the particles that populate the void between the stars.
Engineers have kept Voyager 1 and its twin, Voyager 2, alive for more than 46 years , overcoming technical problems that have doomed other space missions. Both probes face waning power from their nuclear batteries, and there are concerns about their thrusters aging and fuel lines becoming clogged, among other things. But each time there is a problem, ground teams have come up with a trick to keep the Voyagers going, often referencing binders of fraying blueprints and engineering documents from the spacecraft's design and construction nearly 50 years ago.
Suzanne Dodd, NASA's project manager for Voyager 1 and its twin, Voyager 2, recently told Ars that engineers would need to pull off their "biggest miracle" to restore Voyager 1 to normal operations. Now, Voyager 1's voice from the sky has provided engineers with a clue that could help them realize this miracle.
reader comments
Channel ars technica.

- April 11, 2024 | Webb Telescope Uncovers Neutron Star Hidden in Supernova Debris
- April 11, 2024 | How Our Brains Work: Connecting Lab-Grown Brain Cells Yields New Insights
- April 11, 2024 | Double Trouble: Decoding the Pain-Depression Feedback Loop
- April 11, 2024 | Elemental Surprise: Physicists Discover a New Quantum State
- April 11, 2024 | A Real Life Eye of Sauron? New Technology To Detect Airborne Threats Instantly
NASA’s Longest-Lived Mission: Voyager Probes Log 45 Years in Space
By Jet Propulsion Laboratory August 19, 2022
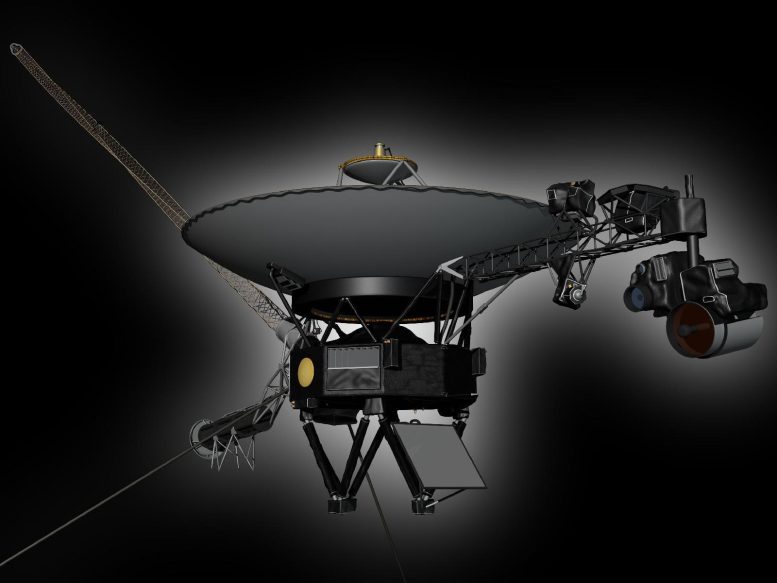

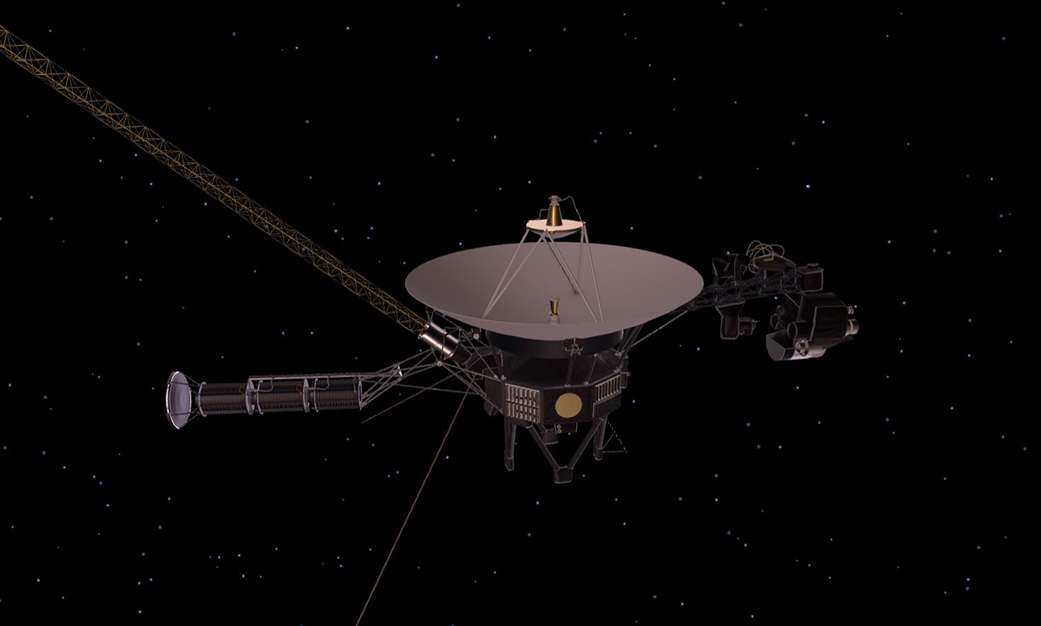
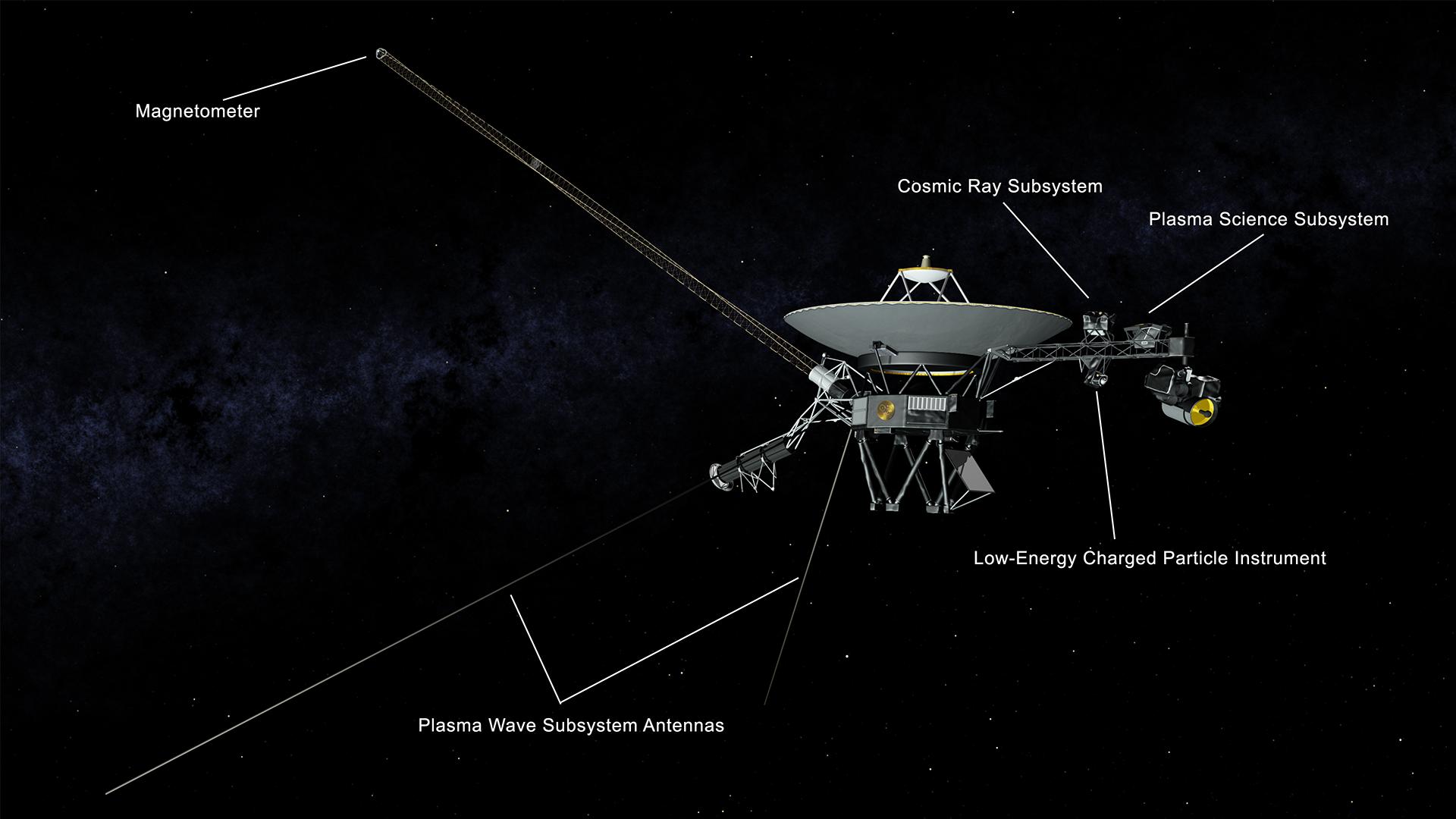
This artist’s rendering shows NASA’s Voyager spacecraft. On the boom to the right, the Cosmic Ray Science instrument, Low Energy Charged Particle detector, the Infrared Spectrometer and Radiometer, Ultraviolet Spectrometer, Photopolarimeter and Wide and Narrow Angle Cameras are visible. The bright gray square is an optical calibration plate for the instruments. The Golden Record, containing images and sounds from Earth, is the yellow circle on the main spacecraft body. The dish is the spacecraft’s high-gain antenna for communications with Earth. The magnetometer boom stretches out to the upper left. The radio isotope thermoelectric generators, Voyager’s power source, are visible to the lower left. The two long thin rods extending out to the left are antennas used by the Plasma Wave instrument. The Planetary Radio instrument also used these antennas when it was turned on. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA ’s longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, NASA’s twin Voyager spacecraft inspired the world with pioneering visits to Jupiter , Saturn , Uranus , and Neptune . Their journey continues 45 years later as both probes explore interstellar space, the region outside the protective heliosphere created by our Sun. Researchers – some younger than the spacecraft – are now using Voyager data to solve mysteries of our solar system and beyond.
NASA’s twin Voyager probes have become, in many ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they transmit data about 38,000 times slower than a 5G internet connection, and they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones.
Despite this, the Voyagers remain on the cutting edge of space exploration. Managed and operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory ( JPL ) in Southern California, they are the only probes to ever explore interstellar space – the galactic ocean that our Sun and its planets travel through.
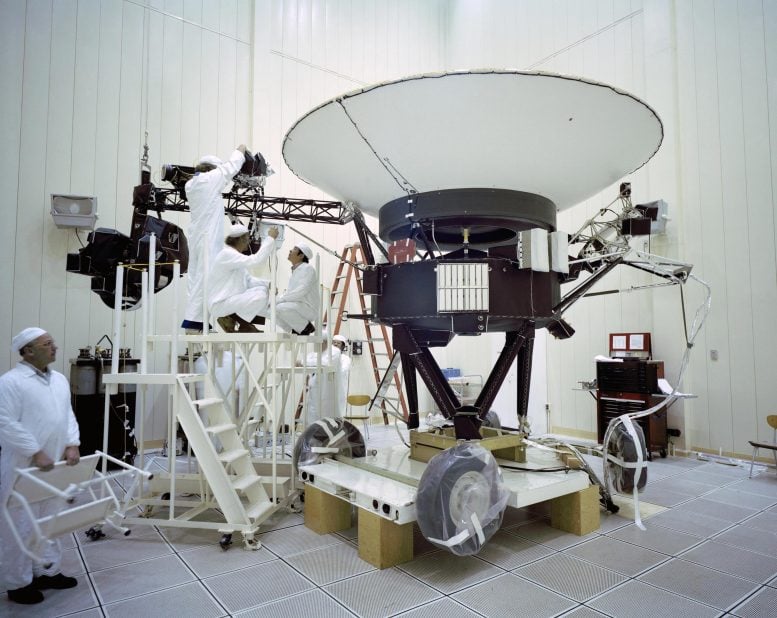

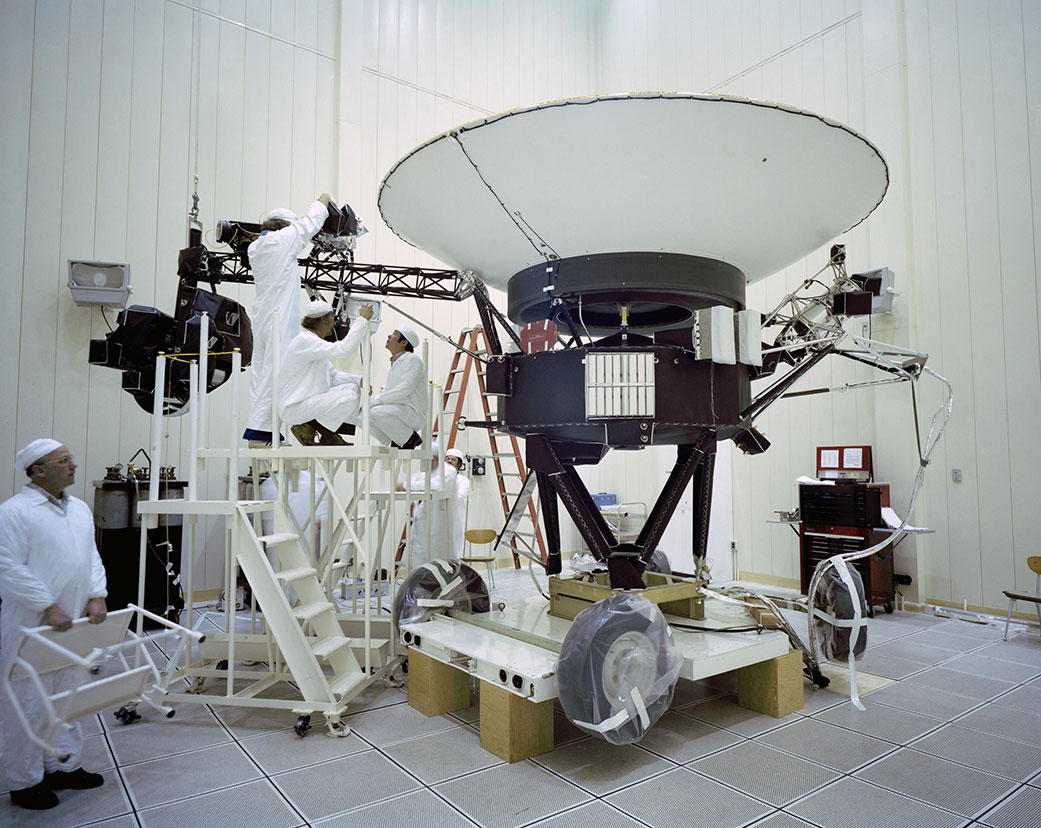
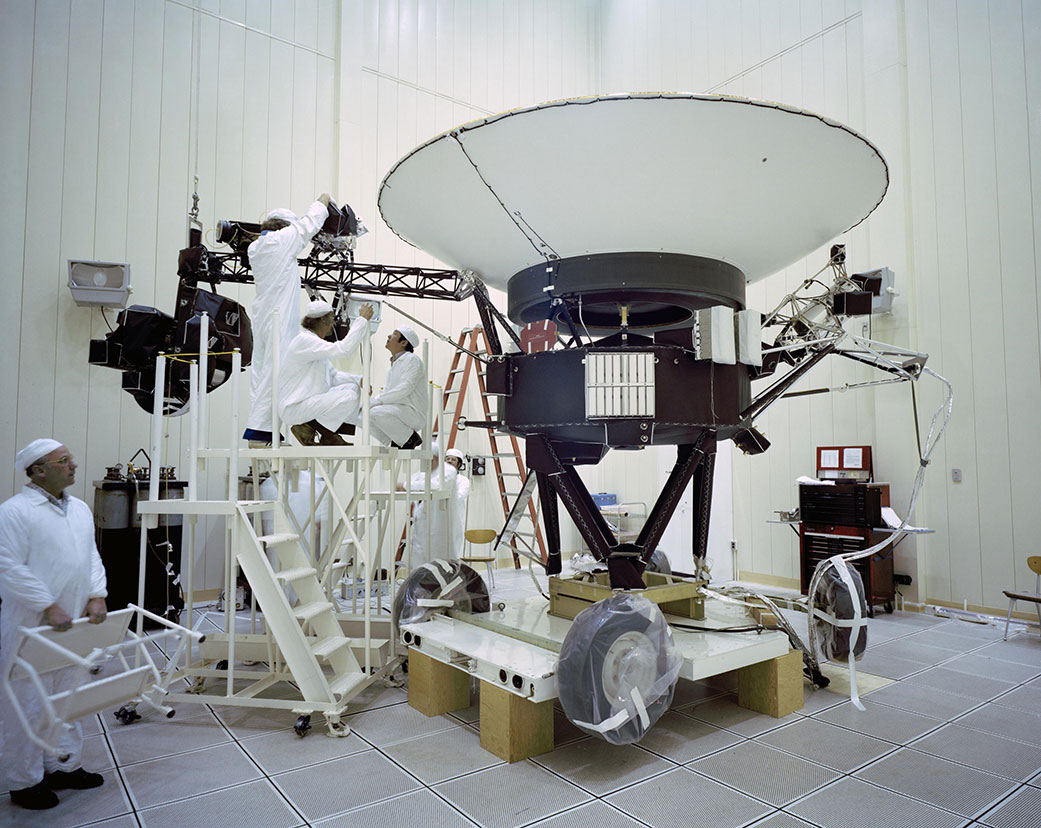
This archival image taken at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on March 23, 1977, shows engineers preparing the Voyager 2 spacecraft ahead of its launch later that year. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Sun and the planets reside in the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun’s magnetic field and the outward flow of solar wind (charged particles from the Sun). Scientists – some of them younger than the two distant spacecraft – are combining Voyager’s observations with data from newer missions to get a more complete picture of our Sun and how the heliosphere interacts with interstellar space.
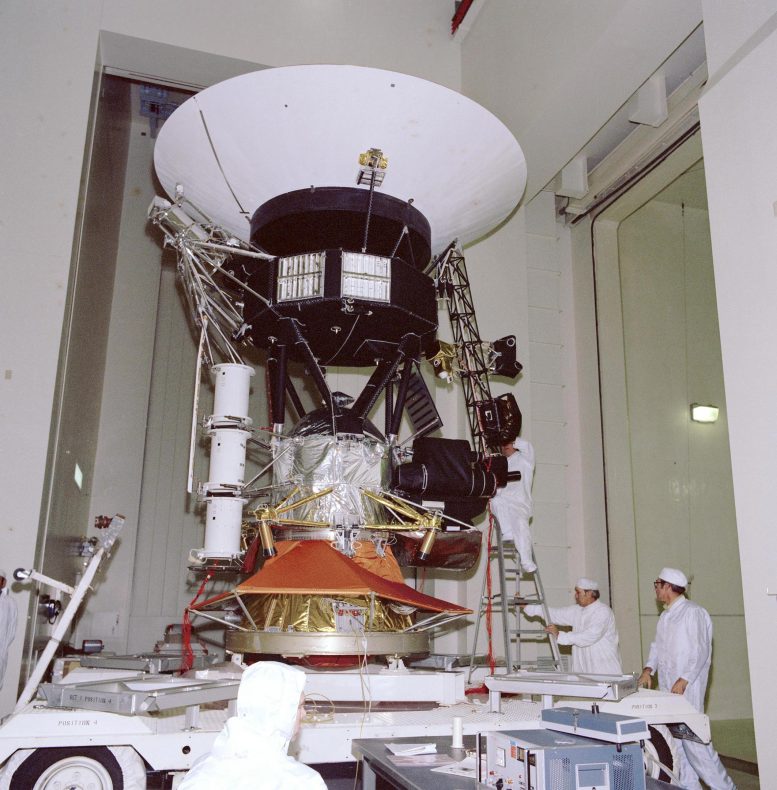

This archival photo shows engineers working on vibration acoustics and pyro shock testing of NASA’s Voyager on November 18, 1976. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
“The heliophysics mission fleet provides invaluable insights into our Sun, from understanding the corona or the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere, to examining the Sun’s impacts throughout the solar system, including here on Earth, in our atmosphere, and on into interstellar space,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the Sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can.”
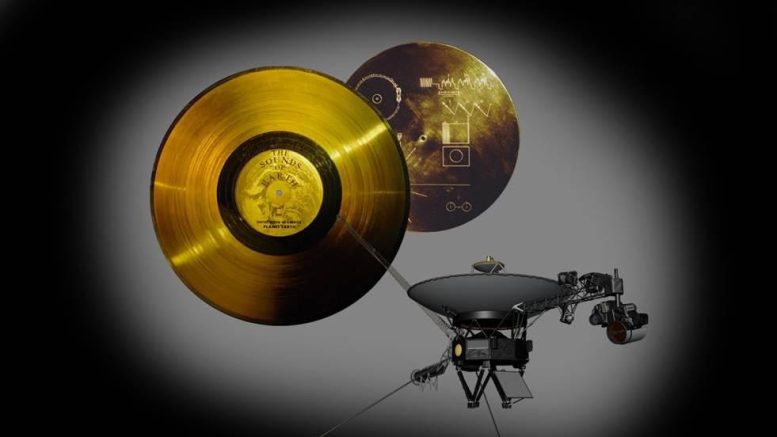

This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA’s Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Voyagers are also ambassadors for humanity, each carrying a golden record containing images of life on Earth, diagrams of basic scientific principles, and audio that includes sounds from nature, greetings in multiple languages, and music. The gold-coated records serve as a cosmic “message in a bottle” for anyone who might encounter the space probes. At the rate gold decays in space and is eroded by cosmic radiation, the records will last more than a billion years.
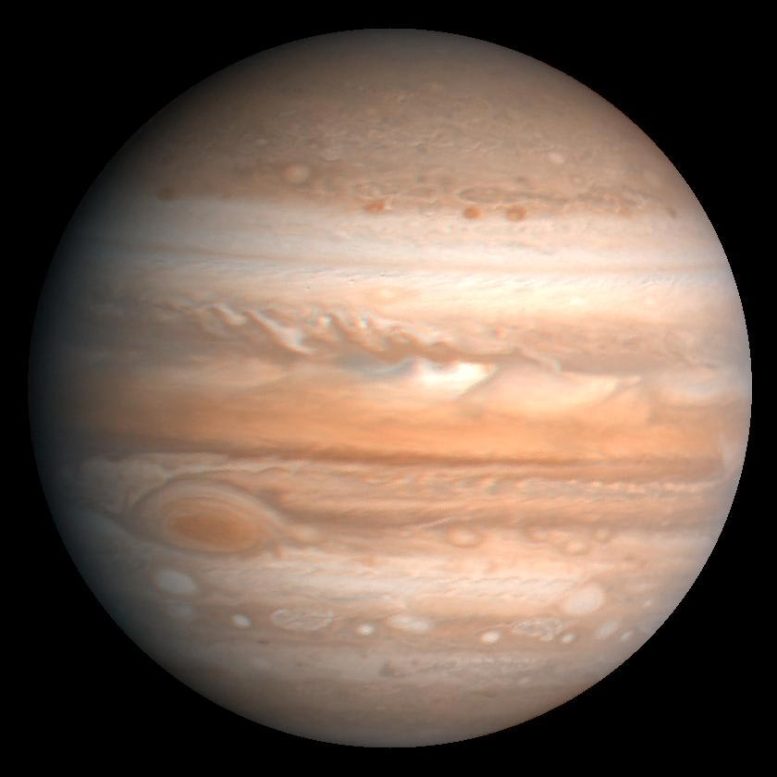

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. Credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
Beyond Expectations
Voyager 2 launched on August 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on September 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn , with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system’s two largest planets and their moons. Voyager 2 also became the first and only spacecraft to fly close to Uranus (in 1986) and Neptune (in 1989), offering humanity remarkable views of – and insights into – these distant worlds.
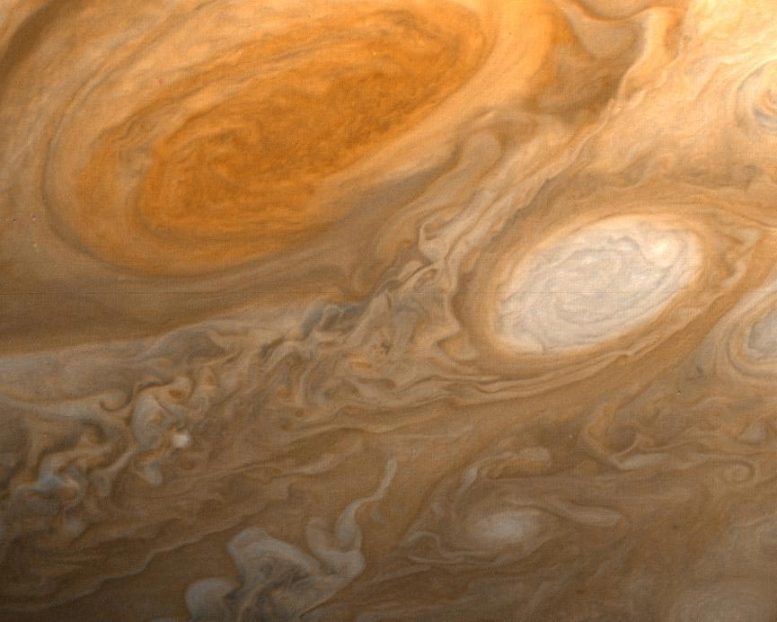

This photo of Jupiter was taken by NASA’s Voyager 1 on the evening of March 1, 1979, from a distance of 2.7 million miles (4.3 million kilometers). The photo shows Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (top) and one of the white ovals. Credit: NASA/JPL
While Voyager 2 was conducting these flybys, Voyager 1 headed toward the boundary of the heliosphere. Upon exiting it in 2012 , Voyager 1 discovered that the heliosphere blocks 70% of cosmic rays, or energetic particles created by exploding stars. Voyager 2, after completing its planetary explorations, continued to the heliosphere boundary, exiting in 2018 . The twin spacecraft’s combined data from this region has challenged previous theories about the exact shape of the heliosphere.
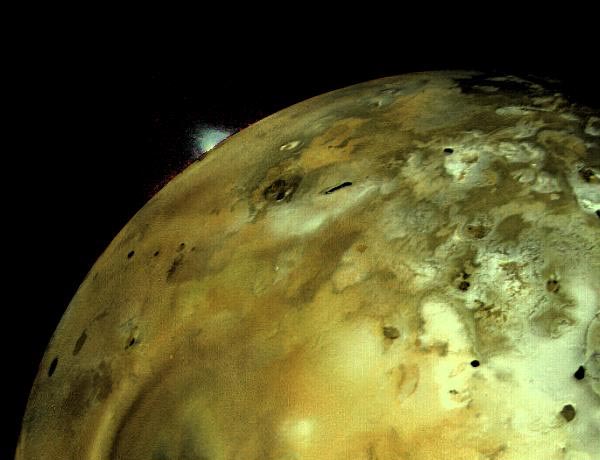

NASA’s Voyager 1 acquired this image of a volcanic explosion on Io on March 4, 1979, about 11 hours before the spacecraft’s closest approach to the moon of Jupiter. Credit: NASA/JPL
“Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory,” said Linda Spilker, Voyager’s deputy project scientist at JPL. “This is the first time we’ve been able to directly study how a star, our Sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere, helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars, upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions.”
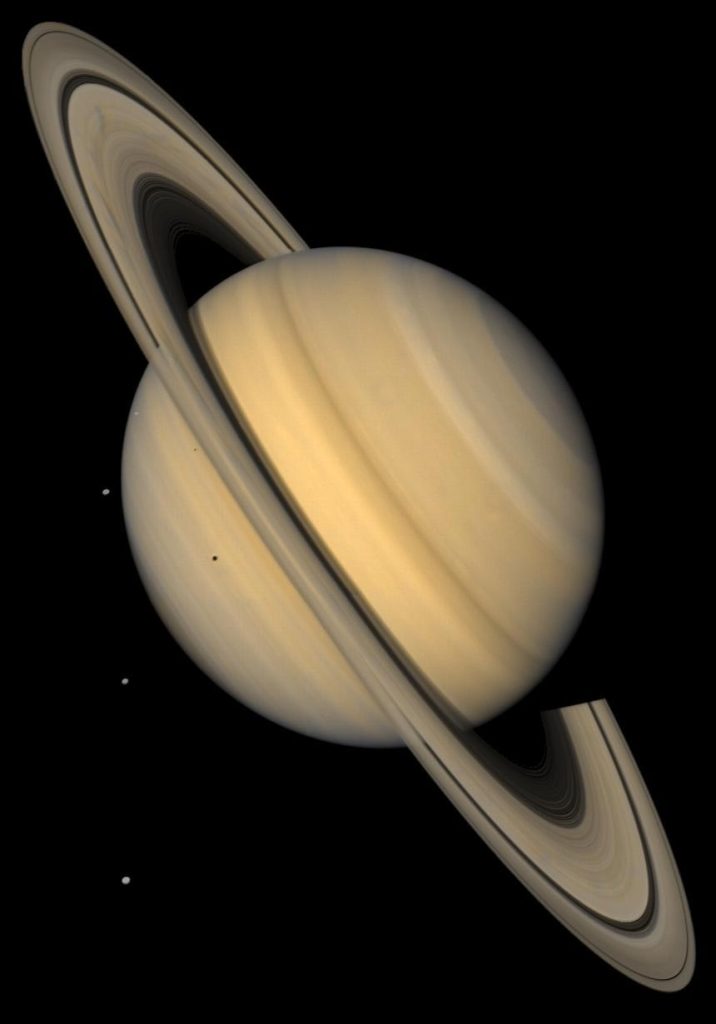
This approximate natural-color image from NASA’s Voyager 2 shows Saturn, its rings, and four of its icy satellites. Three satellites Tethys, Dione, and Rhea are visible against the darkness of space. Credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
The Long Journey
Over the years, the Voyager team has grown accustomed to surmounting challenges that come with operating such mature spacecraft, sometimes calling upon retired colleagues for their expertise or digging through documents written decades ago.
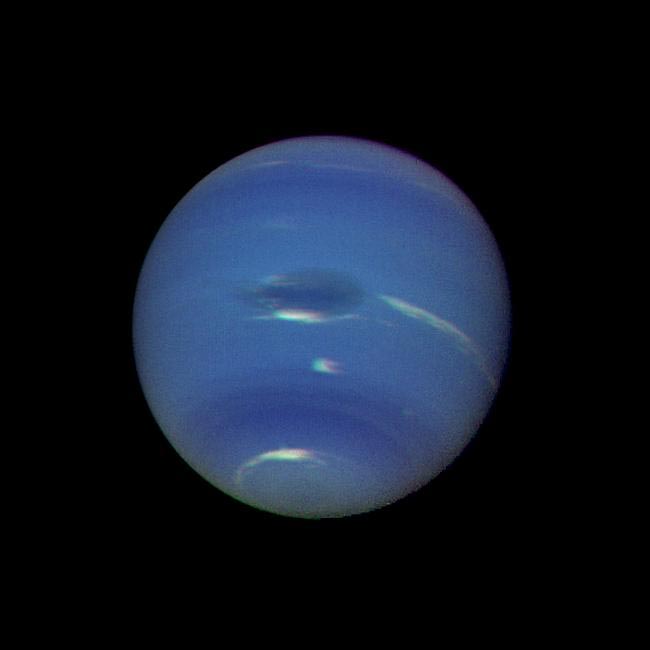

Neptune’s green-blue atmosphere was shown in greater detail than ever before in this image from NASA’s Voyager 2 as the spacecraft rapidly approached its encounter with the giant planet in August 1989. Credit: NASA/JPL
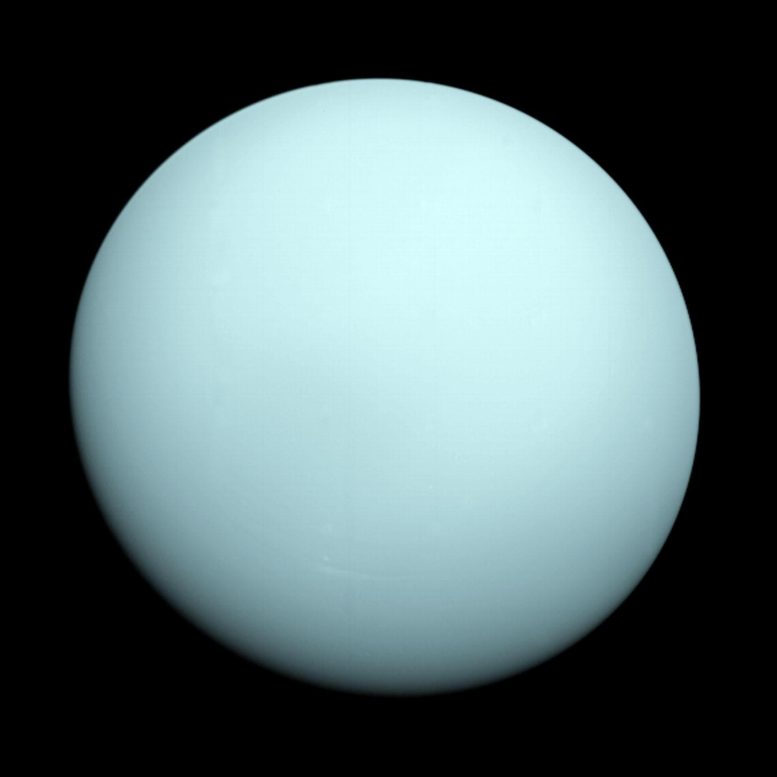

This is an image of the planet Uranus taken by the spacecraft Voyager 2 in 1986. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
This image, taken by NASA’s Voyager 2 early in the morning of August 23, 1989, is a false color image of Triton, Neptune’s largest satellite; mottling in the bright southern hemisphere is present. Credit: NASA/JPL
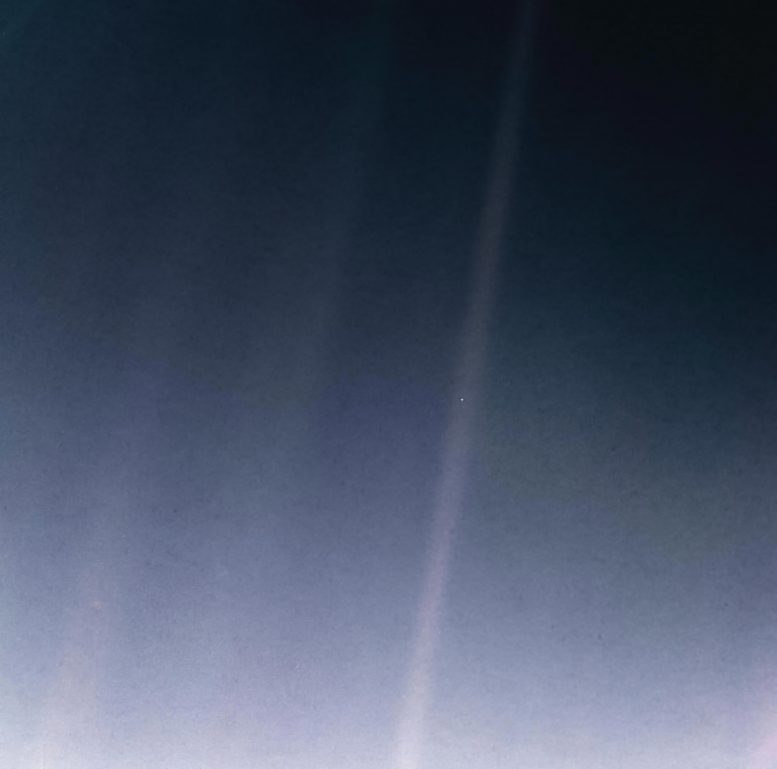

This updated version of the iconic “Pale Blue Dot” image taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft uses modern image-processing software and techniques to revisit the well-known Voyager view while attempting to respect the original data and intent of those who planned the images. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Each Voyager is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator containing plutonium, which gives off heat that is converted to electricity. As the plutonium decays, the heat output decreases and the Voyagers lose electricity. To compensate , the team turned off all nonessential systems and some once considered essential, including heaters that protect the still-operating instruments from the frigid temperatures of space. All five of the instruments that have had their heaters turned off since 2019 are still working, despite being well below the lowest temperatures they were ever tested at.
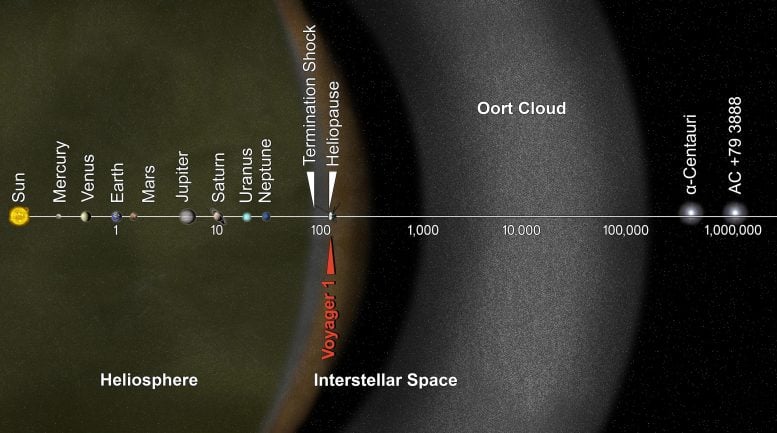
This illustrated graphic was made to mark Voyager 1’s entry into interstellar space in 2012. It puts solar system distances in perspective, with the scale bar in astronomical units and each set distance beyond 1 AU (the average distance between the Sun and Earth) representing 10 times the previous distance. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Recently, Voyager 1 began experiencing an issue that caused status information about one of its onboard systems to become garbled. Despite this, the system and spacecraft otherwise continue to operate normally, suggesting the problem is with the production of the status data, not the system itself. The probe is still sending back science observations while the engineering team tries to fix the problem or find a way to work around it.
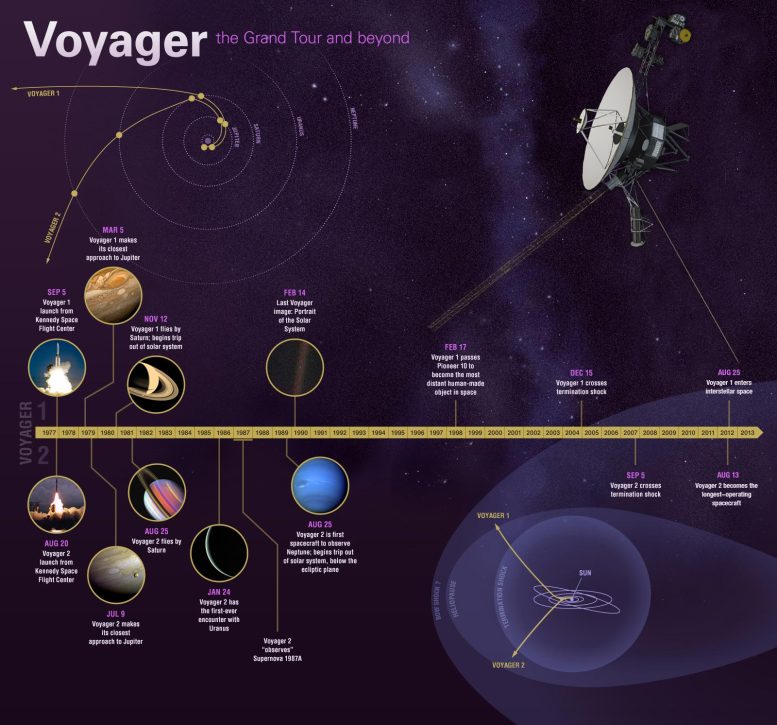
This graphic highlights some of the Voyager mission’s key accomplishments. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
“The Voyagers have continued to make amazing discoveries, inspiring a new generation of scientists and engineers,” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager at JPL. “We don’t know how long the mission will continue, but we can be sure that the spacecraft will provide even more scientific surprises as they travel farther away from the Earth.”

This graphic provides some of the mission’s key statistics from 2018, when NASA’s Voyager 2 probe exited the heliosphere. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More About the Mission
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
More on SciTechDaily

Voyager 2 Illuminates Boundary of Interstellar Space 11 Billion Miles From Earth

Voyager 2 Probe Enters Interstellar Space, Over 18 Billion Kilometers from Earth
Mysteries abound: nasa studying the edge of the sun’s magnetic bubble.

It’s Official – Voyager 1 Has Entered Interstellar Space

Hear the Eerie Sounds of Interstellar Space Captured by NASA’s Voyager
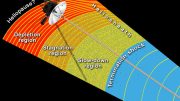
NASA’s Voyager 1 Explores the Outer Limits of Our Heliosphere
Nasa’s interstellar boundary explorer charts 11 years of change to heliosphere.


IBEX Reveals How Solar Wind Changes Our Heliosphere
9 comments on "nasa’s longest-lived mission: voyager probes log 45 years in space".
How is information transmitted from Voyager back to Earth and vice versa? WiFi? I want WiFi that strong for my house. Serious question.
“The uplink communications are executed via S-band microwave communications. The downlink communications are carried out by an X-band microwave transmitter on board the spacecraft, with an S-band transmitter as a back-up. All long-range communications to and from the two Voyagers have been carried out using their 3.7-meter (12 ft) high-gain antennas. The high-gain antenna has a beamwidth of 0.5° for X-band, and 2.3° for S-band.[38]: 17 (The low-gain antenna has a 7 dB gain and 60° beamwidth.)[38]: 17
Because of the inverse-square law in radio communications, the digital data rates used in the downlinks from the Voyagers have been continually decreasing the farther that they get from the Earth. For example, the data rate used from Jupiter was about 115,000 bits per second. That was halved at the distance of Saturn, and it has gone down continually since then.[38] Some measures were taken on the ground along the way to reduce the effects of the inverse-square law. In between 1982 and 1985, the diameters of the three main parabolic dish antennas of the Deep Space Network were increased from 64 to 70 m (210 to 230 ft)[38]: 34 dramatically increasing their areas for gathering weak microwave signals.
Whilst the craft were between Saturn and Uranus the onboard software was upgraded to do a degree of image compression and to use a more efficient Reed-Solomon error-correcting encoding.[38]: 33
Then between 1986 and 1989, new techniques were brought into play to combine the signals from multiple antennas on the ground into one, more powerful signal, in a kind of an antenna array.[38]: 34 This was done at Goldstone, California, Canberra, and Madrid using the additional dish antennas available there. Also, in Australia, the Parkes Radio Telescope was brought into the array in time for the fly-by of Neptune in 1989. In the United States, the Very Large Array in New Mexico was brought into temporary use along with the antennas of the Deep Space Network at Goldstone.[38]: 34 Using this new technology of antenna arrays helped to compensate for the immense radio distance from Neptune to the Earth.”
Amazing accomplishment for humanity. This shows what humans can do when their energy is not consumed by fighting with each other. Not only is this a model for scientific inspiration, it’s a great argument for world peace.
The Voyager probes are *not* the only interstellar vehicles. You forgot Pioneer 10.
There are five interstellar probes, all launched by the American space agency NASA: Voyager 1, Voyager 2, Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11 and New Horizons. As of 2019, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and Pioneer 10 are the only probes to have actually reached interstellar space. The other two are on interstellar trajectories.
Good catch!
The communications accomplishment exceeds even the accomplishment of placing the probes on trajectory.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Email address is optional. If provided, your email will not be published or shared.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Voyager 1 Stories

NASA’s Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters
The efforts should help extend the lifetimes of the agency’s interstellar explorers. Engineers for NASA’s Voyager mission are taking steps to help make sure both spacecraft, launched in 1977, continue to explore interstellar space for years to come. One effort…

NASA’s Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy
The plan will keep Voyager 2’s science instruments turned on a few years longer than previously anticipated, enabling yet more revelations from interstellar space.
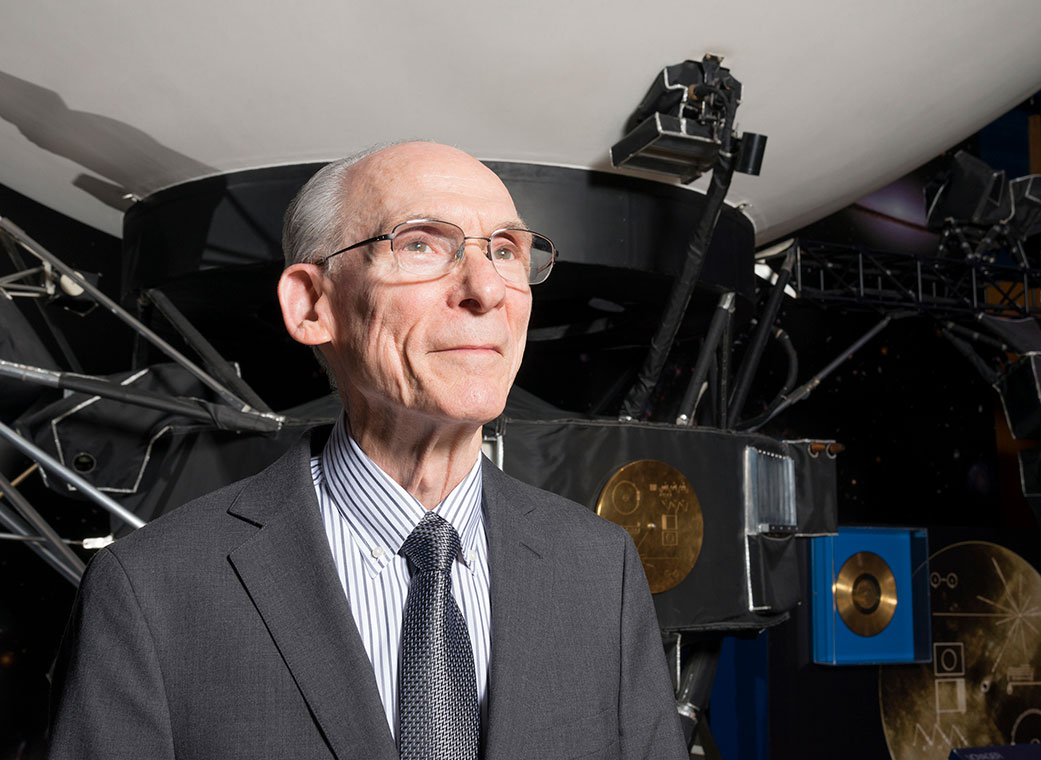

Edward Stone Retires After 50 Years as NASA Voyager’s Project Scientist
Stone’s remarkable tenure on NASA’s longest-operating mission spans decades of historic discoveries and firsts. Edward Stone has retired as the project scientist for NASA’s Voyager mission a half-century after taking on the role. Stone accepted scientific leadership of the historic…

Engineers Solve Data Glitch on NASA’s Voyager 1
A critical system aboard the probe was sending garbled data about its status. Engineers have fixed the issue but are still seeking the root cause. Engineers have repaired an issue affecting data from NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft. Earlier this year,…

Voyager, NASA’s Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA’s longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA’s twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape…

10 Things: Going Interstellar
Humanity’s great leap into interstellar space – the space between the stars – has begun. Here are 10 things we’ve learned about going interstellar.

Engineers Investigating NASA’s Voyager 1 Telemetry Data
While the spacecraft continues to return science data and otherwise operate as normal, the mission team is searching for the source of a system data issue. The engineering team with NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is trying to solve a mystery:…
Studying the Edge of the Sun’s Magnetic Bubble
Our corner of the universe, the solar system, is nestled inside the Milky Way galaxy, home to more than 100 billion stars. The solar system is encased in a bubble called the heliosphere, which separates us from the vast galaxy…

40 Years On, Remembering Voyager’s Legacy at Saturn
Voyager 2 made its closest approach to Saturn on Aug. 25, 1981. The mission revealed a planet so phenomenal scientists had to go back.
As NASA’s Voyager 1 Surveys Interstellar Space, Its Density Measurements Are Making Waves
Until recently, every spacecraft in history had made all of its measurements inside our heliosphere, the magnetic bubble inflated by our Sun. But on August 25, 2012, NASA’s Voyager 1 changed that. As it crossed the heliosphere’s boundary, it became…

Interstellar Mission
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence.

Mission Statistics
Launch Date
Sept. 5, 1977
About the mission
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
Voyagers 1 and 2 were designed to take advantage of a rare planetary alignment that occurs only once in 176 years and remain the most well traveled spacecraft in history. Both spacecraft carry a sort of time capsule called the Golden Record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
Instruments
- Imaging system
- Infrared interferometer spectrometer
- Ultraviolet spectrometer
- Triaxial fluxgate magnetometer
- Plasma spectrometer
- Low-energy charged particles detectors
- Cosmic Ray System (CRS)
- Photopolarimeter System (PPS)
- Plasma Wave System (PWS)
Mission Highlights
Sept. 1, 2013

Interactive 3D model of Voyager 1. View the full interactive experience at Eyes on the Solar System .
Advertisement
How Voyager Works
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
At this moment, two spacecraft that were launched from Earth in 1977 hurtle through space at more than 30,000 mph (48,280 km/h). They are both several billion miles away, farther from Earth than any other man-made object. On Aug. 25, 2012, one of them crossed into interstellar space, making the first spacecraft to leave the solar system
Voyager 1 and 2 carry coded messages to potential alien civilizations. They have already taught scientists a great deal about the heliosheath , the outermost layer of the solar system. But none of this is even what they were designed for.
The Voyager spacecrafts were built to fly past the outer planets ( Jupiter , Saturn , Neptune and Uranus ) and study them closely, the first time in human history they'd been observed up close. The spacecraft succeeded magnificently, advancing planetary science by vast leaps. It was only after they’d accomplished their primary mission that they continued on to become Earth’s most far-ranging explorers.
Yet it was a matter of extremely good luck and timing that the missions were possible at all -- and an equal stroke of bad luck that almost scuttled the Voyager project before it ever left the ground. These ambitious missions were the product of new advances in the science and math of orbital trajectories, but they were almost cast by the wayside in favor of the expensive space shuttle program. Virtually every unmanned space mission undertaken today relies on knowledge and experience gained by the Voyagers.
We’ll take a close look at the ungainly Voyager space probes and all the technical equipment they carry on board. We’ll trace their trajectory from the development stages to their ultimate fate light years away from Earth. There will be stops at the largest planets in our solar system along the way. And if you’re wondering what's on the golden records each Voyager carries as messages for alien life forms, we’ll give them a spin. Will any aliens ever find them?
Voyager 1 and 2: The Grand Tour
Voyager equipment, to neptune and beyond, voyager golden record.

The 1970s were a transitional period for the U.S. space effort. The Apollo program was coming to a close, and NASA was trying to figure out what form manned spaceflight would take. The Mariner missions expanded our knowledge of the inner planets by sending space probes to fly past (and in some cases orbit) Mars , Venus and Mercury . There were tentative plans to send a Mariner mission to visit some of the outer planets, but using chemical rocket propulsion, such a trip would take 15 years or more.
At the same time, important advances were being made in the science of gravity-assisted orbital trajectories . While the math and physics involved are pretty complicated, the basic idea is that a spacecraft can use the gravity of a nearby planet to give it a large boost in velocity as long as the spacecraft follows the proper orbit. The higher the mass of the planet, the stronger the gravitational force, and the bigger the boost. That meant that once a space probe reached Jupiter (the most massive planet in our solar system ), it could use Jupiter’s gravity like a slingshot and head out to explore the more distant planets.
In 1965, an engineer named Gary Flandro noticed that in the mid-1970s, the outer planets would be aligned in such a way as to make it possible for a spacecraft to visit them all using a series of gravity-assisted boosts [source: Evans ]. This particular alignment wasn't just a once-in-a-lifetime event -- it wouldn't occur again for another 176 years. It was an amazing coincidence that the technical ability to accomplish such a mission was developed a few years before the planets lined up to allow it.
Initially, the ambitious project, known as the Grand Tour, would have sent a series of probes to visit all the outer planets. In 1972, however, budget projections for the project were approaching $900 million, and NASA was planning development of the space shuttle [source: Evans ]. With the immense shuttle development costs looming, the Grand Tour was cancelled and replaced with a more modest mission profile. This would be an extension of the Mariner program, referred to as the Mariner Jupiter-Saturn mission (MJS) . Based on the Mariner platform and improved with knowledge gained from Pioneer 10’s 1973 fly-by of Jupiter, the new probes eventually took the name Voyager. Design was completed in 1977. Optimistic NASA engineers thought they might be able to use gravity-assisted trajectories to reach Uranus and Neptune if the initial mission to visit Jupiter and Saturn (and some of their moons) was completed successfully. The idea of the Grand Tour flickered back to life.
The final Voyager mission plan looked like this: Two spacecraft (Voyager 1 and Voyager 2) would be launched a few weeks apart. Voyager 1 would fly past Jupiter and several of Jupiter’s moons from a relatively close distance, scanning and taking photos. Voyager 2 would also fly past Jupiter, but at a more conservative distance. If all went well, both probes would be catapulted toward Saturn by Jupiter’s gravity. Voyager 1 would then investigate Saturn, specifically the rings, as well as the moon Titan. At that point, Voyager 1’s trajectory would take it out of the solar system’s ecliptic (the plane of the planets’ orbits), away from all other planets, and eventually out of the solar system itself.
Meanwhile, Voyager 2 would visit Saturn and several of Saturn’s moons. If it was still functioning properly when that was completed, it would be boosted by Saturn’s gravity to visit Uranus and Neptune before also leaving the ecliptic and exiting the solar system. This was considered a long shot, but amazingly, everything worked as planned.
Next, what kind of hardware did the Voyagers carry into space?
Voyager 2 launched from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on board a Titan-Centaur rocket on Aug. 20, 1977. Voyager 1 launched on Sept. 5, 1977. Why is the numbering reversed? Once en route to the outer planets, Voyager 1 passed by Voyager 2 and reached Jupiter first. NASA thought the public would be confused if Voyager 2 started reporting back first, so the numbering doesn't follow the launch order.

Both Voyager spacecraft are identical. They don't have a sleek, aerodynamic design because there's no aerodynamic friction in space to worry about. Weighing 1,592 pounds (722 kilograms), they're made up of a main bus, a high-gain antenna, three booms that held scientific instruments and the power supply, and two other antennae.
The main bus is the body of the Voyager. It's a 10-sided box 5.9 feet (1.8 meters) across, and it contains some scientific instruments, electronics and a fuel tank for the rocket thrusters. The thrusters are used to reorient the craft as it moves through space.
Mounted on top of the main bus, the high-gain antenna is 12 feet (3.7 meters) across and looks like a satellite dish. This antenna is how the Voyagers receive commands from Earth and send the data they gather back. No matter where a Voyager spacecraft flies, the high-gain antenna always points toward Earth.
One of the booms extending off of the main bus carries Voyager’s radioisotope thermoelectric power supply . Pellets of plutonium dioxide release heat through natural decay. This heat is converted into electricity using a series of thermocouples. Although the power output isn't very strong, it powers the electronics and instruments on board the Voyagers for a very long time. Power isn't expected to deplete completely until 2020. The power supply was placed on a boom to keep the radiation from interfering with the other scientific instruments.
The other two booms carry a series of instruments. These include:
- Magnetometer
- Cosmic ray detector
- Plasma detector
- Photopolarimeter
- Infrared interferometer
- Spectrometer
- Ultraviolet spectrometer
- Low energy charged particle detector
- Plasma wave detector
[source: Evans, Dethloff & Schorn ]
Perhaps the most significant instruments on board the Voyagers, as far as the public is concerned, are the cameras. Also mounted on the instrument boom, the cameras have a resolution of 800x800, with both wide-angle and narrow-field versions. The cameras returned unprecedented photos of the outer planets and gave us views of our solar system that we had never before witnessed (including the famous departure shot showing both Earth and Earth’s moon in the same frame). The boom carrying the cameras could be moved independently from the rest of the craft.
The Voyager’s computer system was very impressive as well. Knowing the craft would be on its own much of the time, with the lag between command and response from Earth growing longer the farther the craft went into space, engineers developed a self-repairing computer system . The computer has multiple modules that compare the data they receive and the output instructions they decide on. If one module differs from the others, it's assumed to be faulty and is eliminated from the system, replaced by one of the backup modules. It was tested shortly after launch, when a delay in boom deployment was misread as a malfunction. The problem was corrected successfully.
In the next section, we’ll find out what we learned from the Voyager missions.
While the Voyagers themselves did all the data gathering, there were important mission elements on the ground as well. The Voyagers’ signals became increasingly difficult to detect as they flew out into the outer solar system, so NASA improved a worldwide network of radio receiving stations to better detect them. A series of 230-foot (70-meter) radio dishes pull in the Voyager data and send signals out to it, maintaining almost continuous communication [source: Evans ].

Although the lifetime mission cost for Voyager exceeded $750 million, by 1989 the spacecrafts had returned enough scientific data to fill 6,000 editions of the Encyclopedia Britannica [source: Evans ]. The science modules on board were chosen from proposals submitted by research teams across the United States. The information about Jupiter , Saturn , Uranus and Neptune (and many of their moons) that we learned from the Voyager missions wasn't just vast in quantity, but also in influence. It shaped science textbooks in schools across the U.S., informed public perceptions of the solar system and laid the foundation for the modern space program. Much of what we know about the outer planets came from Voyager. That’s not to mention the thousands of photographs taken from vantage points humans had never experienced before. Those brilliant images of Jupiter and Saturn fired the public’s imagination and fueled enthusiasm for future space exploration.
From Voyager, we learned more about the weather on Jupiter; the rings around Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus; volcanic activity on Jupiter's moon Io; the masses and densities of Saturn’s moons; the atmospheric pressure on Titan, Saturn's largest moon; the magnetic field of Uranus; and a persistent weather system on Neptune as large as Earth , known as the Great Dark Spot . By the time Voyager 2 reached Neptune, it was 1989. More than 10 years had passed since launch, and many of the scientists working on the original mission had moved on. Voyager had passed by Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus in 1979, 1981 and 1986, respectively.
So where are they now? The two Voyagers aren't together. Voyager 1 is moving north (relative to the orientation of Earth out of the solar system), while Voyager 2 is moving south. In 2007, they both entered the heliosheath, the outermost section of the solar system. There, the solar wind meets interstellar magnetic fields and forms a boundary with a shock wave. The Voyagers traversed the shock wave and sent data back, giving astronomers their first idea of the shape and location of the heliosheath. On Sept. 21, 2013, Voyager scientists reported that Voyager 1 left the solar system on Aug. 25, 2012.
Although some instruments on the Voyagers are no longer working, they do continue to send back important information. Imagine a car that has been on the road continuously since 1977, and you'll get some idea of how amazing these spacecraft are. At their current distance, it takes radio signals traveling at the speed of light more than 14 hours to reach Earth. The craft are running low on fuel for their orienting thrusters and will have to power down some instruments in the coming years as their plutonium runs out as well. By 2020, they will be dark and silent.
Yet they will continue on their current trajectory, moving over 30,000 mph (48,280 km/h), arcing out into the Milky Way for tens of thousands of years. With no atmosphere in space, they will never corrode, and there is little for them to crash into in interstellar space. It will take them about 40,000 years before they even come within light years of another star . The Voyagers may be traveling for hundreds of thousands or even millions of years.
What if the Voyagers meet an intelligent alien civilization some day? We’ve left a message for them.

When NASA realized that the Voyagers would eventually travel beyond the edge of our solar system , they decided it might be a good idea to include some kind of message to any intelligent aliens who might some day find them. A committee headed by astronomer Carl Sagan put these messages together. They're contained on gold-plated copper discs, which are engraved much like a vinyl record album. A portion of the disc contains audio information, including a variety of music, greetings spoken in 55 different languages (including some that are very obscure or long extinct) and a selection of nature sounds. The discs also include 122 images, encoded as vibrations on the disc with instructions for decoding.
On each disc’s cover plate are several symbols that depict the method of playing back the record (a stylus and mounting platter are included as well). The image decoding instructions are revealed, describing the “image start” signal, the aspect ratio of the images, and a reproduction of the first image, so the aliens would know if they got it right. A star map clearly showing the location of Earth completes the picture.
If the aliens wonder how long the Voyager they find has been traveling, they can examine the piece of uranium-238 attached to the main bus near the record. Examining the isotope ratios (assuming they know the half-life of uranium-238), they could then deduce how long the sample had been in space.
What music will the aliens hear when they play the record? Mostly traditional music from a variety of cultures, such as Native Americans chants, Scottish bagpipes and African ritual music. It is also something of a “greatest hits” collection of classical music. The most contemporary songs are “Johnny B. Goode” by Chuck Berry and a jazz number by Louis Armstrong.

The images on the record are varied, and include maps of Earth, images of the other planets in our solar system, pictures of various animals and several images of humans. Carl Sagan wrote a book about the record, called "Murmurs of Earth." A companion CD-ROM was released decades later.
The Voyager discs are similar to a plaque that was placed aboard Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11, although the creators of the Voyager discs spent a lot of time making sure the aliens could decode it. Many Earth scientists could not decode the information on the Pioneer plaque. At the time, some voiced concerns that any hostile aliens finding the Voyager disc would have a map leading them directly to Earth. However, the Voyagers will spend tens of thousands of years in interstellar space before they are anywhere near another star, so the matter isn’t really an immediate concern. If the discs are ever found, it may be so far in the future that humans no longer exist.
For more interesting articles about space exploration, try the next page.
In "Star Trek: The Motion Picture" (the first Star Trek film), much of the plot revolved around a strange electronic life form known as V’Ger. By the end of the film, it is revealed that V’Ger is one of the Voyager space probes (Voyager 6, which never existed in the real world) that has either gained sentience on its own or been given sentience by an alien race. It wants to eradicate all of humanity, but instead evolves into yet another form of life.
Within the fictional Star Trek universe, there is some dispute as to V’Ger’s place in Trek history. Some suggest that V’Ger created the Borg, a cold, logical alien race that would become the primary villains in "Star Trek: The Next Generation." Others think the Borg encountered V’Ger, but that the cyborg aliens existed before the chance meeting.
Voyager Space FAQ
What is the temperature of interstellar space, how far away is voyager 2, how far away is voyager 1, do the voyagers have a camera, what is the difference between voyager 1 and 2, lots more information, related articles.
- Are we not the only Earth out there?
- How Lunar Landings Work
- NASA's 10 Greatest Achievements
- How do spacecraft re-enter the Earth?
- How Fixing the Hubble Spacecraft Works
- How Project Mercury Worked
- How Spaceports Will Work
- How Aliens Work
More Great Links
- Voyager Web site
- Evans, Ben. "NASA's Voyager Missions: Exploring the Outer Solar System and Beyond." Springer; 1st ed 2004. 2nd printing edition (April 15, 2008).
- Dethloff, Henry C & Schorn, Ronald A. "Voyager's Grand Tour: To the Outer Planets and Beyond." Smithsonian (March 17, 2003).
- NASA. “Voyager 2 Proves Solar System Is Squashed.” http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

We finally know why NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft stopped communicating — scientists are working on a fix
The first spacecraft to explore beyond the solar system started spouting gibberish late last year. Now, NASA knows why.

NASA engineers have discovered the cause of a communications breakdown between Earth and the interstellar explorer Voyager 1. It would appear that a small portion of corrupted memory exists in one of the spacecraft's computers.
The glitch caused Voyager 1 to send unreadable data back to Earth, and is found in the NASA spacecraft's flight data subsystem (FDS). That's the system responsible for packaging the probe's science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send it back to mission control.
The source of the issue began to reveal itself when Voyager 1 operators sent the spacecraft a "poke" on March 3, 2024. This was intended to prompt FDS to send a full memory readout back to Earth.
The readout confirmed to the NASA team that about 3% of the FDS memory had been corrupted, and that this was preventing the computer from carrying out its normal operations.
Related: NASA finds clue while solving Voyager 1's communication breakdown case
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space in 2012. Voyager 2 followed its spacecraft sibling out of the solar system in 2018, and is still operational and communicating well with Earth.
After 11 years of interstellar exploration, in Nov. 2023, Voyager 1's binary code — the computer language it uses to communicate with Earth — stopped making sense. Its 0's and 1's didn't mean anything anymore.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"Effectively, the call between the spacecraft and the Earth was still connected, but Voyager's 'voice' was replaced with a monotonous dial tone," Voyager 1's engineering team previously told Space.com .

The team strongly suspects this glitch is the result of a single chip that's responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory ceasing to work.
Currently, however, NASA can’t say for sure what exactly caused that particular issue. The chip could have been struck by a high-speed energetic particle from space or, after 46 years serving Voyager 1, it may simply have worn out.
— Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
— NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
— NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
Voyager 1 currently sits around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from it — and another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft to receive a response via the Deep Space Network's antennas. Solving this communication issue is thus no mean feat.
Yet, NASA scientists and engineers are optimistic they can find a way to help FDS operate normally, even without the unusable memory hardware.
Solving this issue could take weeks or even months, according to NASA — but if it is resolved, Voyager 1 should be able to resume returning science data about what lies outside the solar system.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
SpaceX launches advanced weather satellite for US Space Force (video)
SpaceX launches 23 Starlink satellites in nighttime liftoff (photos, video)
My formal 2024 solar eclipse apology
- jcs Funny timing for this article, when I am streaming an old Star Trek movie. So, surely this didn't cause a 3 byte glitch removing the O, Y and A from Voyager's name buffer? Get it? Reply
- bwana4swahili It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment. Reply
bwana4swahili said: It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment.
- HankySpanky So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists. Reply
HankySpanky said: So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists.
- Classical Motion I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around. Reply
Classical Motion said: I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around.
- jcs ROFLOL! And a hot bald chick delivering the bad news! Reply
- View All 8 Comments
Most Popular
By Tereza Pultarova April 11, 2024
By Keith Cooper April 11, 2024
By Jamie Carter April 11, 2024
By Mike Wall April 11, 2024
By Robert Z. Pearlman April 11, 2024
By Joe Rao April 10, 2024
By Robert Lea April 10, 2024
By Mike Wall April 10, 2024
By Brett Tingley April 10, 2024
By Jamie Carter April 10, 2024
By Jeff Spry April 10, 2024
- 2 Achoo! Baby star 'sneezes' tell astronomers a lot about their development
- 3 A NASA spacecraft spotted something weird orbiting the moon. It was just a lunar neighbor (photos)
- 4 Monster star gains magnetic personality following stellar merger
- 5 Car-sized asteroid gives Earth a super-close shave with flyby closer than some satellites
Voyager Project Information
Not fare well, But fare forward, Voyagers. -- T. S. Eliot, The Dry Salvages
The last two spacecraft of NASA's Mariner series, Voyager 1 and 2 were the first in that series to be sent to explore the outer solar system. Preceeded by the Pioneer 10 and 11 missions, Voyager 1 and 2 were to make studies of Jupiter and Saturn, their satellites, and their magnetospheres as well as studies of the interplanetary medium. An option designed into the Voyager 2 trajectory, and ultimately exercised, would direct it toward Uranus and Neptune to perform similar studies.
Although launched sixteen days after Voyager 2, Voyager 1's trajectory was a faster path, arriving at Jupiter in March of 1979. Voyager 2 arrived about four months later in July 1979. Both spacecraft were then directed on to Saturn with arrival times in November 1980 (Voyager 1) and August 1981 (Voyager 2). Voyager 2 was then diverted to the remaining gas giants, Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). A more detailed table specifying the closest approach distances/times for these encounters is available.
Data collected by Voyager 1 and 2 were not confined to the periods surrounding encounters with the outer gas giants, with the various fields and particles experiments and the ultraviolet spectrometer collecting data nearly continuously during the interplanetary cruise phases of the mission. Data collection continues as the renamed Voyager Interstellar Mission searches for the edge of the solar wind's influence (the heliopause) and exits the solar system.
Some scientific results of the Voyager mission
A comprehensive list of the achievements of Voyager 1 and 2 would be so extensive that space doesn't permit. Here, then, are a (very) few results that would rank near the top of many such lists.
- Discovery of the Uranian and Neptunian magnetospheres, both of them highly inclined and offset from the planets' rotational axes, suggesting their sources are significantly different from other magnetospheres.
- The Voyagers found 22 new satellites: 3 at Jupiter, 3 at Saturn, 10 at Uranus, and 6 at Neptune.
- Io was found to have active volcanism, the only solar system body other than the Earth to be so confirmed. Triton was found to have active geyser-like structures and an atmosphere.
- Auroral zones were discovered at Jupiter, Saturn, and Neptune.
- Jupiter was found to have rings. Saturn's rings were found to contain spokes in the B-ring and a braided structure in the F-ring. Two new rings were discovered at Uranus and Neptune's rings, originally thought to be only ring arcs, were found to be complete, albeit composed of fine material.
- At Neptune, originally thought to be too cold to support such atmospheric disturbances, large-scale storms (notably the Great Dark Spot) were discovered.
- Additional information about Voyager 1
- Voyager 1 experiments
- Voyager 1 data collections
- Additional information about Voyager 2
- Voyager 2 experiments
- Voyager 2 data collections
Other Voyager Information/Data at NSSDCA
NSSDCA Voyager page
Data available on-line
- Voyager cruise magnetic field and plasma data from COHOWeb
- Voyager 1/2 position data in heliographic coordinates.
View selected images from the NSSDCA Photo Gallery taken by Voyager 1/2 of:
- the Solar System family
Data coverage charts for on-line, interplanetary datasets at NSSDCA, PDS, and experiment team sites for Voyager 1 and Voyager 2
Related Information/Data at NSSDCA
Other sources of voyager information/data.
Voyager project page (NASA JPL)
Cosmic Ray Subsystem (CRS) (NASA GSFC) Low-Energy Charged Particle (LECP) (JHU/APL) Magnetometer (MAG) (NASA GSFC) Plasma Science (PLS) (MIT) Plasma Wave System (PWS) (U. of Iowa)
| NSSDCA Planetary page | NSSDCA Space Physics page |
NASA Official: Dr. David R. Williams Version 2.5 Last Updated: 26 November 2018
NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system
Voyager 1 has been sending a stream of garbled nonsense since November. Now NASA engineers have identified the fault and found a potential workaround.

For the past five months, the Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady stream of unreadable gibberish back to Earth. Now, NASA engineers finally know why.
The 46-year-old spacecraft sends regular radio signals as it drifts further from our solar system . But in November 2023, the signals suddenly became garbled, meaning scientists were unable to read any of its data, and they were left mystified about the fault's origins.
In March, NASA engineers sent a command prompt, or "poke," to the craft to get a readout from its flight data subsystem (FDS) — which packages Voyager 1's science and engineering data before beaming it back to Earth.
After decoding the spacecraft's response, the engineers have found the source of the problem: The FDS's memory has been corrupted.
Related: NASA's Voyager 1 sends readable message to Earth after 4 nail-biting months of gibberish
"The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn't working," NASA said in a blog post Wednesday (March 13) . "Engineers can't determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years."
— NASA hears 'heartbeat' signal from Voyager 2 probe a week after losing contact
— Historic space photo of the week: Voyager 2 spies a storm on Saturn 42 years ago
— NASA reestablishes full contact with Voyager 2 probe after nail-biting 2-week blackout
Although it may take several months, the engineers say they can find a workaround to run the FDS without the fried chip — restoring the spacecraft's messaging output and enabling it to continue to send readable information from outside our solar system.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 zipped past Saturn and Jupiter in 1979 and 1980 before flying out into interstellar space in 2012. It is now recording the conditions outside of the sun's protective magnetic field , or heliosphere, which blankets our solar system.
Voyager 1 is currently more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and it takes 22.5 hours for any radio signal to travel from the craft to our planet.

Ben Turner is a U.K. based staff writer at Live Science. He covers physics and astronomy, among other topics like tech and climate change. He graduated from University College London with a degree in particle physics before training as a journalist. When he's not writing, Ben enjoys reading literature, playing the guitar and embarrassing himself with chess.
NASA spacecraft snaps mysterious 'surfboard' orbiting the moon. What is it?
The moon is getting its own time zone, White House memo to NASA reveals
Why I watched the solar eclipse with my kids, a goose and 2,000 trees
- TorbjornLarsson Bon voyage, Voyager! Reply
- Jay McHue What if aliens are doing it to try to communicate with us? 🤪 Reply
Jay McHue said: What if aliens are doing it to try to communicate with us? 🤪
admin said: Voyager 1 has been sending a stream of garbled nonsense since November. Now NASA engineers have identified the fault and found a potential workaround. NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system : Read more
sourloaf said: What does FSB mean?
Rusty Lugnuts said: Where are you seeing "FSB"? The closest thing I can see in the article is "FDS". In modern computers, FSB would most likely refer to the Fr0nt S1ide Bu5, though I have no idea if a system as old as Voyagers, let alone engineered so specifically, would have an FSB. (apparently I can't spell out "Fr0nt S1ide Bu5" or my post gets flagged as spam or inappropriate??)
- SkidWard Just cut the % of ram needed... skip the bad sectors Reply
- kloudykat FDS = fl1ght da1a sub5ystem5 Reply
- 5ft24dave This is pretty old news, like 6 months old. Are you guys just now discovering this? Reply
Commodore Browncoat said: That's about as sane a theory as many of the others that have become ridiculously popular in the past several years, so sure - why not? What reply do you think we should send?
- View All 11 Comments
Most Popular
By Peter Ray Allison April 10, 2024
By Tom Metcalfe April 09, 2024
By Rebecca Sohn April 09, 2024
By Stephanie Pappas April 09, 2024
By Samantha Mathewson April 09, 2024
By Nicoletta Lanese April 09, 2024
By Sascha Pare April 09, 2024
By Emily Cooke April 09, 2024
By Harry Baker April 09, 2024
- 2 Here are the best photos of the April 8 total solar eclipse over North America
- 3 Part of the San Andreas fault may be gearing up for an earthquake
- 4 Pet fox with 'deep relationship with the hunter-gatherer society' buried 1,500 years ago in Argentina
- 5 NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system
- 2 Pet fox with 'deep relationship with the hunter-gatherer society' buried 1,500 years ago in Argentina
- 3 No, you didn't see a solar flare during the total eclipse — but you may have seen something just as special
- 4 Neolithic women in Europe were tied up and buried alive in ritual sacrifices, study suggests
- 5 Superfast drone fitted with new 'rotating detonation rocket engine' approaches the speed of sound

NASA's Voyager 1 probe has been glitching for months and we finally know why
An artist’s concept of the Voyager 1 spacecraft in interstellar space.
After months of sending unusable data to mission control, there’s finally hope for the Voyager 1 spacecraft. NASA engineers pinpointed the cause behind the mission’s odd anomaly, and think they can help the interstellar probe make sense again.
Engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory believe the Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending nonsensical data due to corrupted memory hardware in the spacecraft’s flight data system (FDS). “The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn’t working,” NASA wrote in an update.
FDS collects data from Voyager’s science instruments, as well as engineering data about the health of the spacecraft, and combines them into a single package that’s transmitted to Earth through one of the probe’s subsystems, the telemetry modulation unit (TMU), in binary code.
FDS and TMU have been having trouble communicating with one another. As a result, TMU has been sending data to mission control in a repeating pattern of ones and zeroes. NASA’s engineers aren’t quite sure what corrupted the FDS memory hardware; they think that either the chip was hit by an energetic particle from space or that it’s just worn out after operating for 46 years.
Voyager 1 launched in 1977, less than a month after its twin probe, Voyager 2, began its own journey to space. The probe ventured into interstellar space in August 2012, becoming the first spacecraft to leave the heliosphere.
The problem first began in May 2022, when the probe suddenly started sending nonsensical attitude articulation and control (AACS) data . Engineers resolved the issue by sending the telemetry data through one of the spacecraft’s other computers. In December 2023, Voyager 1 started speaking gibberish again .
On March 1, the team sent a “poke” to the spacecraft’s data system, a command that gently prompts FDS to try different sequences in its software package in an effort to pinpoint the corrupted section. Two days later, Voyager 1 sent a signal that contained a readout of the entire FDS memory , which helped the team pinpoint the source of the glitch by comparing this memory readout with a previous one to look for discrepancies in the code.
“Using the readout, the team has confirmed that about 3% of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations,” NASA wrote in its update.
The engineers are hoping to resolve the issue by finding a way for FDS to operate normally without the corrupted memory hardware, enabling Voyager 1 to begin transmitting data about the cosmos and continue its journey through deep space.
A version of this article originally appeared on Gizmodo .
For the latest news, Facebook , Twitter and Instagram .


- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
The Golden Record
Pioneers 10 and 11, which preceded Voyager, both carried small metal plaques identifying their time and place of origin for the benefit of any other spacefarers that might find them in the distant future. With this example before them, NASA placed a more ambitious message aboard Voyager 1 and 2, a kind of time capsule, intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth.

Engineers Pinpoint Cause of Voyager 1 Issue, Are Working on Solution
Engineers have confirmed that a small portion of corrupted memory in one of the computers aboard NASA’s Voyager 1 has been causing the spacecraft to send unreadable science and engineering data to Earth since last November. Called the flight data subsystem (FDS), the computer is responsible for packaging the probe’s science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send the data to Earth.
In early March , the team issued a “poke” command to prompt the spacecraft to send back a readout of the FDS memory, which includes the computer’s software code as well as variables (values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status). Using the readout, the team has confirmed that about 3% of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations.
The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn’t working. Engineers can’t determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years.
Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again.
Launched in 1977 , the twin Voyager spacecraft flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune. They are both exploring interstellar space, outside the bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun, called the heliosphere. Voyager 2 continues to operate normally.
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
NASA Engineers Make Progress Toward Understanding Voyager 1 Issue
Editor’s note: This blog post was originally published March 13, 2024, on NASA’s Sun Spot blog . Future Voyager blog posts will appear here, on NASA’s Voyager blog.
Since November 2023, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, but the signal does not contain usable data. The source of the issue appears to be with one of three onboard computers, the flight data subsystem (FDS), which is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth by the telemetry modulation unit.
On March 3, the Voyager mission team saw activity from one section of the FDS that differed from the rest of the computer’s unreadable data stream. The new signal was still not in the format used by Voyager 1 when the FDS is working properly, so the team wasn’t initially sure what to make of it. But an engineer with the agency’s Deep Space Network, which operates the radio antennas that communicate with both Voyagers and other spacecraft traveling to the Moon and beyond, was able to decode the new signal and found that it contains a readout of the entire FDS memory.
The FDS memory includes its code, or instructions for what to do, as well as variables, or values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status. It also contains science or engineering data for downlink. The team will compare this readout to the one that came down before the issue arose and look for discrepancies in the code and the variables to potentially find the source of the ongoing issue.
This new signal resulted from a command sent to Voyager 1 on March 1. Called a “poke” by the team, the command is meant to gently prompt the FDS to try different sequences in its software package in case the issue could be resolved by going around a corrupted section.
Because Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach the spacecraft and another 22.5 hours for the probe’s response to reach antennas on the ground. So the team received the results of the command on March 3. On March 7, engineers began working to decode the data, and on March 10, they determined that it contains a memory readout.
The team is analyzing the readout. Using that information to devise a potential solution and attempt to put it into action will take time.
Engineers Working to Resolve Issue With Voyager 1 Computer
Editor’s note: This blog post was originally published Dec. 12, 2023, on NASA’s Sun Spot blog . Future Voyager blog posts will appear here, on NASA’s Voyager blog. A previous version of this post identified the TMU as the telecommunications unit. It is the telemetry modulation unit.
Engineers are working to resolve an issue with one of Voyager 1’s three onboard computers, called the flight data system (FDS). The spacecraft is receiving and executing commands sent from Earth; however, the FDS is not communicating properly with one of the probe’s subsystems, called the telemetry modulation unit (TMU). As a result, no science or engineering data is being sent back to Earth.
Among other things, the FDS is designed to collect data from the science instruments as well as engineering data about the health and status of the spacecraft. It then combines that information into a single data “package” to be sent back to Earth by the TMU. The data is in the form of ones and zeros, or binary code. Varying combinations of the two numbers are the basis of all computer language.
Recently, the TMU began transmitting a repeating pattern of ones and zeros as if it were “stuck.” After ruling out other possibilities, the Voyager team determined that the source of the issue is the FDS. This past weekend the team tried to restart the FDS and return it to the state it was in before the issue began, but the spacecraft still isn’t returning useable data.
It could take several weeks for engineers to develop a new plan to remedy the issue. Launched in 1977, the spacecraft and its twin, Voyager 2, are the two longest-operating spacecraft in history. Finding solutions to challenges the probes encounter often entails consulting original, decades-old documents written by engineers who didn’t anticipate the issues that are arising today. As a result, it takes time for the team to understand how a new command will affect the spacecraft’s operations in order to avoid unintended consequences.
In addition, commands from mission controllers on Earth take 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is exploring the outer regions of our solar system more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth. That means the engineering team has to wait 45 hours to get a response from Voyager 1 and determine whether a command had the intended outcome.
Introducing the Voyager Mission Blog

Launched in 1977, NASA’s twin Voyager spacecraft are the agency’s longest-operating and farthest-flung probes. Voyager 1 visited Jupiter and Saturn, revealing new features of both planets and their moons. Voyager 2 followed its twin to Jupiter and Saturn before changing its trajectory to fly by Uranus and Neptune. It remains the only spacecraft to visit our solar system’s two ice giant planets.
Continuing their legacy as science pioneers, the Voyagers are the only two probes to journey into interstellar space – the space between stars. This region lies outside the heliosphere , the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields emitted by our Sun. By directly sampling the interstellar environment, the Voyagers are providing data that spacecraft closer to Earth can’t replicate. This helps scientists study both the shape of the heliosphere and its interaction with the ocean of interstellar material that the Sun is traveling through.
Readers of this blog can find occasional updates on mission science, the health of the spacecraft, and the creative solutions engineers have needed to come up with in order to keep the venerable spacecraft operating after nearly 50 years.
For more about Voyager, go to www.nasa.gov/voyager and follow along on X (formerly Twitter) at @NASAVoyager . Take Voyager’s Grand Tour with NASA’s Eyes .
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 calla.e. cofield @jpl.nasa.gov

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time. For a full 3D, immersive experience click on View Voyagers link below to launch the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app. View Voyager.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
A poster of the planets and moons visited during the Voyager program. The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of the two gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, to fly near them while collecting data for transmission ...
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space on November 5, 2018 and scientists hope to learn more about this region. Both spacecraft are still sending scientific information about their surroundings through the Deep Space Network, or DSN. The primary mission was the exploration of Jupiter and Saturn. After making a string of discoveries there — such ...
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018. Mission Type.
Because Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach the spacecraft and another 22.5 hours for the probe's response to reach antennas on the ground. So the team received the results of the command on March 3. On March 7, engineers began working to decode the data ...
Voyager, either of a pair of robotic U.S. interplanetary probes launched to observe and to transmit information to Earth about the giant planets of the outer solar system and the farthest reaches of the Sun's sphere of influence. Voyager 1 and 2 were the first spacecraft to reach interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 ...
Spacecraft. The identical Voyager spacecraft are three-axis stabilized systems that use celestial or gyro referenced attitude control to maintain pointing of the high-gain antennas toward Earth. The prime mission science payload consisted of 10 instruments (11 investigations including radio science). A 3D model of NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft.
Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and the interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. It was launched 16 days after its twin Voyager 2.
The one-way travel time for a radio signal to reach Voyager 1 from Earth is about 22.5 hours, meaning it takes roughly 45 hours for engineers on the ground to learn how the spacecraft responded to ...
Caltech/NASA-JPL. 209. It's been four months since NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft sent an intelligible signal back to Earth, and the problem has puzzled engineers tasked with supervising the probe ...
Voyager 2, was the first of two twin probes NASA sent to investigate the outer planets of our solar system. The probe was launched aboard a Titan IIIE-Centaur from Cape Canaveral Space Launch ...
After Voyager 1 took its last image (the "Solar System Family Portrait" in 1990), the cameras were turned off to save power and memory for the instruments expected to detect the new charged particle environment of interstellar space. Mission managers removed the software from both spacecraft that controls the camera.
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space . The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA 's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space.. Launched in 1977, NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft inspired the world with pioneering visits to Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.Their journey continues 45 years later as both probes explore interstellar space, the region outside the protective ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape…
About the mission. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
The 1970s were a transitional period for the U.S. space effort. The Apollo program was coming to a close, and NASA was trying to figure out what form manned spaceflight would take. The Mariner missions expanded our knowledge of the inner planets by sending space probes to fly past (and in some cases orbit) Mars, Venus and Mercury.There were tentative plans to send a Mariner mission to visit ...
Voyager 1 currently sits around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from it — and another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft ...
Titan III E-Centaur. On-orbit mass: 721.9 Kg. Power System: Radioisotope Thermal Generators (RTGs) of 420 W. The last two spacecraft of NASA's Mariner series, Voyager 1 and 2 were the first in that series to be sent to explore the outer solar system. Preceeded by the Pioneer 10 and 11 missions, Voyager 1 and 2 were to make studies of Jupiter ...
Voyager 1, meanwhile, continues to press outward, conducting studies of interplanetary space. Eventually, its instruments may be the first of any spacecraft to sense the heliopause -- the boundary between the end of the Sun's magnetic influence and the beginning of interstellar space. (Voyager 1 entered Interstellar Space on August 25, 2012.)
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 zipped past Saturn and Jupiter in 1979 and 1980 before flying out into interstellar space in 2012. It is now recording the conditions outside of the sun's protective ...
Voyager 1 launched in 1977, less than a month after its twin probe, Voyager 2, began its own journey to space. The probe ventured into interstellar space in August 2012, becoming the first ...
The Voyager spacecraft are the third and fourth human spacecraft to fly beyond all the planets in our solar system. Pioneers 10 and 11 preceded Voyager in outstripping the gravitational attraction of the Sun but on February 17, 1998, Voyager 1 passed Pioneer 10 to become the most distant human-made object in space.
NASA hasn't fixed Voyager 1 yet, but engineers now know what's vexing the spacecraft. The glitch paused Voyager 1's science work and kicked off a long-distance diagnosis process. The team ...
The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth. Launched in 1977, both Voyager spacecraft began a historic journey and each carried a unique 'time capsule' along with them. Click to learn more. The Golden Record ...
Launched in 1977, NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft are the agency's longest-operating and farthest-flung probes. Voyager 1 visited Jupiter and Saturn, revealing new features of both planets and their moons. Voyager 2 followed its twin to Jupiter and Saturn before changing its trajectory to fly by Uranus and Neptune.